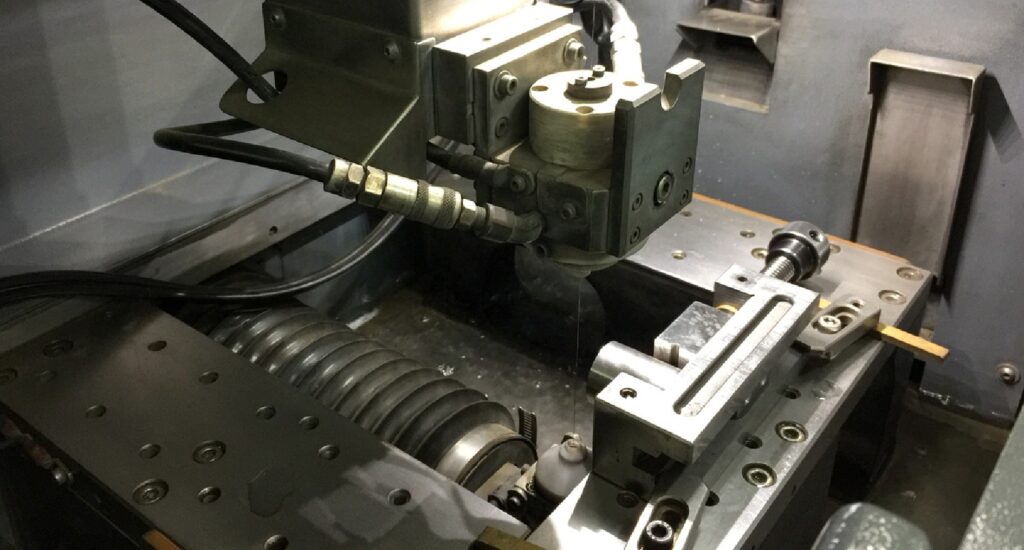
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) is a process that applies CNC technology with electrical sparks to form simple or complex shapes. Sometimes referred to as spark machining, EDM creates profiles when current discharges and sparks occur between two electrodes—the wire and the workpiece. As the wire moves through the workpiece, it cuts the desired shape, and eventually, the material detaches it from the workpiece.
Here is what you need to know before purchasing your first or next CNC wire EDM.
How Does Electrical Discharge Machining Work?
As mentioned, electrical discharge machining begins when a spark is created between two electrodes, producing temperatures reaching 8000 to 12000 degrees Celsius and vaporizing the conductive material. These electrical current discharges are continuous, in a tiny gap between the two electrodes. This spark gap is maintained by the EDM machine’s controls, ensuring a constant distance as the discharge occurs millions of times per second.
The spark is controlled with high precision and restricted to only involve the workpiece’s surface and does not affect heat treating below the surface. The wire, workpiece, and electric spark are submerged in dielectric fluid, usually deionized water,
The conductivity of the deionized water is carefully controlled, creating an ideal environment for the EDM process. The deionized water also provides cooling during the wire-erosion process, as it is sometimes called, and it flushes away the tiny metal particles.
Electrical discharge machining is considered a non-traditional machining method, in contrast to traditional CNC machining methods such as drilling, milling, and threading. Wire EDM uses a wire as the tool electrode, and the wire is wound between two spools. As the wire moves through the metal, the spools supply fresh wire. Depending on how fast the wire is replaced, wire consumption could be one of the main expenses of the EDM process.
What are the Two Main Types of EDM Machines?
There are two primary types of EDM, wire and sinker EDM, sometimes called ram EDM. However, our focus will be on the wire EDM machine and the wire-cut EDM process. Each EDM works differently, so here is a brief look at both EDM machine tools:
Conventional EDM Machines
You will hear conventional EDM, also called ram EDM, sinker EDM, die sinking, and cavity-type EDM. Suitable for creating complex shapes, the process involves precision machining graphite electrodes with conventional machining methods, such as CNC mills and lathes. The electrode is a negative impression of the cavity and will form and burn or “sink” into the workpiece.
