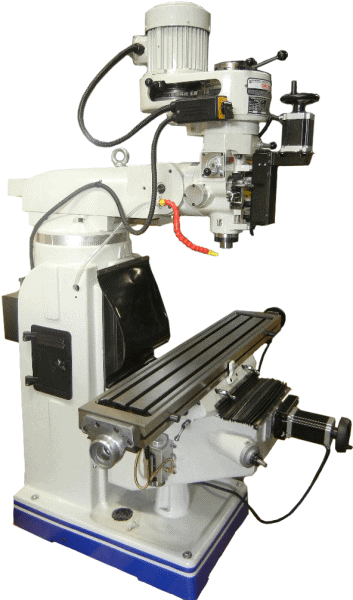
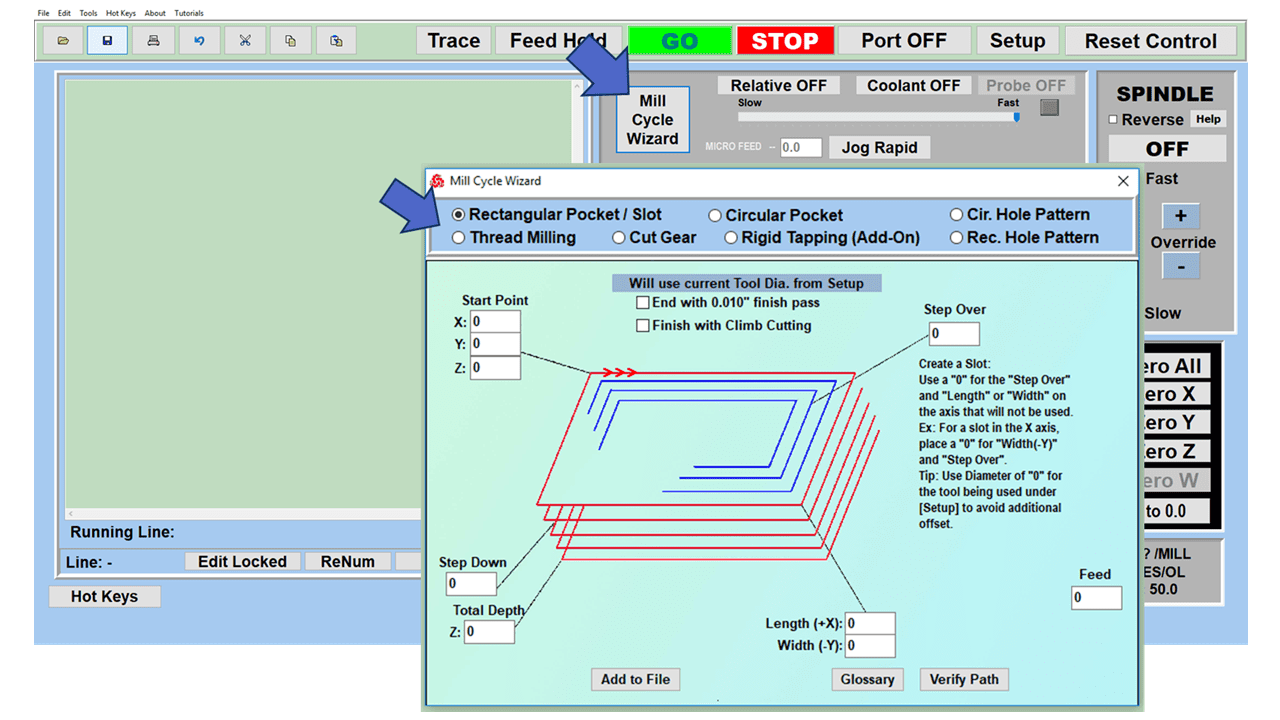
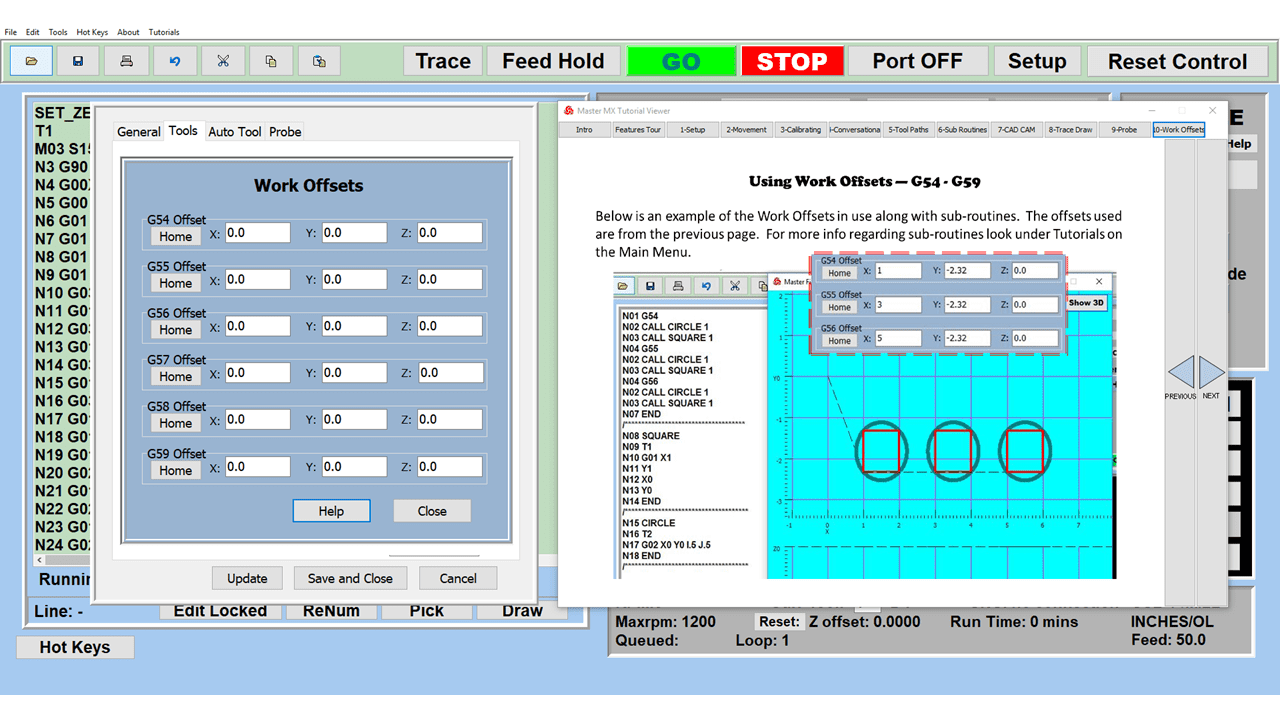
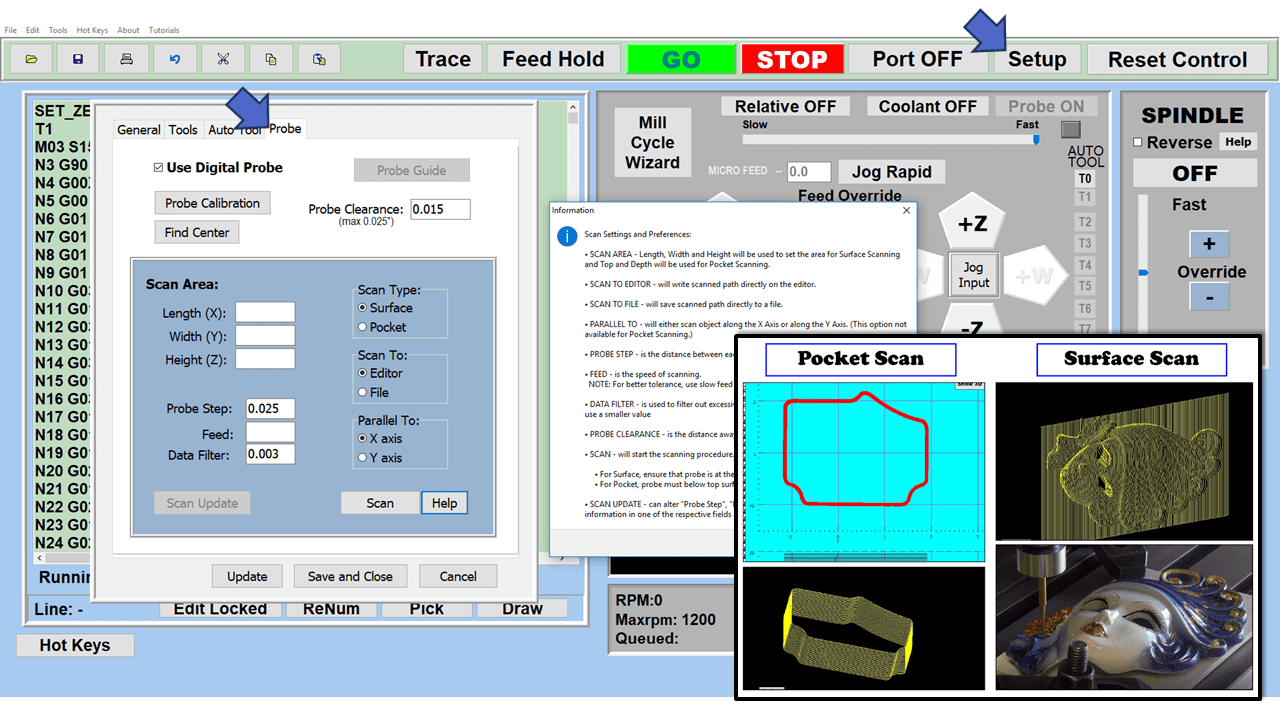
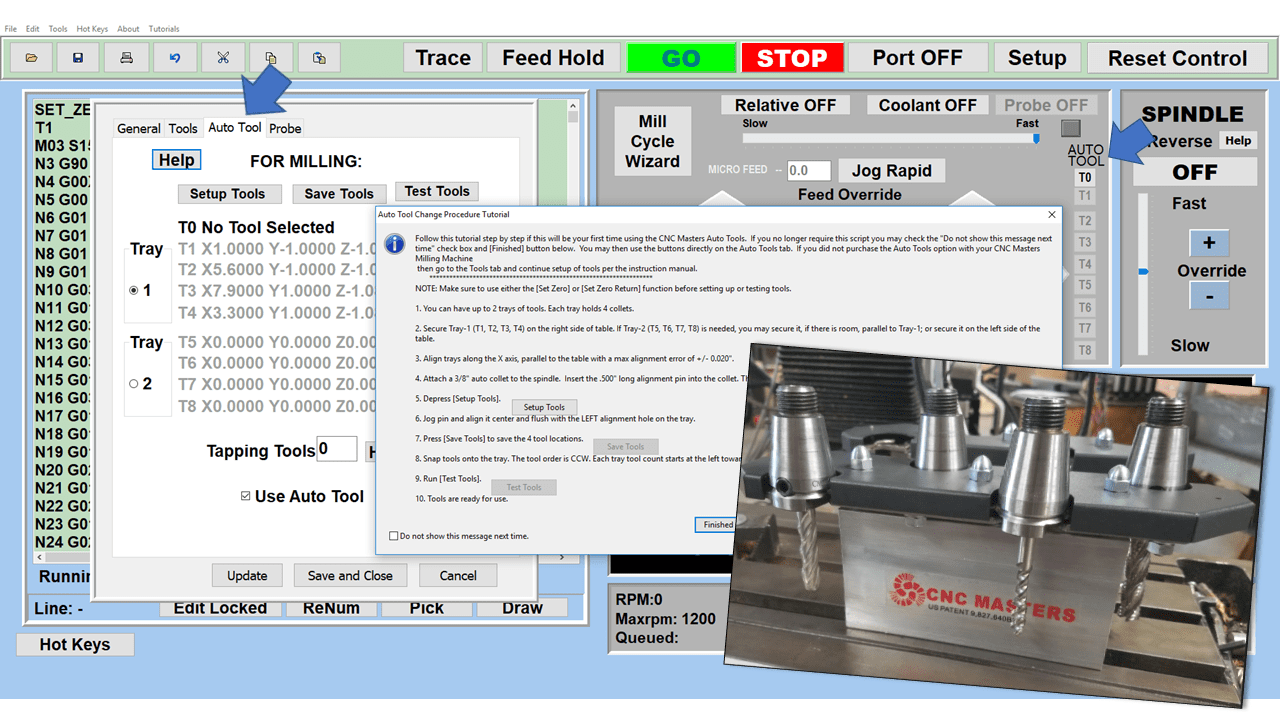
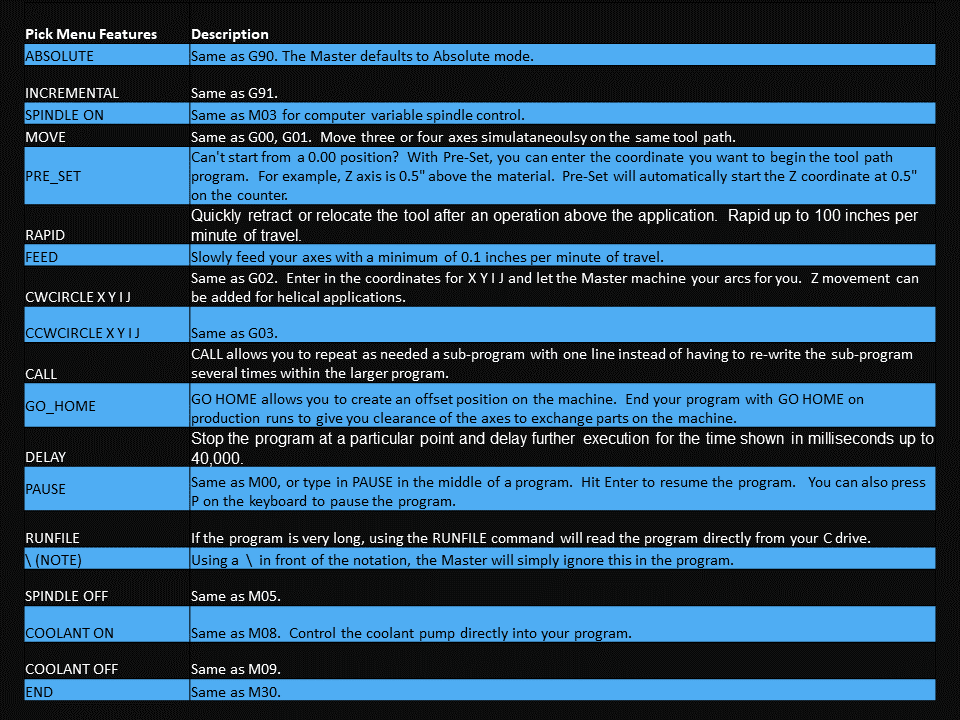
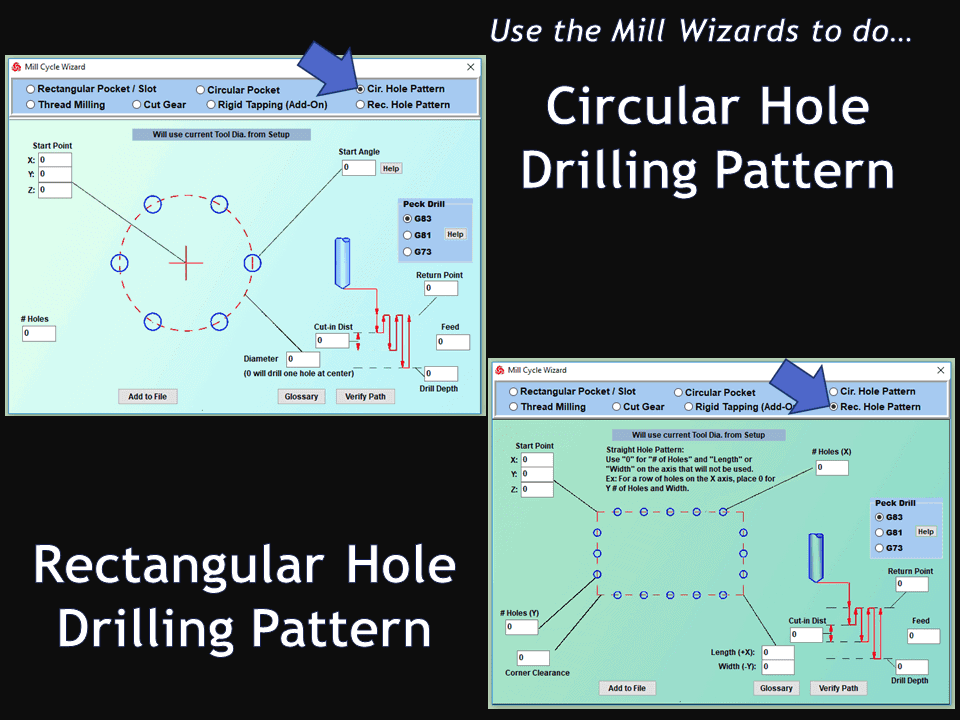
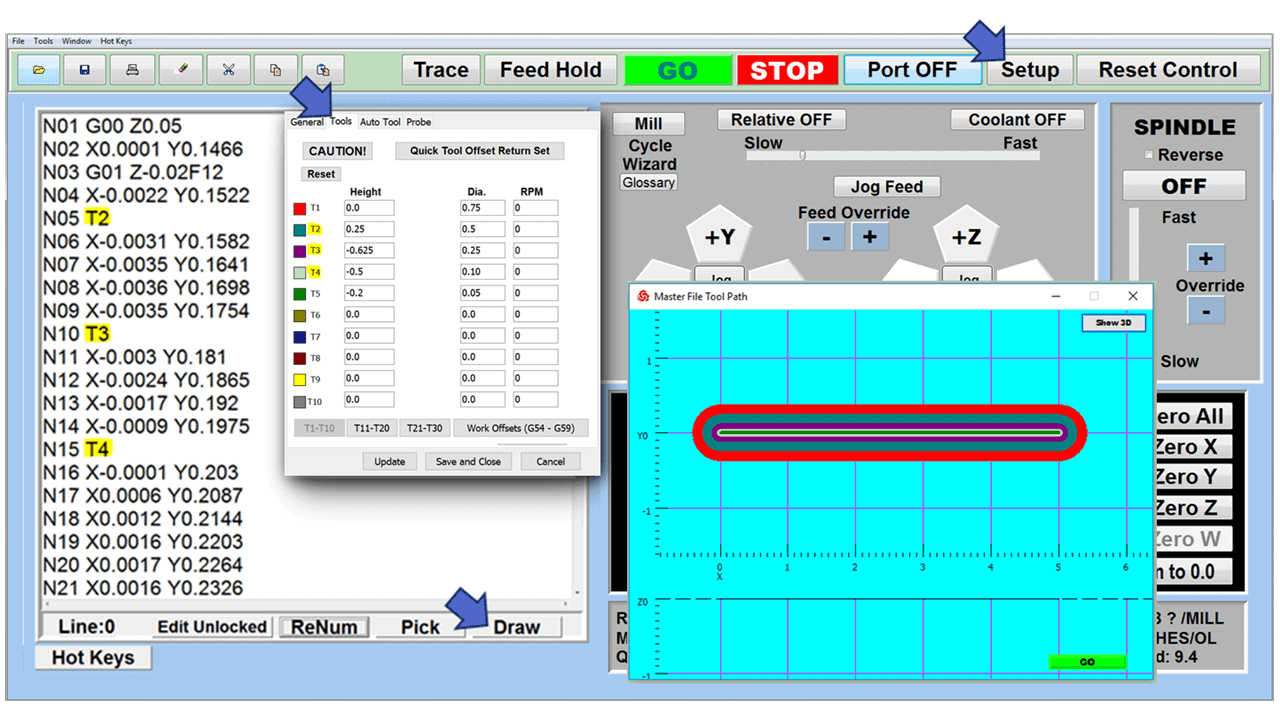
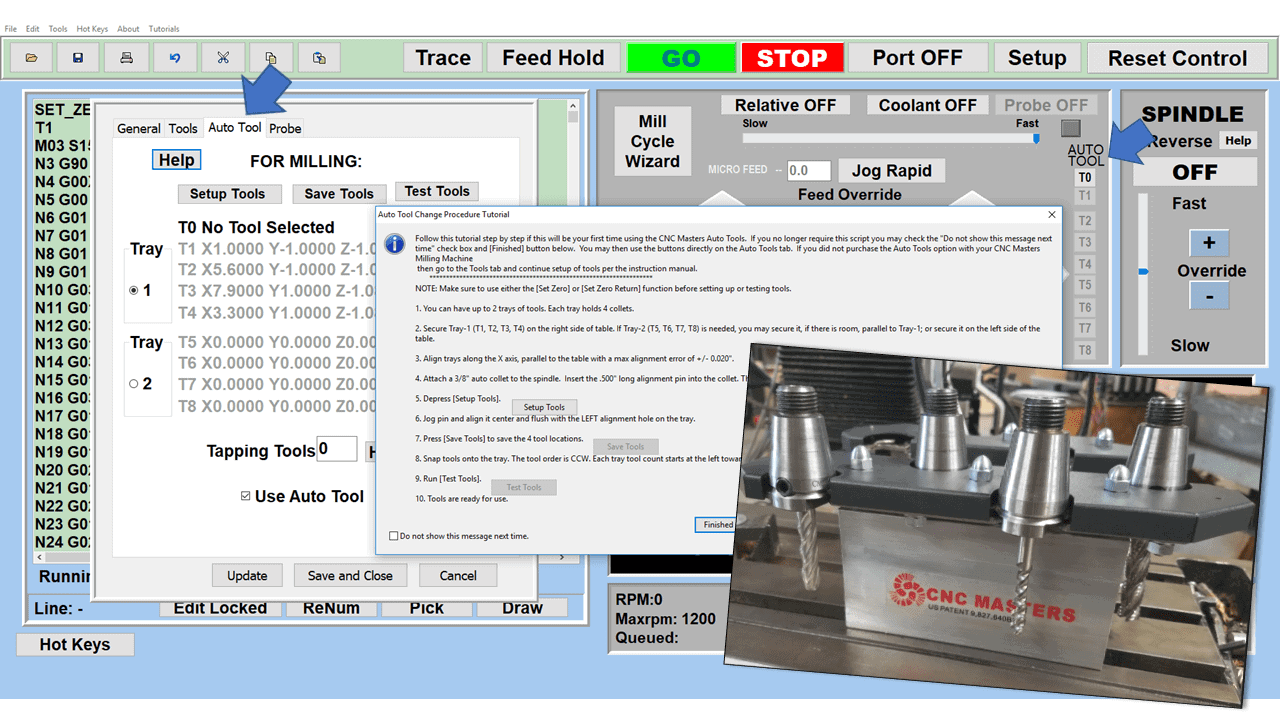
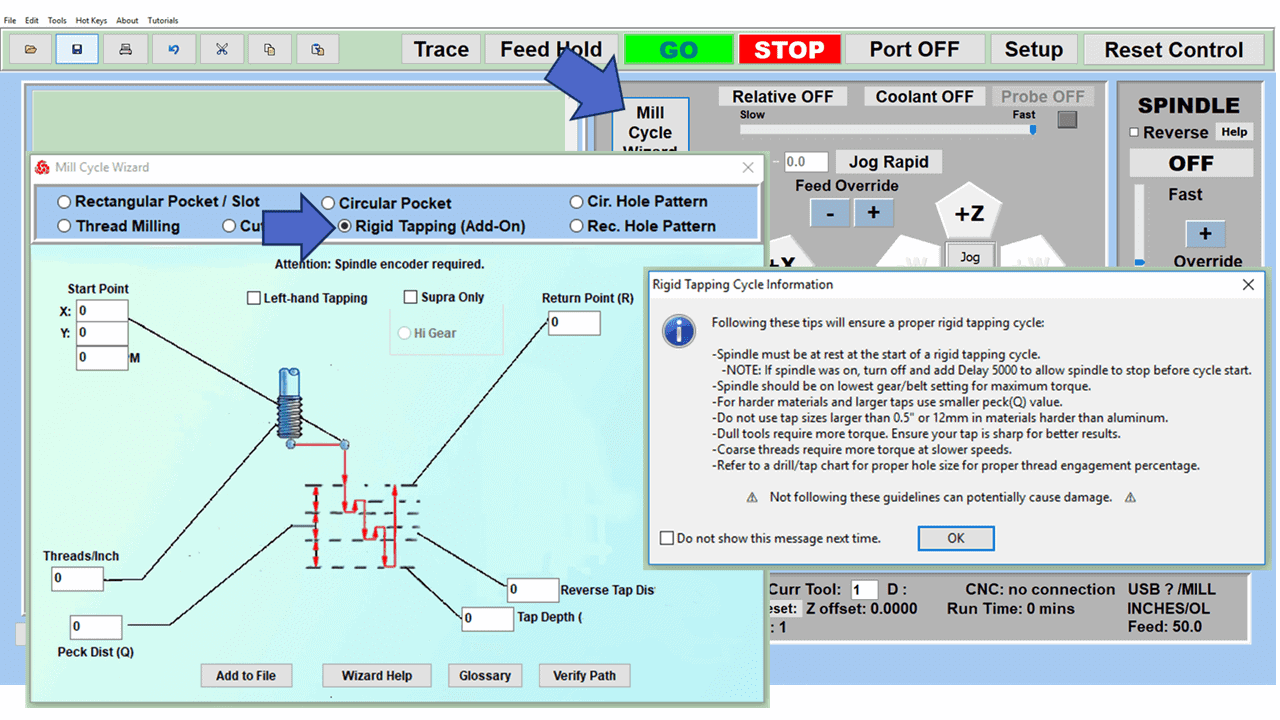
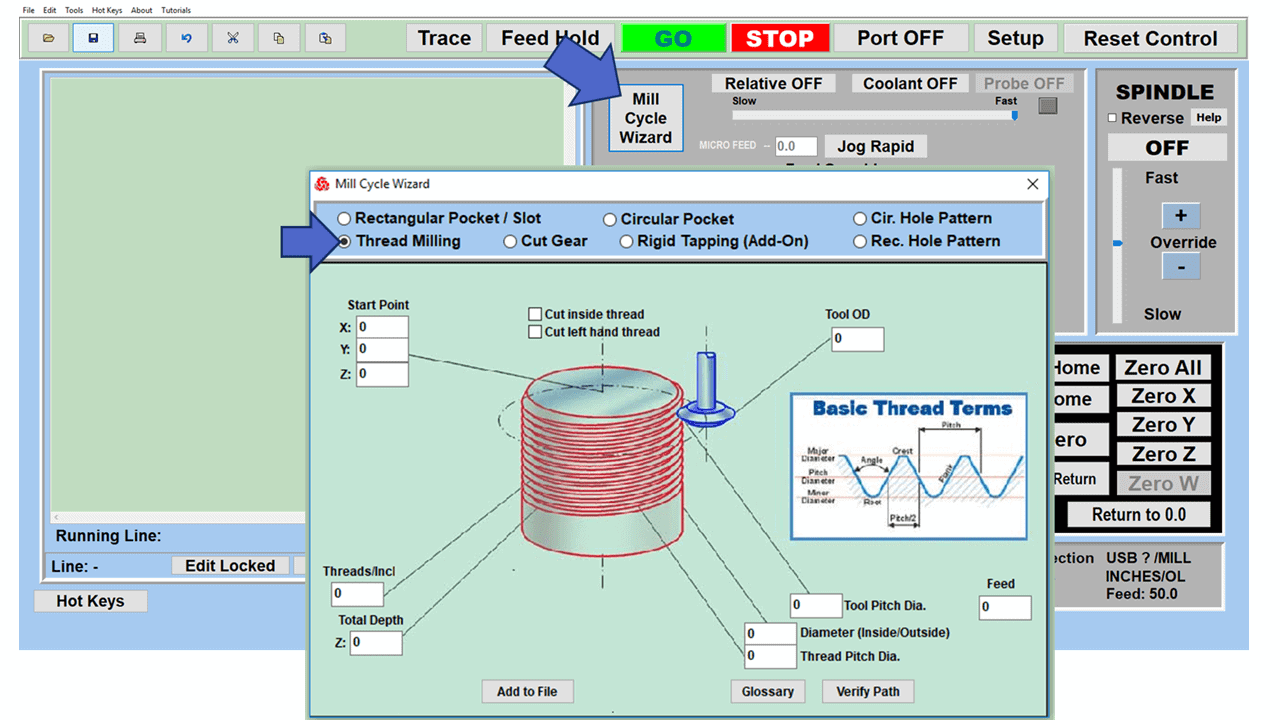
