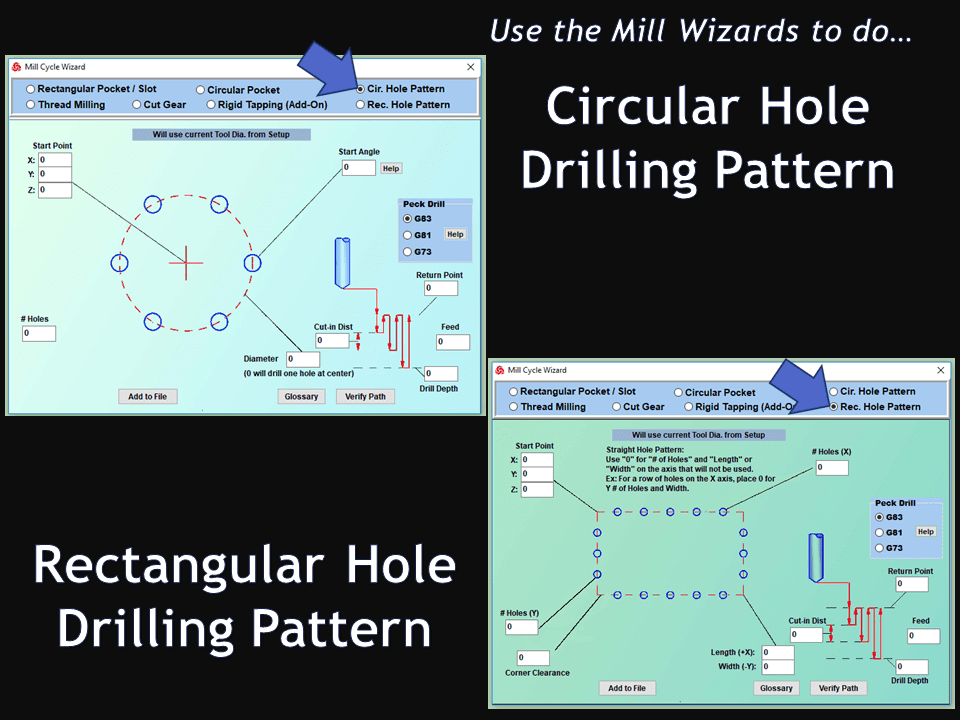
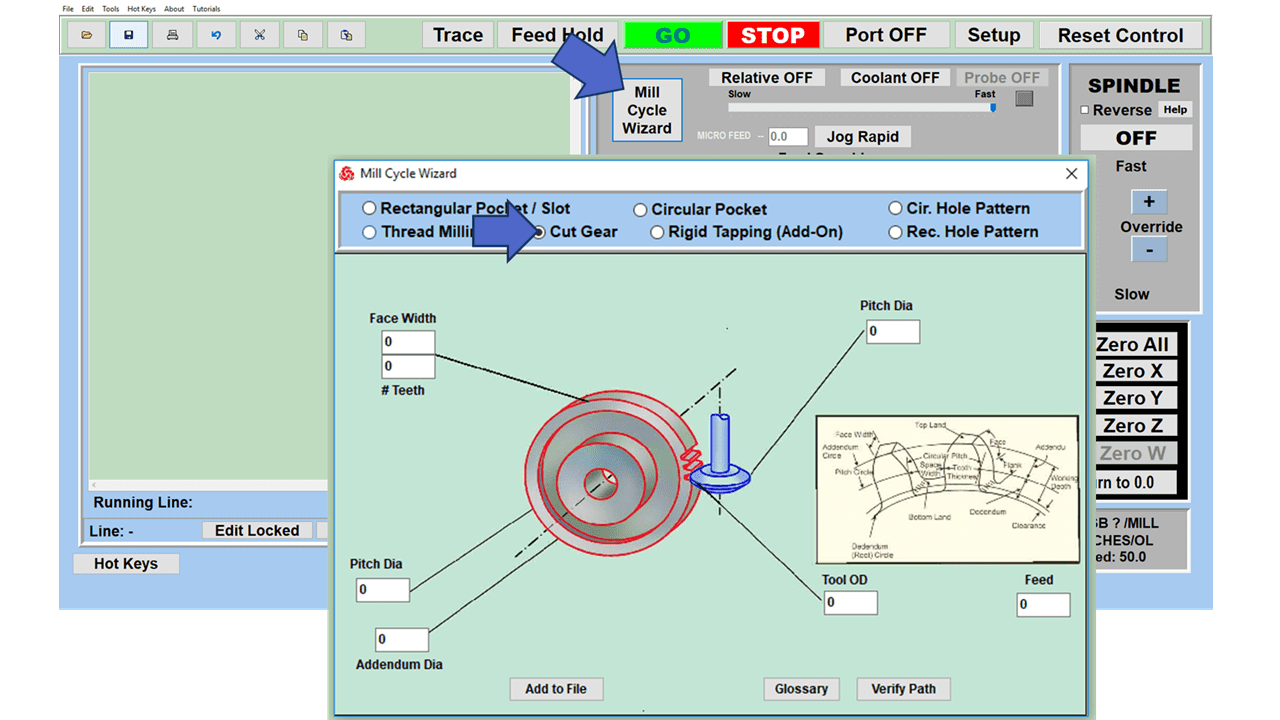
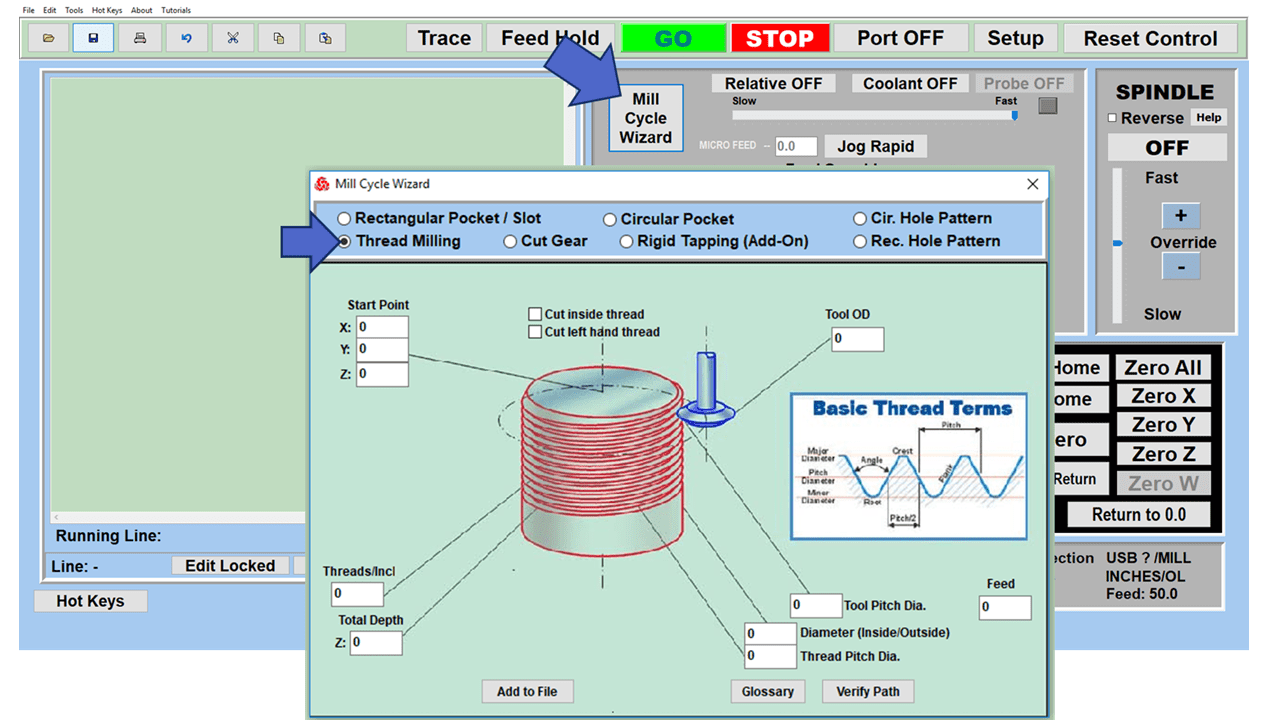
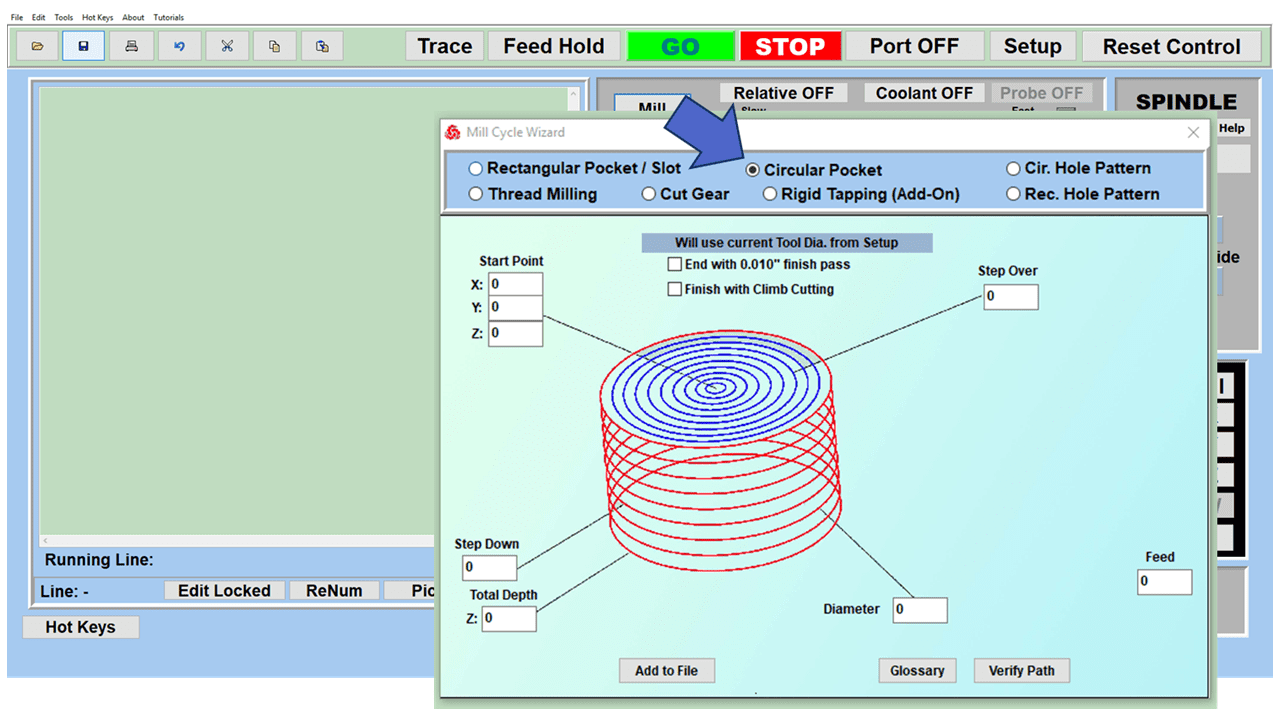
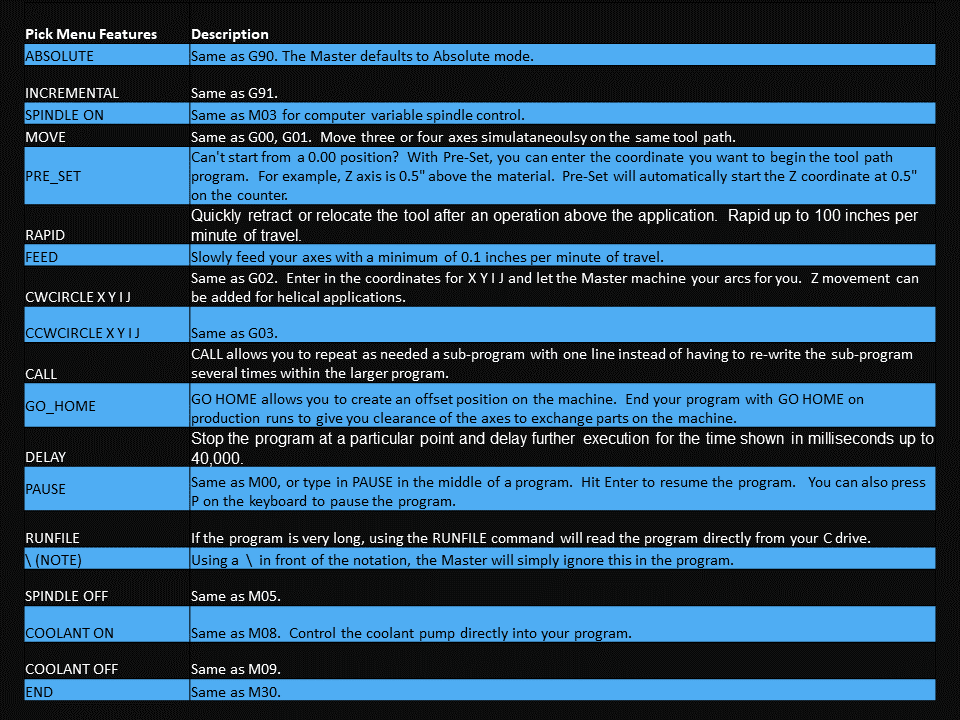