A lesser-known EDM, similar to the ram EDM machine, is the small-hole EDM that uses cylindrical electrodes to machine holes.
Wire EDM Machines
Unlike ram EDM, wire EDM, or spark-eroding EDM, employs a thin heated wire as the electrode and creates a shape through wire erosion and burning. Diamond guides hold the wire steady as it moves through the workpiece to form a specific shape without touching the metal. An automated feeder allows the wire to continuously unspool, ensuring the wire is available for a smooth and uninterrupted shape.
Occasionally, the wire EDM process requires a cut through the middle of the workpiece instead of from the outside. When that happens, the aforementioned hole-drilling EDM is used to burn a “starter hole” in the metal so the wire can be threaded through the workpiece.
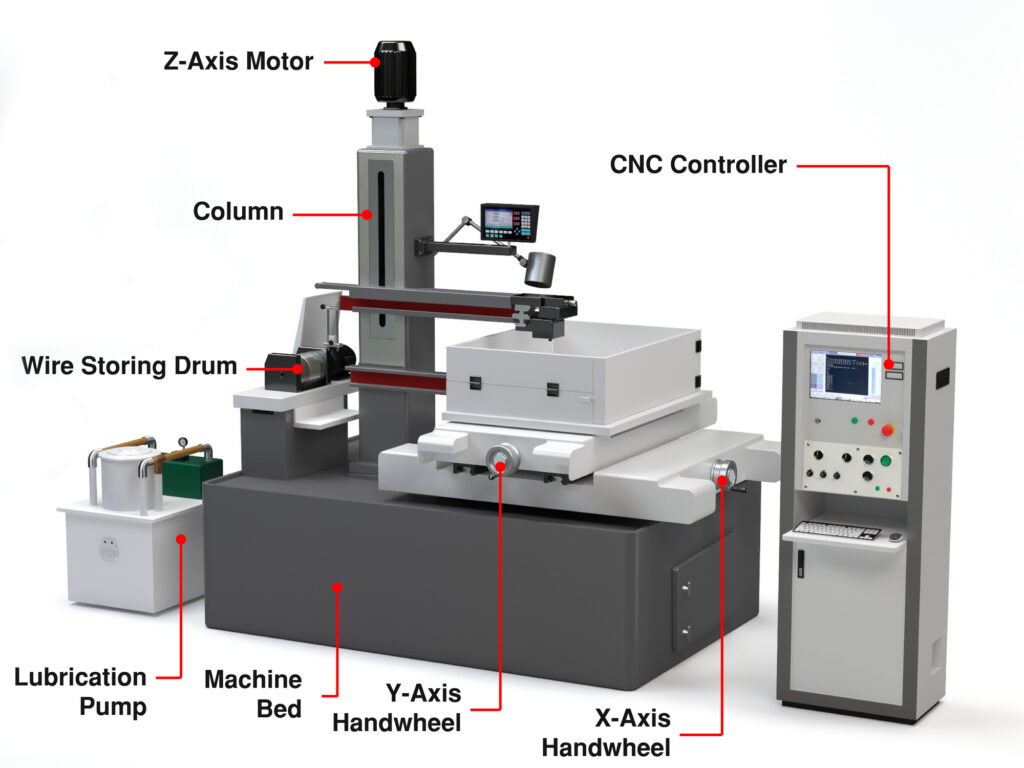
What are the Components Of A Wire EDM Machine?
The machine comprises several parts that work together to give a material the desired shape. Below are the components of the machine.
1. CNC EDM Controls
The CNC automation controls the wire EDM machining process, including the sequencing of the wire path and managing the cutting process automatically.
2. Power Supply
The power supply unit provides pulses (from 100V to 300V) to the wire electrode and the workpiece. It also controls the frequency and strength of the electrical charges passing through the wire electrode to interact with the workpiece. A quality power supply unit delivers the required charges during wire EDM machining.