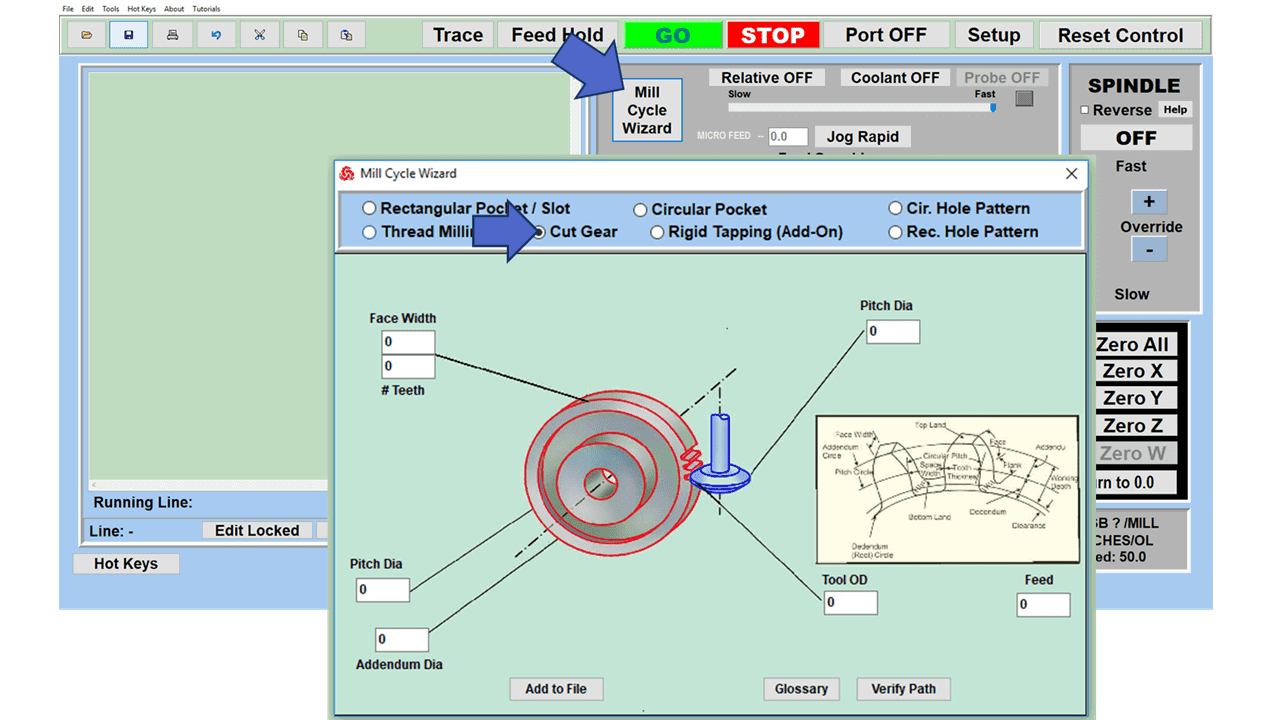
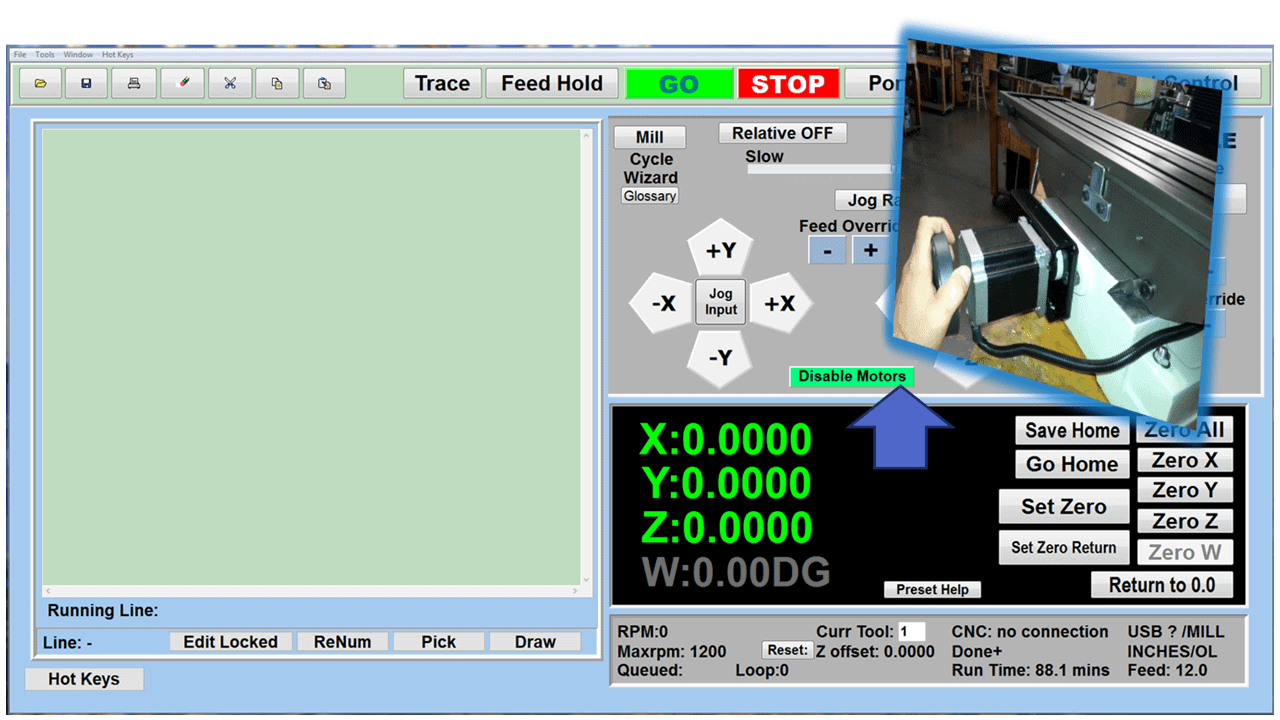
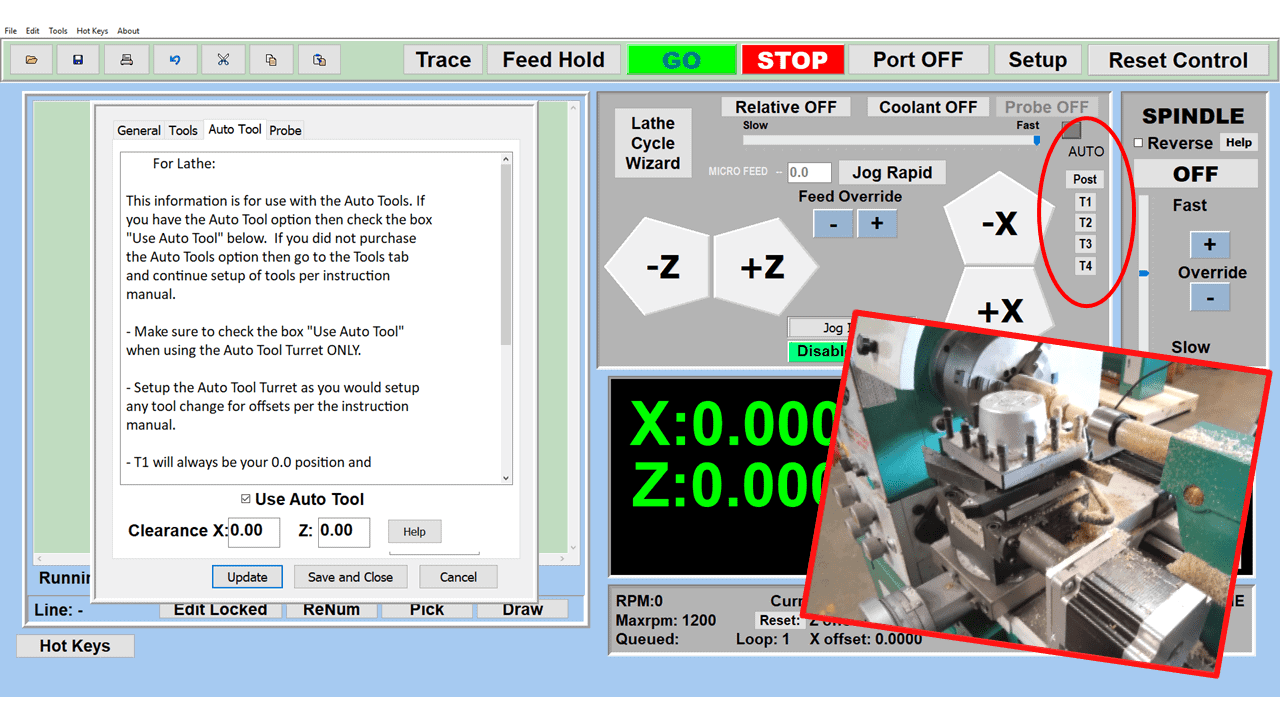
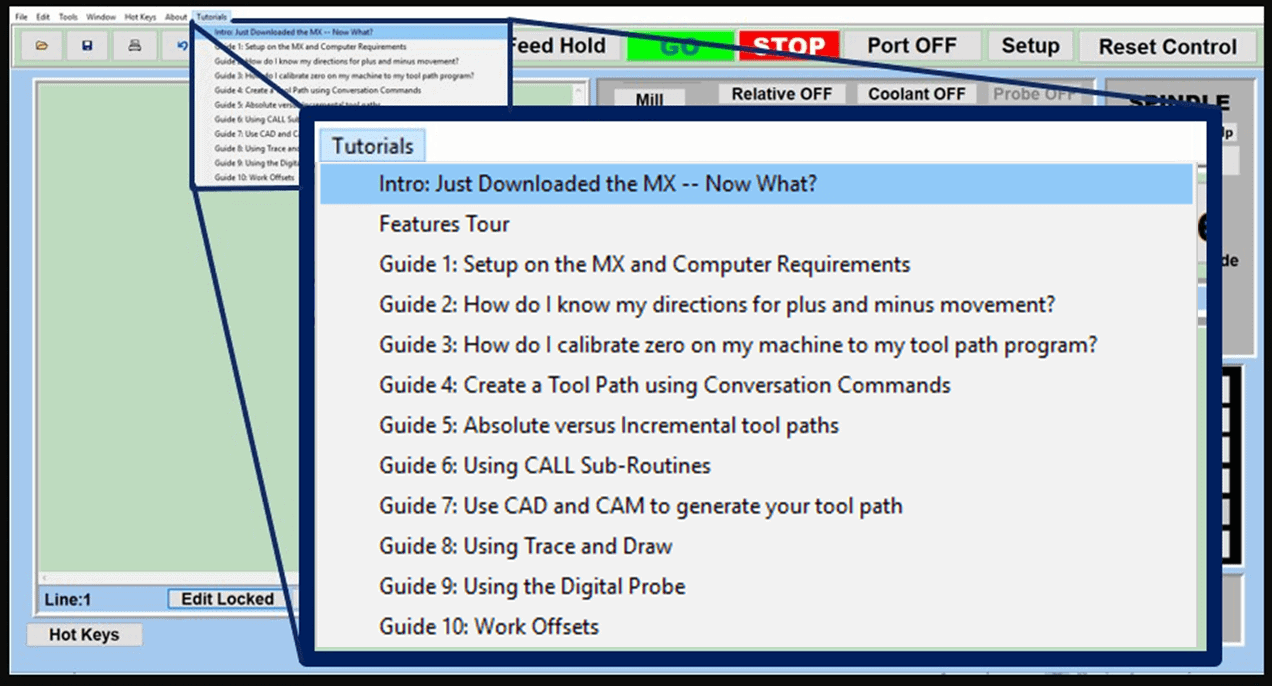
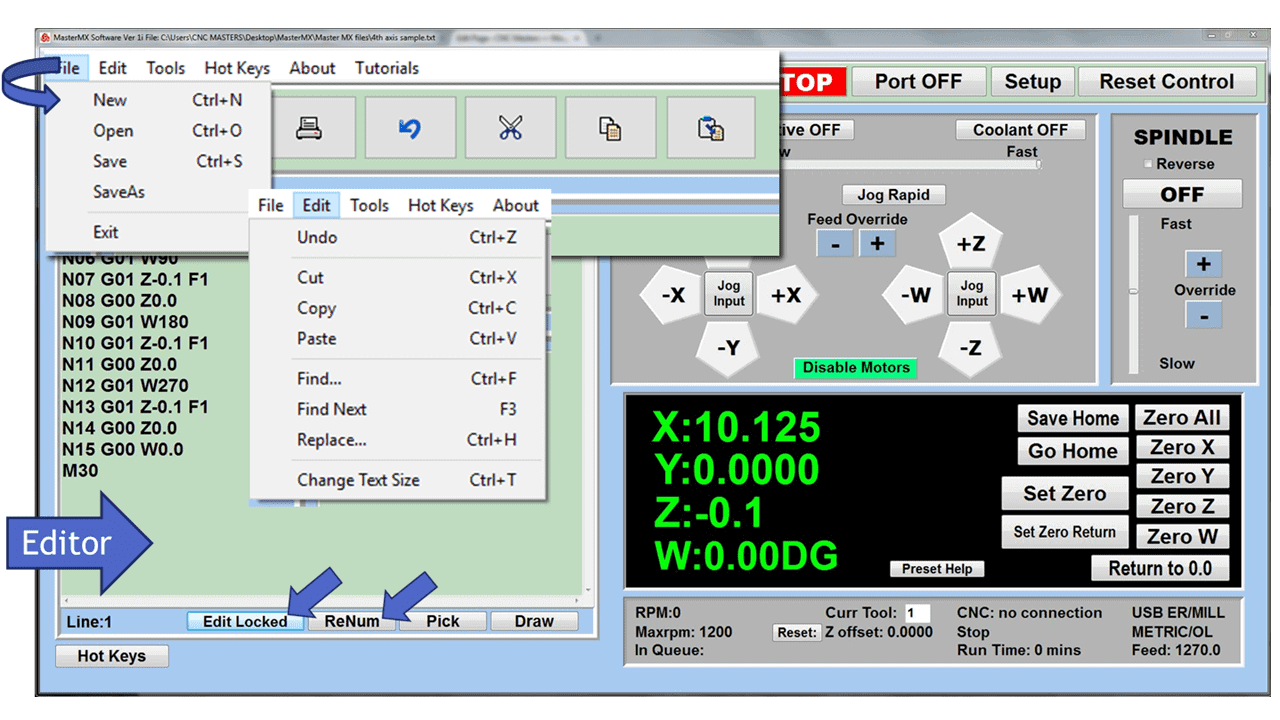
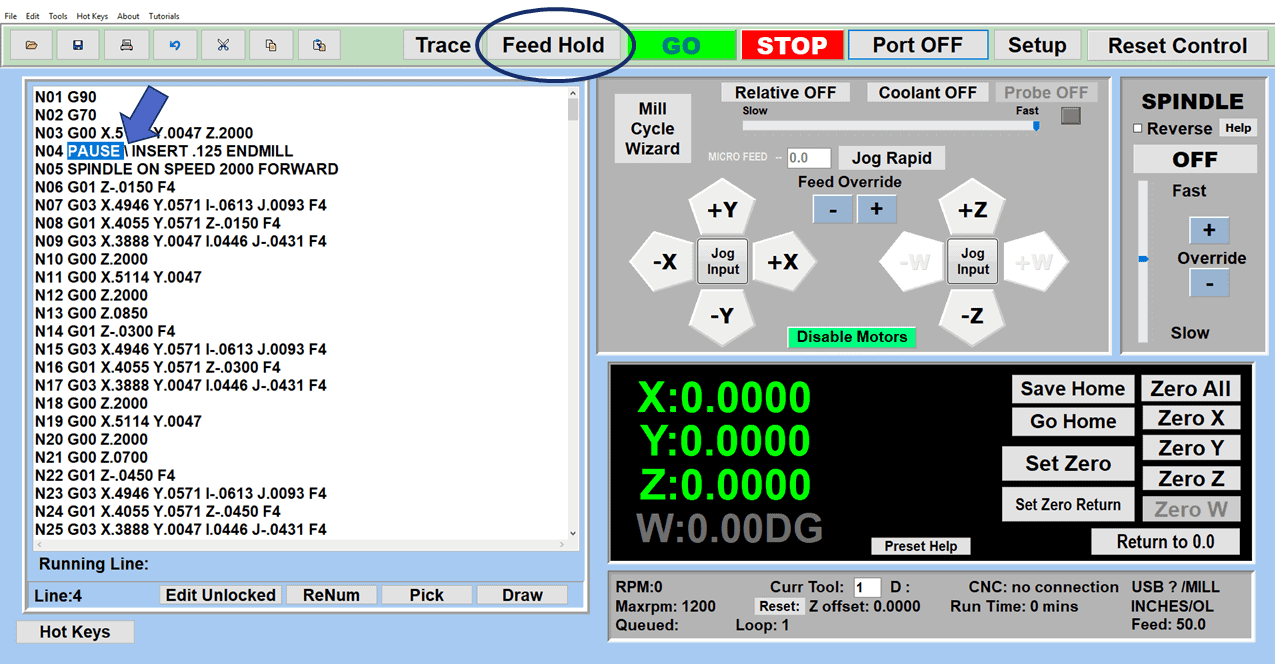
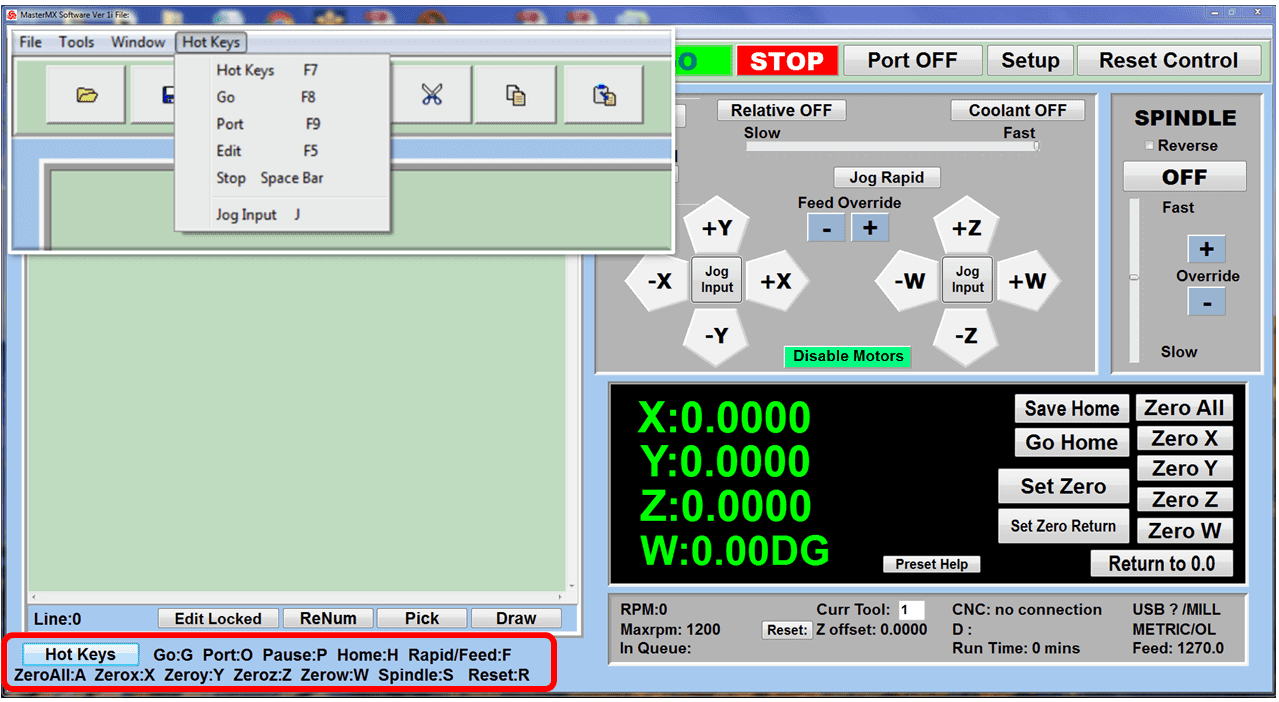
In CNC machining, there are two primary types of milling machines: the vertical milling machine, with a Bridgeport milling machine being an excellent example, and the horizontal milling machine. Although the milling operations on the two styles of milling machines might vary, the milling machine parts that make them up have much in common.
We’ve created a list of the essential parts of a CNC milling machine that you should know and understand, starting from the floor and moving up.
What Is A Milling Machine?
Milling machines, whether manual machines or CNC machines, are essential to the modern manufacturing process. They remove metal from workpieces, getting the desired shape and dimensions using a spinning tool called a milling cutter. Unlike a CNC router or CNC lathe machine, on which a workpiece spins and the cutting tool moves into it to create cylindrical shapes, the milling machine employs end mills, face mills, dovetail cutters, and various other milling cutters to machine flat and irregular surfaces, including those that are concave or convex.
Milling machines are not all that complicated in theory: A machine operator fastens a workpiece to the machine tool’s work table using a work holding device, such as a clamp or vise. The workpiece is moved through the X and Y-axis as the milling cutter removes the material and a skilled worker or CNC program directs it on a manual or CNC milling machine.