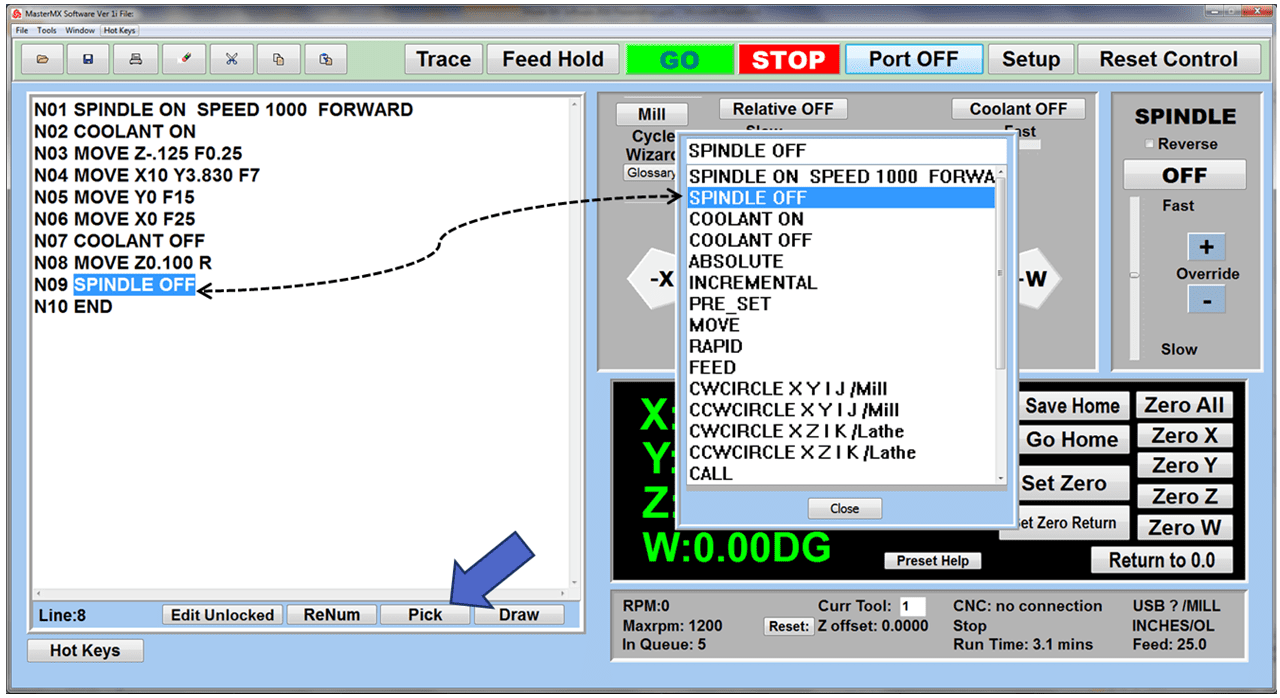
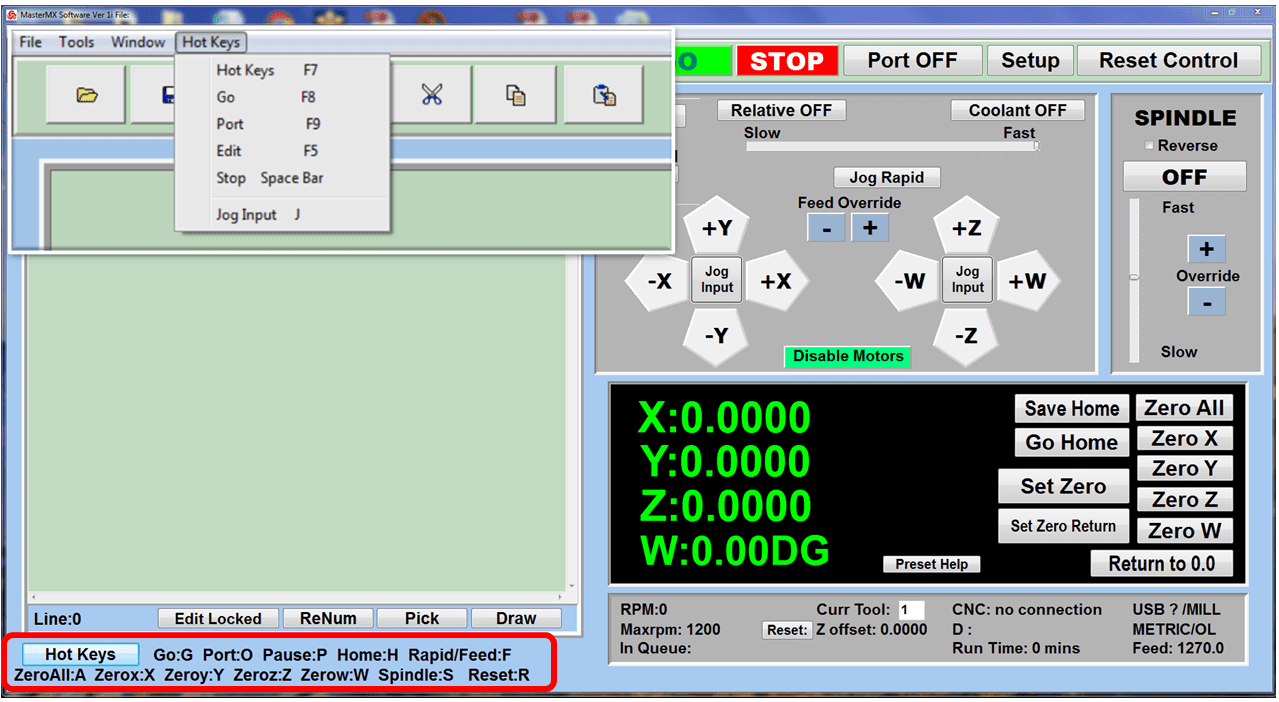
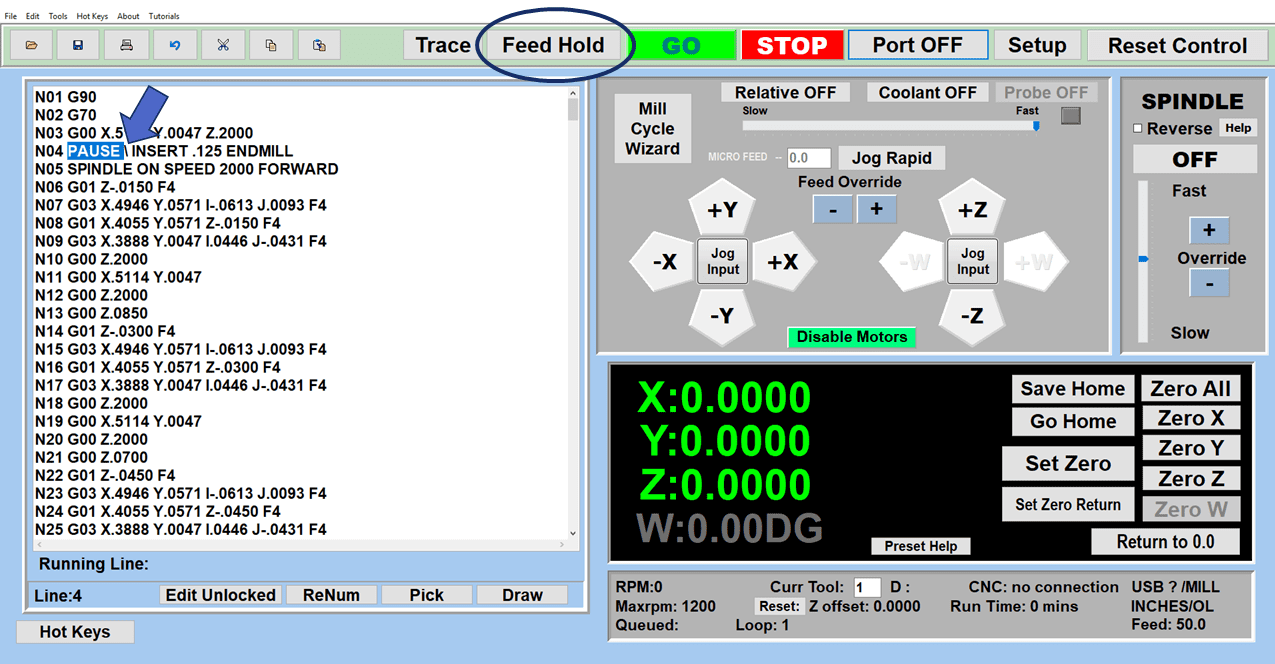
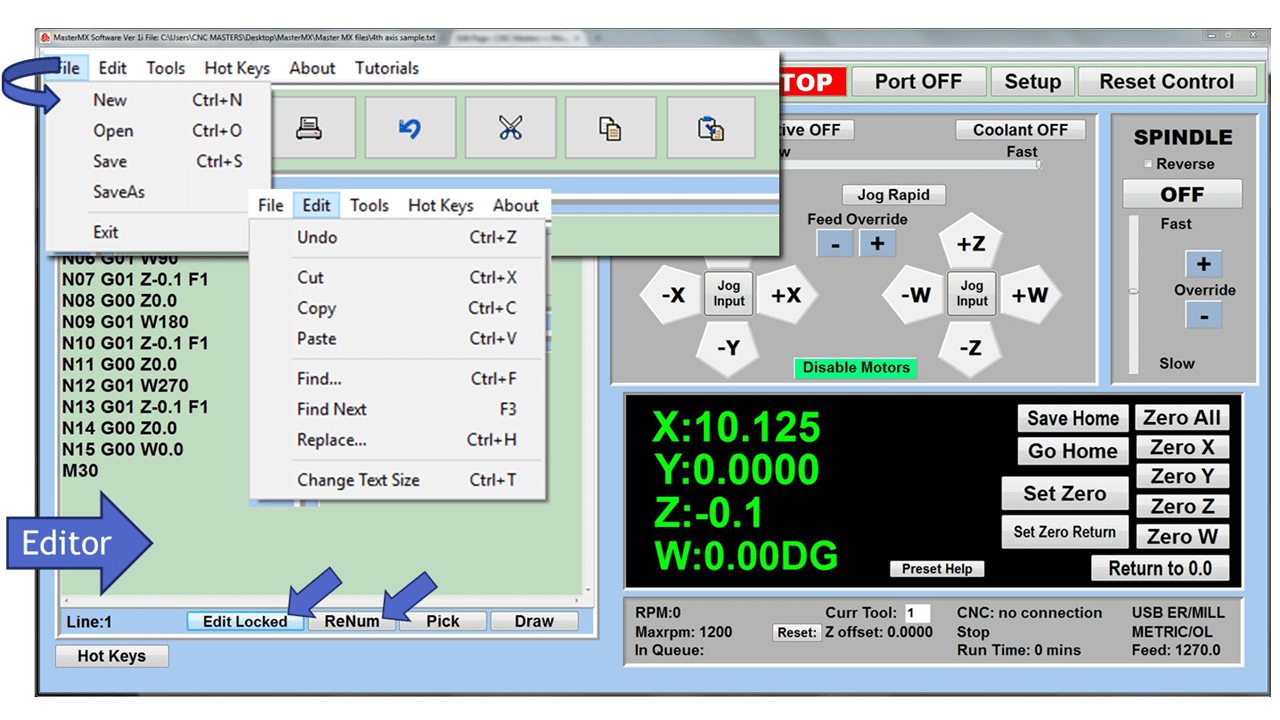
As we look toward 2024, the manufacturing industry is poised to undergo significant transformations that could redefine its landscape. Technological advancements, combined with shifts in consumer behavior and expectations, are paving the way for more efficient, sustainable, and customer-focused manufacturing than ever before.
These manufacturing trends encompass various areas such as automation, digitalization, sustainability, labor shortages, and workforce retention with each having far-reaching implications on how manufacturers operate and plan for the future. These trends could mean significant change is needed in your manufacturing processes. Learn more as we look at seven key trends the manufacturing sector will likely encounter in the coming year.