3. Wire
A graphite electrode removes even hard materials with die-sinking EDM, but the wire serves as the electrode to create the electrical discharge during wire EDM. The shape and thickness of the workpiece directly influence the wire’s diameter, typically ranging from 0.05 to 0.25mm. The main types of wires include brass, zinc-coated, and diffusion-annealed wires.
4. Dielectric Medium
The wire-cut EDM process must be completed in a tank filled with dielectric fluid, preventing the workpiece particles from attaching to the wire. The medium used most often is deionized water which cools the process and gives the workpiece an excellent surface finish.
5. Electrodes
The electrodes in the machine are the wire and workpiece. The servo motor controls the wire electrode, ensuring it does not come in contact with the workpiece electrode anytime during the wire EDM cutting process.
How Do I Choose the Right Wire for My Project?
Getting the right spark erosion comes from choosing the right EDM wire for your project. Consider the following EDM wire properties:
Tensile strength
Tensile strength refers to the wire’s ability to resist stretching and breaking. High-tensile EDM wire offers the best edge straightness, making it an excellent choice for single-pass parts and in smaller diameter wires to reduce breakage. High-tensile wire works well whenever straightness, accuracy, and a fine surface finish are required.
Fracture resistance
Fracture resistance describes the wire’s resilience or toughness and its ability to resist the effects of the active environment surrounding the spark gap.
Conductivity
Conductivity measures the wire’s ability to carry an electrical current, and the higher the wire’s conductivity, the more power it can deliver to the workpiece. Because high conductivity is more efficient, cutting speeds are typically increased.
Vaporization temperature
A low vaporization temperature of the wire aids in flushing the particles from the spark gap, which is already tiny enough without having these “chips” take up room. As a result, moly and tungsten wires, with their higher vaporization temperatures, cut more slowly and flush poorly. However, they are satisfactory for roughing cuts where speed is not an issue. Even though melting produces particles, low-temp electrode alloys carry more water and contaminants away from the gap, aiding in flushing.
Hardness
Hardness is not the same as tensile strength. Instead, it refers to the wire’s ductility or ability to undergo elongation. EDM wires are either soft or hard, with the hard wire threading better than a softer wire and a soft wire taper-cutting better. A hard wire will also provide the best auto-threading reliability.
What is a Wire EDM Machine Used For?
Wire-EDM has developed into micromachining technology with precision beyond the reach of general machining. And the processing range is also relatively broad since practically any metal-conductive material can be managed without regard to the material’s hardness. Wire EDM is considered one of the most cost-effective methods for machining hard and conductive materials. Unlike conventional machining methods, wire EDM does not produce high driving force, resulting in relatively accurate and high-speed machining. This fact helps to explain why wire EDM is becoming popular with manufacturers.
Here is a list of its other advantages:
- Wire EDM creates simple or complex shapes that would be challenging to produce with conventional machining centers and cutting tools.
- CNC-controlled cutting works on many stainless steel alloys while maintaining a low Ra surface roughness
- Dimensional accuracy for tight-tolerance parts
- No contact between the wire and the workpiece, allowing for the machining of fragile sections and weak materials.
- The process leaves few burrs
- Custom tooling is typically not required
- The working fluid of wire EDM is non-flammable, allowing for unmanned operation, while automatic control enhances the ease of use.
- No high-impact cutting to create stresses that can deform the material.
- Because wire-cut EDM efficiently processes any conductive material, it takes less time and reduces waste and cleanup time.
- EDM is applicable for machining small parts and highly detailed parts that are too delicate for other machining methods.
- It works for single-piece prototyping.
Are There Drawbacks to CNC EDM?
Although wire EDM offers many benefits to manufacturing companies, there are also disadvantages:
- It is only compatible with materials that conduct electricity.
- Composite or dielectric-coated materials are not candidates for wire EDM.
- An oxide layer can develop on the cut surface of some materials, causing expensive additional finishing operations.
- EDM requires a high initial investment and maintenance costs.
What are Some Applications for Wire EDM?