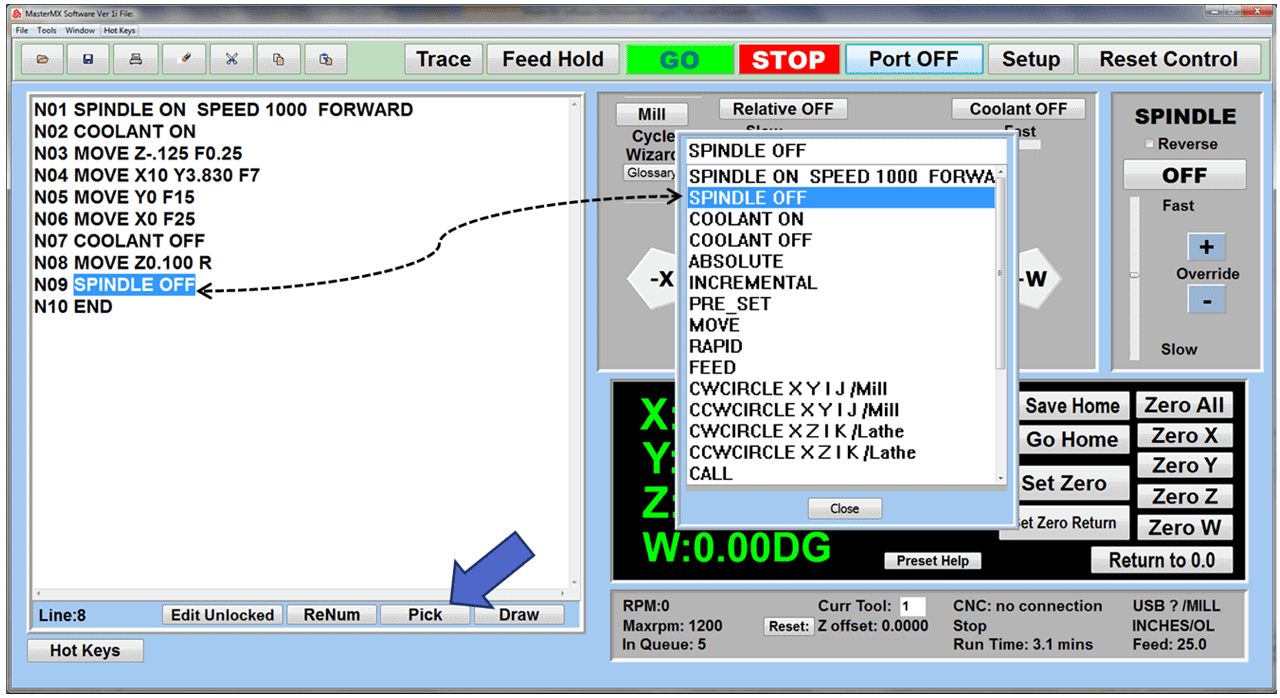
CNC Controller
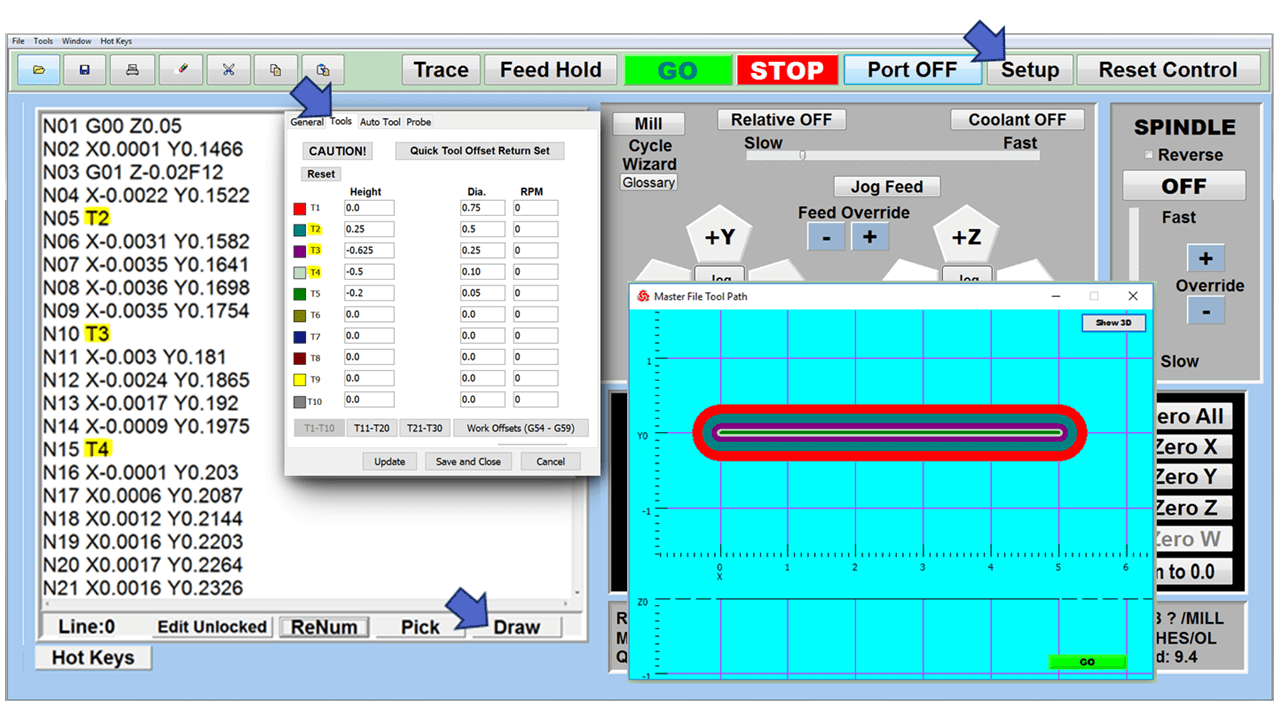
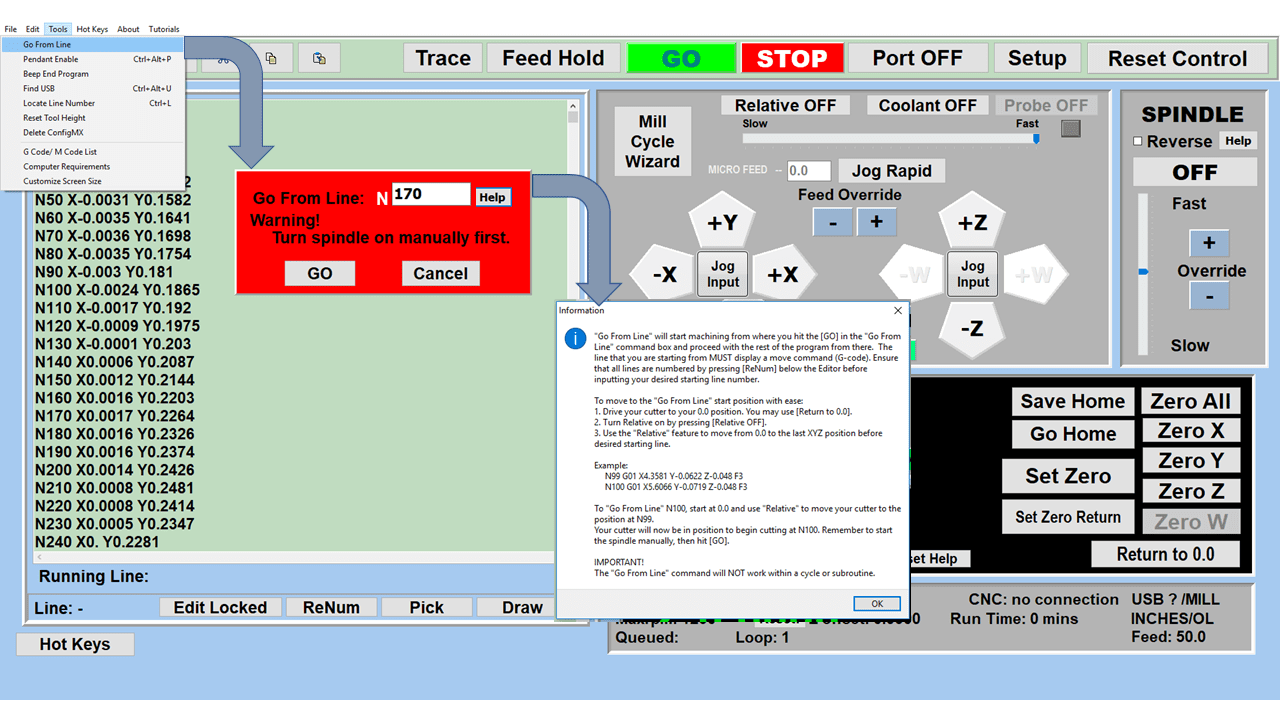
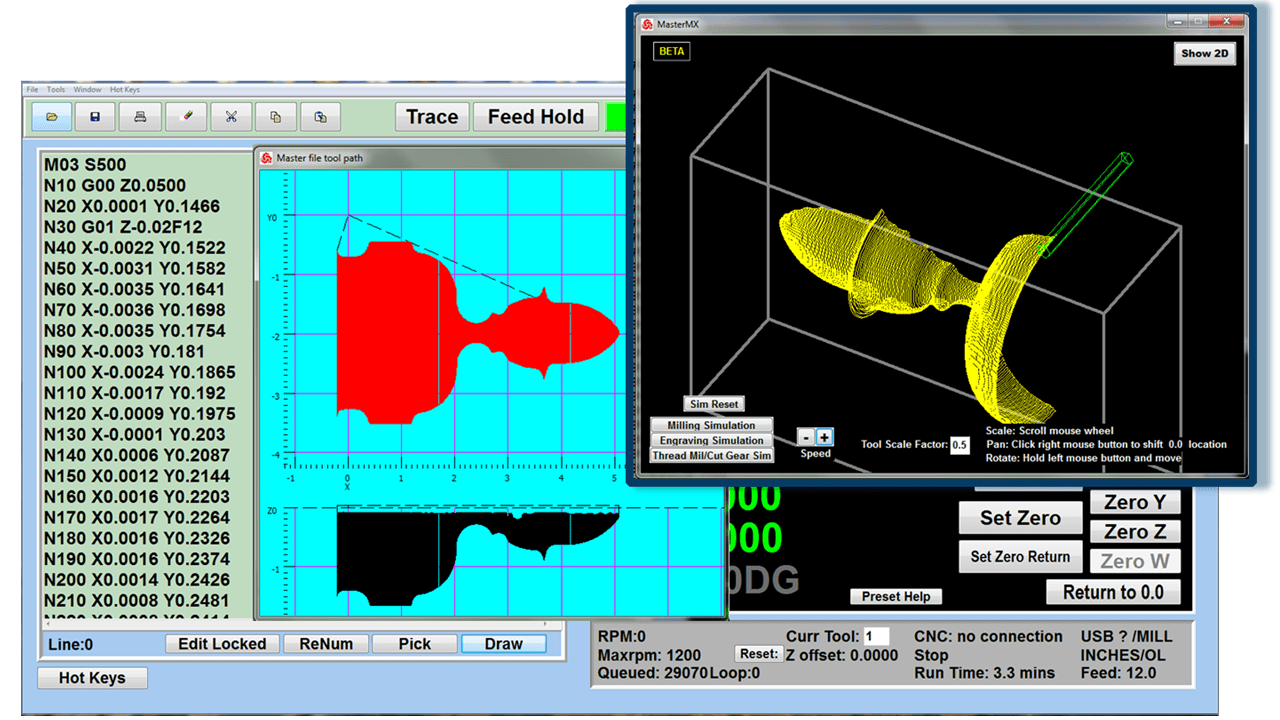
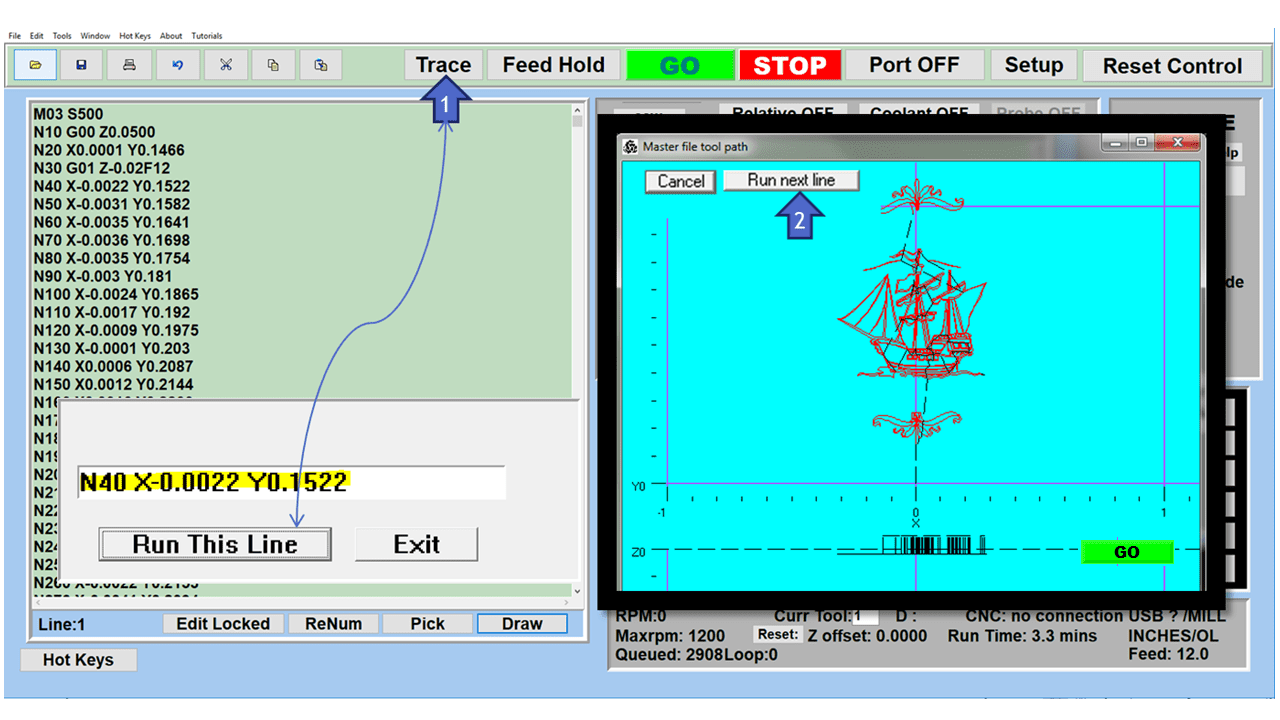
At the heart of a CNC mill is the CNC controller, a sophisticated computer system that converts a digital design into commands that drive the machine’s movements. The controller interprets G-code or other programming languages, outlining the tool paths and movements necessary to create the desired part. It precisely controls aspects such as speed, feed rate, and coordination of the spindle and tool changer. The CNC controller is the interface through which operators input data, monitor the milling process, and make adjustments as needed. Advanced CNC controllers also offer features like real-time feedback, error detection, and adaptive control, enhancing the precision and reliability of the milling process.
Column and Base
The cast iron column and base support the other parts of the milling machine operations. The column rests on the base and typically houses the oil and coolant system. The base is the foundation carrying the weight of everything on the machine, while the column takes the direct weight of the knee and work table. The weight of these two components ensures there is minimum vibration and better surface finishes even after the heaviest cuts.
Control Panel
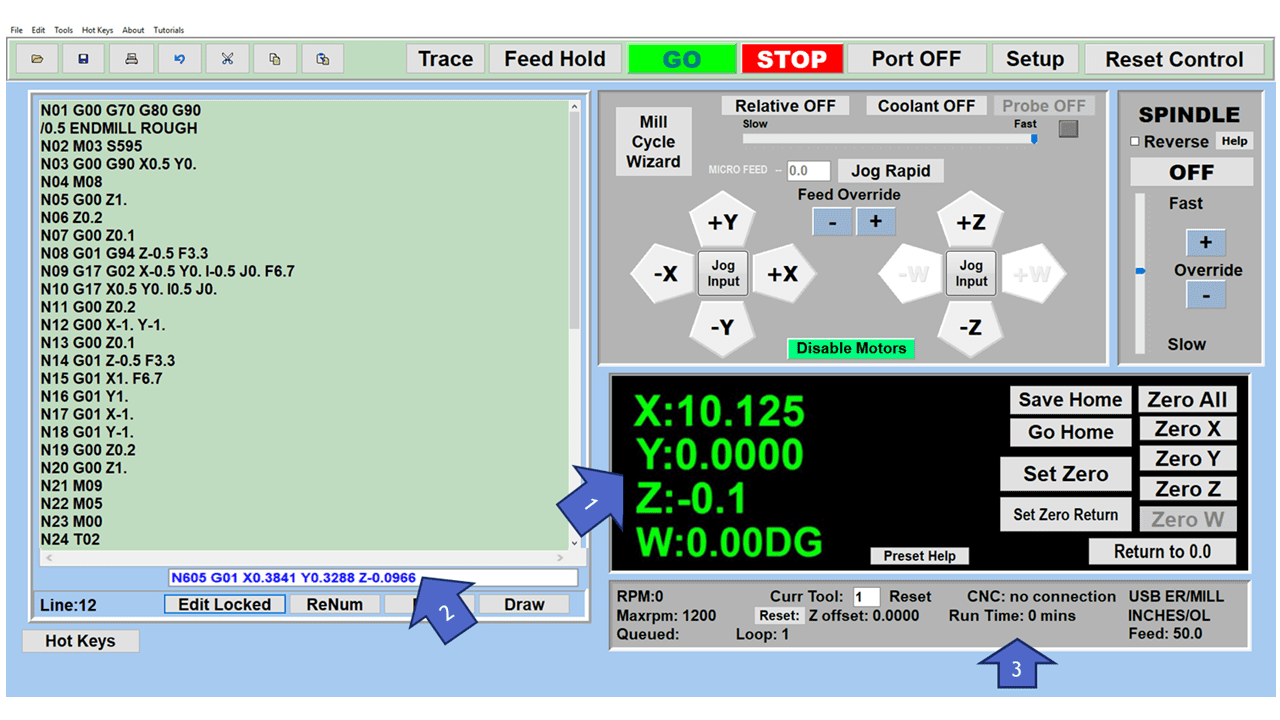
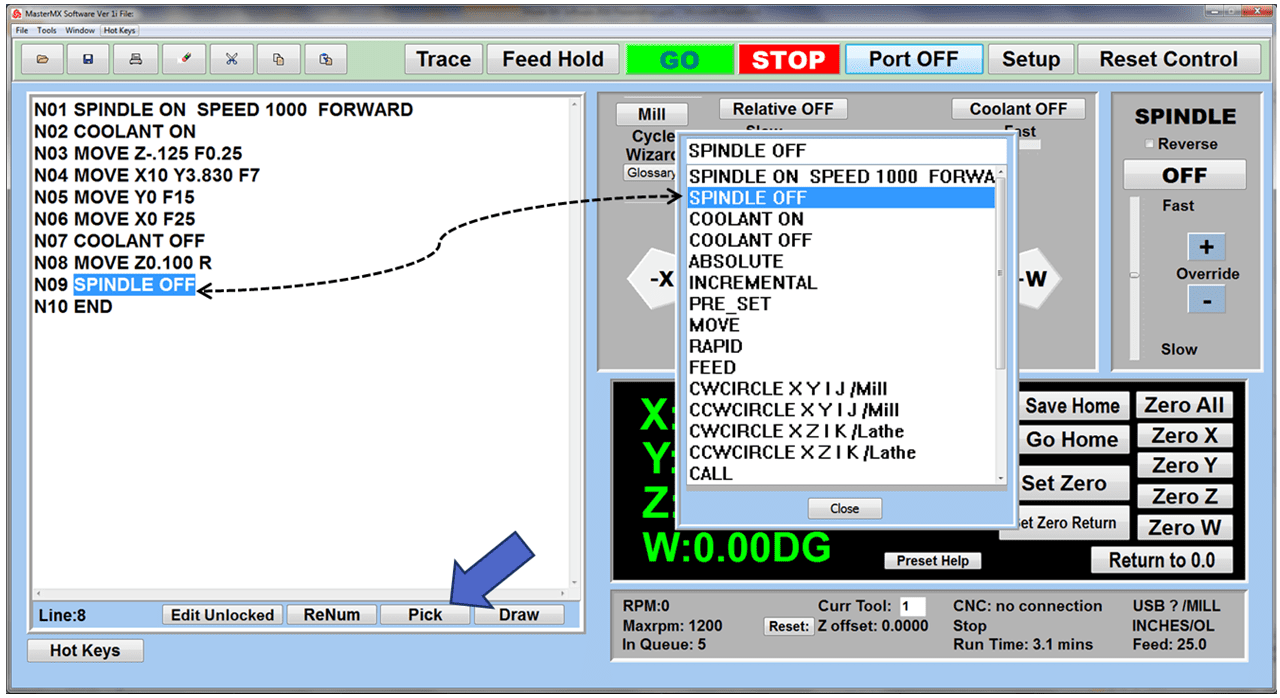
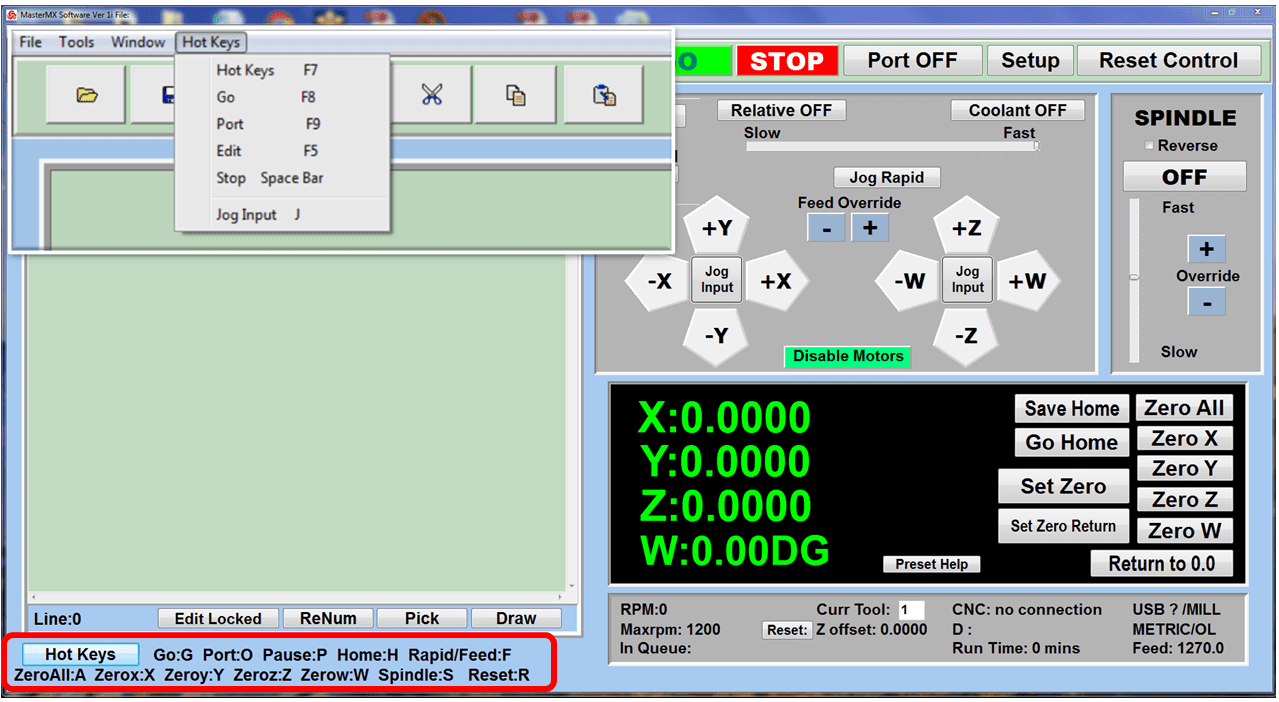
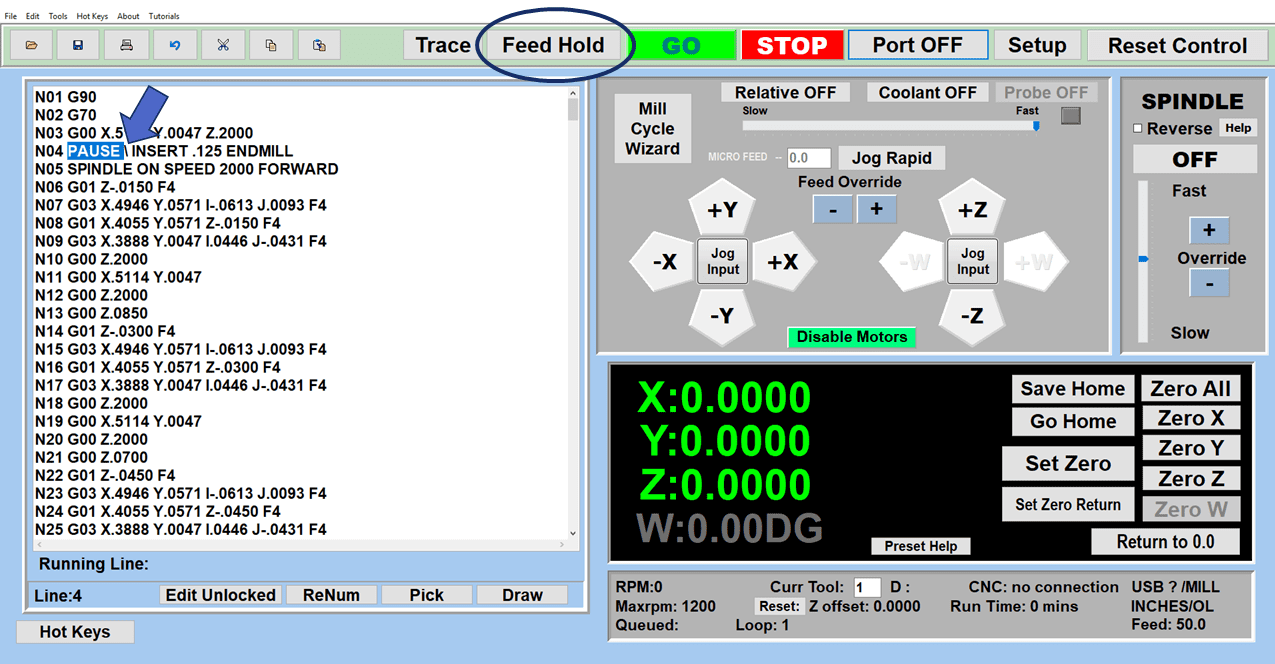
The control panel on a CNC mill is where the operator runs the machine. It has buttons, switches, and usually a screen to show information. The operator uses it to start and stop the mill, control how fast it moves, and pick different ways to use the machine. The screen shows important details like the path the tool is taking and if there are any problems. In modern CNC mills, the control panel can be quite advanced, letting the operator program the mill, see what’s happening as the machine works, and even try out the milling process virtually before actually starting.
Automatic Tool Changer (ATC)
The tool changer is a critical component of a CNC mill, serving as the mechanism that automatically switches between different tools during the machining process. This feature is essential for complex operations requiring multiple tools, such as drilling, milling, and tapping. The tool changer operates under the control of the CNC system, allowing for seamless transitions and minimizing manual intervention. It typically consists of a magazine or carousel that holds a variety of tools and a robotic arm or other mechanism for selecting and changing the tools. The efficiency and capacity of the tool changer are crucial for high-volume production, as they significantly reduce setup time and increase the overall efficiency of the milling process.