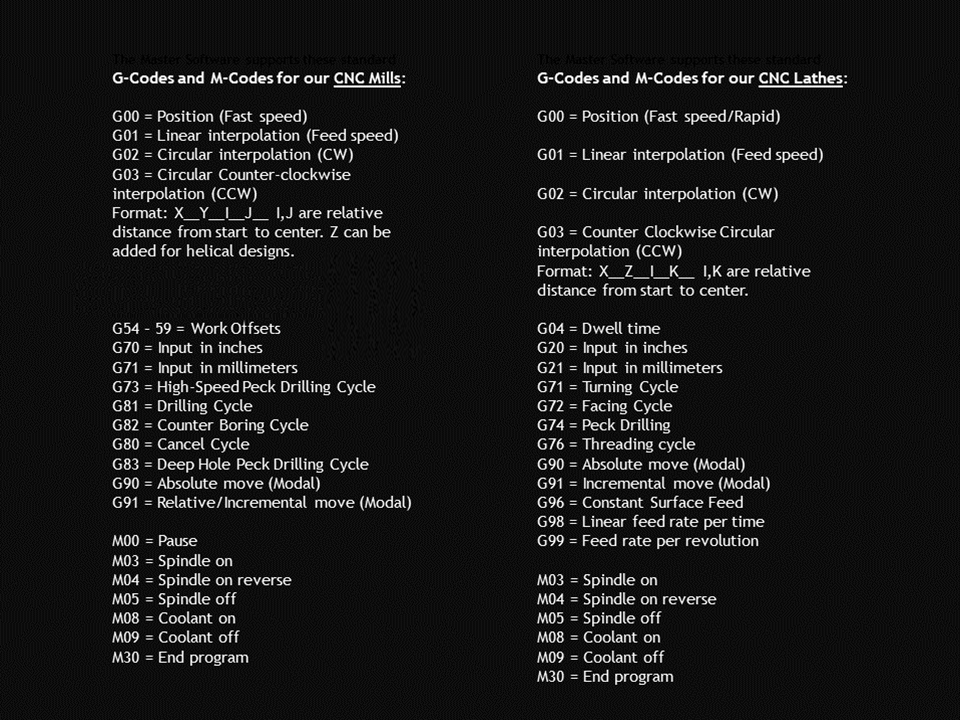
1. Artificial Intelligence Will Take Center Stage
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in manufacturing continues to accelerate the Fourth Industrial Revolution or Industry 4.0. AI algorithms optimize and streamline manufacturing operations to boost productivity, improve quality control, and reduce operational costs. Machine learning, a subset of AI, enables predictive maintenance by recognizing potential equipment failures before it can cause significant downtime. AI-powered robotics enhances precision and efficiency, and using AI in supply chain forecasting reduces waste and improves delivery times.
AI offers numerous benefits, including its ability to analyze huge chunks of data quickly and in real-time. With the use of Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) devices and sensors, data collected from machines, equipment, and production lines can be processed and analyzed by AI algorithms, enabling manufacturers to understand their production processes more effectively.
Another advantage of AI technology in manufacturing is its ability to identify irregularities and equipment defects. With machine-learning algorithms trained to recognize patterns in the data, manufacturers can make informed decisions and detect quality issues early on in the production process.
Overall, AI can assist manufacturers in implementing the aforementioned predictive maintenance systems, optimizing supply chain management, proactively identifying and addressing workplace safety hazards, and enhancing decision-making. This digital transformation continues to reshape the manufacturing landscape, driving innovation and competitiveness.
2. Robotics and Automation Help Manufacturers Stay Competitive
Intelligent manufacturing includes robotic process automation where robots take on repetitive and dangerous jobs like assembly, welding, and material handling, freeing human resources to focus on more complex and creative tasks. Robotic technology accomplishes these repetitive tasks faster, more accurately, and without the fatigue inherent in human labor. Manufacturers can combine robots with IoT sensors and big data analytics to create a more adaptable and responsive production environment.
Ultimately, the advanced technologies in robotic automation drive smart manufacturing, improving efficiency, decreasing errors, cutting equipment downtime, and enhancing worker safety. Plus, robots can work nonstop, allowing manufacturers to operate 24/7 and significantly increase productivity.
Yet, the rise of robotics and automation also poses challenges, particularly concerning job displacement and the need to close the skills gap. As these technologies evolve, manufacturing companies must manage the transition sustainably and beneficially.
3D printing (a.k.a. additive manufacturing) has revolutionized the manufacturing industry by enabling the creation of complex, custom, and scalable designs with high precision. It works by stacking multiple thin layers of material on top of each other using a digital model, resulting in a three-dimensional object. This advanced manufacturing technique reduces material waste and produces parts with intricate geometries that would otherwise be impossible to machine using traditional manufacturing techniques. Moreover, 3D printing can accelerate product development since companies can create and test prototypes rapidly, decreasing the time to market for new products.
Smart factories have used this cutting-edge technology for several years because it eliminates many of the limitations of part geometry while streamlining the manufacturing process, thus saving time and reducing costs. Industries like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare benefit from this innovation as it enables the production of intricate parts and the ability to create spare parts as needed, avoiding supply chain disruptions.
4. Supply Chain Disruptions Will Keep Reshoring on the Front Burner
Get ready for another significant change in manufacturing! Global issues like the war in Ukraine and the pandemic caused considerable disruptions in the supply chain that are likely to continue. However, manufacturers are finding a way to adapt and improve the situation with restoring.
Reshoring refers to bringing domestic manufacturing and services back to the United States from overseas. This business strategy emerged as a response to the challenges and costs associated with offshoring such as increased shipping expenses, communication difficulties, and quality control issues.
And reshoring isn’t just a tiny shift. A 2022 report from The Reshoring Initiative reveals a whopping 364,000 reshoring and foreign direct investment (FDI) jobs for 2022. That’s a 53% increase from the previous record set in 2021.