Although many industries use wire EDM machines for prototyping and production runs, the following three represent the industries that are most likely to use them:
Aerospace Industry
Wire EDM produces tight-tolerance parts and components, an essential requirement for aerospace part manufacturing. Along with the waterjet cutting process, EDM is the choice for creating pieces that will not withstand the high temperature and stress associated with traditional machining processes.
Aerospace industry parts, including turbine blades and landing gear components, rely on an excellent surface finish and must be highly accurate. Manufacturers have been using the wire-EDM process for many years with exceptional results.
Automotive Industry
Automotive parts often have complex shapes and are produced from hard materials. Because of this, they prefer wire EDM machines that do not rely on mechanical forces to make their parts. The wire EDM process applies to creating holes, cavities, and custom parts like bumpers, dashboards, and car doors.
Medical Industry
Wire EDM machines produce complex and accurate parts for all medical fields, including optometry and dentistry. The metals that work well with wire EDM machines are often used to make medical equipment.
Because the wire’s diameter determines the cut’s size, the wire EDM machine can add tiny features to parts like dental implants and syringe components without endangering their structural integrity.
What Materials Can Be Cut Using Wire-EDM?
You can cut any conductive material, including, but not limited to, carbon steel, stainless steel, titanium, aluminum, brass, bronze, Hastelloy, high-alloy steel, Inconel, tungsten, and more. Because of its accuracy, the EDM wire-cut method has become preferred in all industries.
Regardless of the material type, many machine parts can be produced quickly using EDM wire. However, creating parts or prototypes will depend on the workpiece’s dimensions, thickness, and length.
What are Some of the Most Reputable Wire-EDM Brands?
The following wire-EDM brands have stellar reputations, but the best wire-EDM machine for your specific operation will depend on the type of parts you intend to produce. Many claim that Makino offers the best wire EDM machines in 2023 because of their speed, accuracy, and ease of use.
Nonetheless, all the machine tool brands are on this list because they have shown superior performance over time. Here are the top five wire EDM machine manufacturers for 2023:
1. Makino
Makino is well-respected throughout the machine tool industry for their high-quality CNC machines. Their wire EDM machines are no exception with more than a dozen wire EDM models from which to choose.
2. Mitsubishi
Mitsubishi offers five separate lines of wire EDM machines, and their MX600 has the highest accuracy level and can produce the smallest possible parts of all their models.
3. FANUC
The wire EDM machines offered by FANUC are marketed under the proprietary name, ROBOCUT. FANUC has three ROBOCUT models: a small model for compact parts, a medium-sized all-around model, and a model for larger parts.
4. ONA
ONA has four series of wire EDM machines: compact, modular, hole-drilling, and custom models. Their compact options have smaller footprints but deliver high-precision cuts. Their modular wire EDM machines are known for their flexibility. ONA can supply a wire EDM machine for most applications, part sizes, and geometries.
5. Sodick
Sodick offers six different wire EDM machines, at least one of which can accommodate any size part. Each of the machines is linear-motor driven, resulting in vibration-free operation and zero backlash, enabling high-accuracy cutting and fine surface finishes. Sodick is the only company in the EDM industry to guarantee the positional accuracy of their wire EDM machines for 10 years.
How Much Does a Wire EDM Machine Cost?
A new AgieCharmilles CUT C 350 Wire EDM has a starting price of $99,000, while more popular brands will be closer to the $125,000 to $150,000 price range. For comparison, a 2020 Makino U3 Wire EDM Machine sells for $100,000, a 2000 Mitsubishi RA90 Wire Cut is $19,500, and a 2004 Makino U86 is priced at just under $50,000.
Conclusion
Wire EDM is a versatile and precise machining process that produces complex shapes and geometries. A favorite of the automotive, aerospace, and medical industries, where parts need to meet tight tolerances, wire EDM, can also be used to create prototypes or single pieces. We hope this article has given you a better understanding and appreciation of this unique and essential machine tool!