Knee
The knee is attached to the column by dovetail ways and is supported and adjusted up and down by an elevating screw, also called a vertical positioning screw, running vertically from the base. The vertical movement can be achieved by either a hand crank or power feed. The handle to move the saddle in the transverse direction (cross feed, or in and out) is also located on the knee, while the gearing mechanism is enclosed within the knee. Some milling machines have power table feed in the transverse direction, and that unit is on the knee, as well.
The saddle is on top of the knee moving transversely to the column and providing motion in a horizontal direction to the workpiece. It is also made of cast iron.
Power Feed Mechanism
The power feed mechanism is contained in the knee. The power feed mechanism is used to control longitudinal (left and right), transverse (in and out), and vertical (up and down) feeds. Feed rates are changed for some knee milling machines by turning the speed selection handle. Most milling machines have a rapid traverse lever to provide a temporary increase in the speed of the longitudinal, transverse, or vertical feeds.
Work Table
As its name suggests, most of the machining work happens on the work table. The table is a rectangular piece of cast iron with T-slots for clamping a workpiece directly to it or fastening a vise or other work holding device to hold smaller parts and machine them safely and efficiently.
The longitudinal variable speed power feed and handles are part of the work table. In addition, an X-axis leadscrew under the table engages with a nut and assists the table in moving horizontally, either under power or manually.
Motor (Servo/Stepper)
Motors in a CNC mill, which can be either servo or stepper types, play a crucial role in translating the commands from the CNC controller into precise movements of the machine’s axes. Stepper motors are typically used for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, operating in fixed steps that provide decent accuracy for many applications. However, for higher precision and smoother motion, servo motors are often preferred. Servo motors use feedback systems to continuously adjust for position and velocity, ensuring exact adherence to the CNC controller’s commands. The choice between servo and stepper motors depends on the specific requirements of the machining task, such as the needed speed, accuracy, and complexity of movements.