Why is reshoring so important? There are several reasons:
- Reduced Costs: Although foreign manufacturers typically operate with lower overhead including cheap labor, manufacturers have found these savings offset by the time and money spent transporting goods internationally. Automaker Ford Motor Company leads the car industry in reshoring manufacturing to the US. The company has found that domestic facilities actually boost design and manufacturing competitiveness.
- Enhanced Control: Companies have found that increased dependence on distant manufacturers creates vulnerability during turbulent times. With reshoring, companies have greater oversight and control over parts and production processes. Apple recently contracted with Broadcom for US-based chip manufacturing as part of its efforts to decrease dependence on manufacturing in China.
- Faster Time to Market: Domestic manufacturing helps speed up product time to hit the market, meaning faster responses to changes in demand. When the pandemic created a sudden need for ventilators, US companies could pivot and produce them domestically – thanks to the agility of reshored manufacturing.
- Local Job Creation: Reshoring doesn’t just benefit manufacturers; it also stimulates local economies by creating jobs. General Electric has brought back some of its appliance manufacturing operations to Kentucky, creating hundreds of jobs and boosting the local economy. Walmart’s strategic plan extending through 2030 includes $350 billion in American manufacturing and 750,000 potential jobs.
Reshoring can stimulate the economy by generating jobs, fostering innovation, and improving the speed to market of goods and services. Companies want to become more resilient and less susceptible to global crises that impact their supply chain, so this trend will likely continue.
5. Digital Twins Become Increasingly Popular
Digital twins have rapidly emerged as a critical component of smart manufacturing. A digital twin replicates a physical asset or process in simulation software, enabling real-time monitoring, testing, and optimization. During manufacturing, these digital clones can encompass an entire production line, a single machine, or even a part.
Digital twins optimize operations because they are used to track, monitor, and diagnose equipment, leading to significant improvements in production efficiency and reduction in downtime. Digital twins can predict potential failures before they occur and reduce the time spent on maintenance, thereby extending the lifespan of machines.
Moreover, these virtual replicas create the ability to test changes to the production process or machinery in a risk-free environment, fostering innovation. This capability can be especially beneficial for complex or high-value manufacturing.
In addition, digital twins support the integration of manufacturing processes with other business areas such as supply chain management. By providing a real-time view of production status, they can help streamline operations and enhance coordination which results in quicker decision-making and improved responsiveness to changes in demand.
Digital twins in smart manufacturing provide the catalyst for next-generation, Industry 4.0 technologies, enhancing connectivity and automation while promoting an environment of continuous improvement and innovation.
6. Enhanced Focus on Sustainability and Carbon Neutrality
Sustainability and carbon neutrality are becoming increasingly integral components of the manufacturing sector. This shift comes from a growing awareness of the environmental impact of manufacturing activities, long-term socio-economic benefits, and the continued incentivization of sustainable practices.
Manufacturers are employing several strategies to reduce emissions and attain carbon neutrality. These include using renewable energy sources, optimizing energy efficiency in production processes, and adopting circular economy models emphasizing the reuse and recycling of materials. Such practices reduce the carbon footprint and decrease raw material consumption and waste generation.
Investments in cleaner, more efficient technology and infrastructure are critical. For instance, using AI and IoT in predictive maintenance can minimize energy waste, while advanced materials can reduce product weight and energy consumption.
The journey towards sustainability and carbon neutrality in manufacturing is challenging. Still, the rewards – a healthier environment, cost savings, enhanced brand reputation, and increased customer loyalty – make it a worthwhile pursuit.
7. Labor Shortages Will Continue to Haunt Manufacturing
Global manufacturing faces labor shortages, a problem exacerbated by an aging workforce and the onset of Industry 4.0. The widening gap between the demand for skilled labor and the supply of workers with those skills is troubling. Several measures address this issue such as companies investing in workforce development programs and training existing workers to meet the evolving needs of the industry.
Additionally, partnerships with educational institutions have been encouraging curriculum alignment with industrial requirements. Technology has come to the rescue, with automation and robotics filling in for labor-intensive roles. While these efforts have begun to mitigate the problem, a long-term strategic approach to workforce planning and development remains essential to tackle future labor shortages in manufacturing.
CNC Masters in 2024 and Beyond
Driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and a greater emphasis on sustainability, the manufacturing landscape in 2024 is evolving rapidly. Since our founding in 1990, CNC Masters has worked to provide the machines you need to adapt to change and harness new technologies to stay competitive in 2024 and beyond.