Ram
The ram is a movable overhanging arm on a vertical milling machine. The ram is mounted on top of the column, and the milling head is attached to it on one end. On Bridgeport milling machines, the operator can extend and swivel the ram to cover more of the work table when machining a larger workpiece.
Overhanging Arm (Horizontal Milling Machine)
The overhanging arm, often called the overarm, is a horizontal cat iron beam on the top of the column on a horizontal milling machine. Similar to the ram on a vertical milling machine, it’s usually a single cast iron piece sliding on the dovetail way.
Spindle
One of the essential parts of the milling machine is the spindle. It holds and drives the cutting tools and also a drill chuck, collets, and other tool holders. Many vertical milling machines are de facto drilling machines in addition to doing side milling, flat milling, and various other types of cutting that require high-quality tooling.
Because of the different shapes and mechanical application methods of the milling cutters, the milling machine can perform various milling jobs, including plane milling, surface milling, angular milling, groove milling, gear milling, and cam milling. You can use a forming milling cutter to machine complex contours and an indexing head to mill a helical groove.
Arbor Support (Horizontal Milling Machine)
The arbor support is a casting with a bearing that supports the arbor’s outer end and aligns the arbor’s outer end with the spindle. Arbor support prevents the springing of the outer end of the arbor in cutting operations. Multiple cutting tools can be mounted on the arbor for gang milling, offering higher productivity with the arbor support reinforcing the arbor to allow for heavier cuts.
CNC Vertical Milling Machines Built in the USA
At CNC Masters, we stand out from the competition by integrating the best features of manual vertical milling machines and milling machines with CNC capabilities. Our design works well with customers accustomed to manual controls since they discover how easy it is to learn the CNC machines, without the steep learning curve.
Look at our lineup of CNC Supra Vertical Knee Mills in two popular sizes. If you’re looking for a great CNC machine tool that fits on a benchtop, consider our CNC Jr benchtop mill. All our machines come with a one-year warranty and the best customer support you’ll find anywhere.
We can also offer you a CNC conversion kit if you’re a transition user.