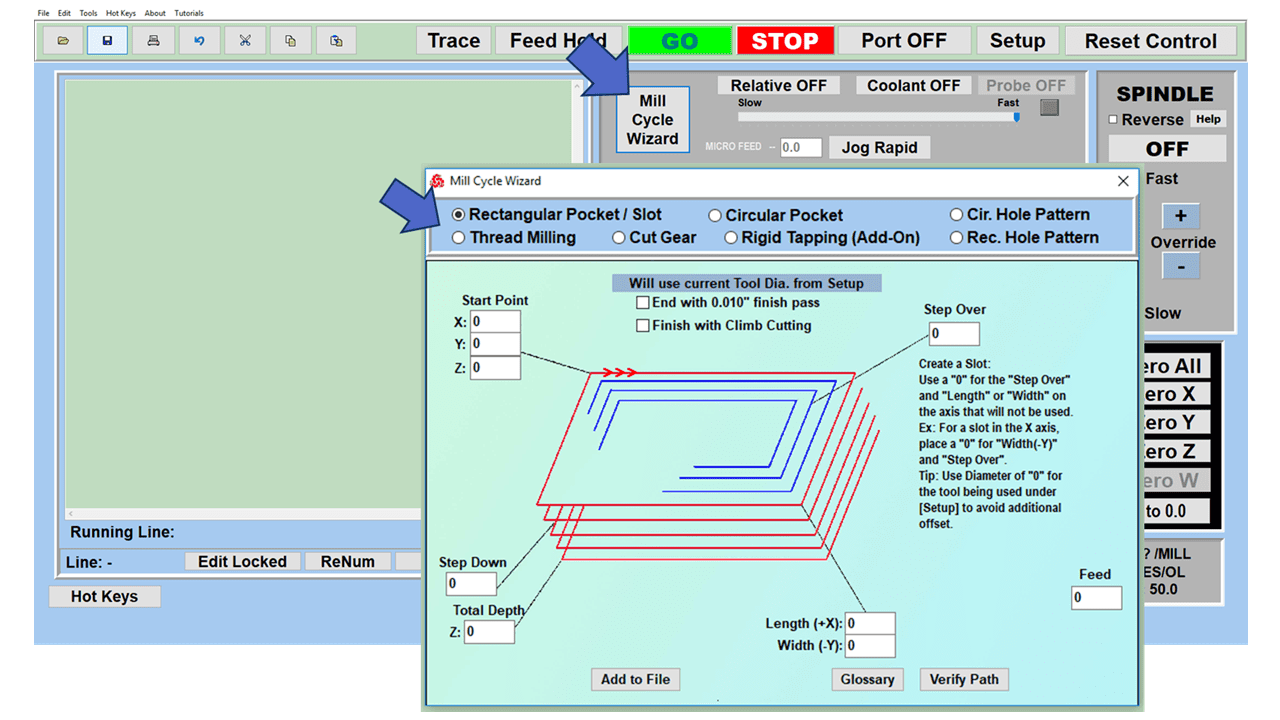
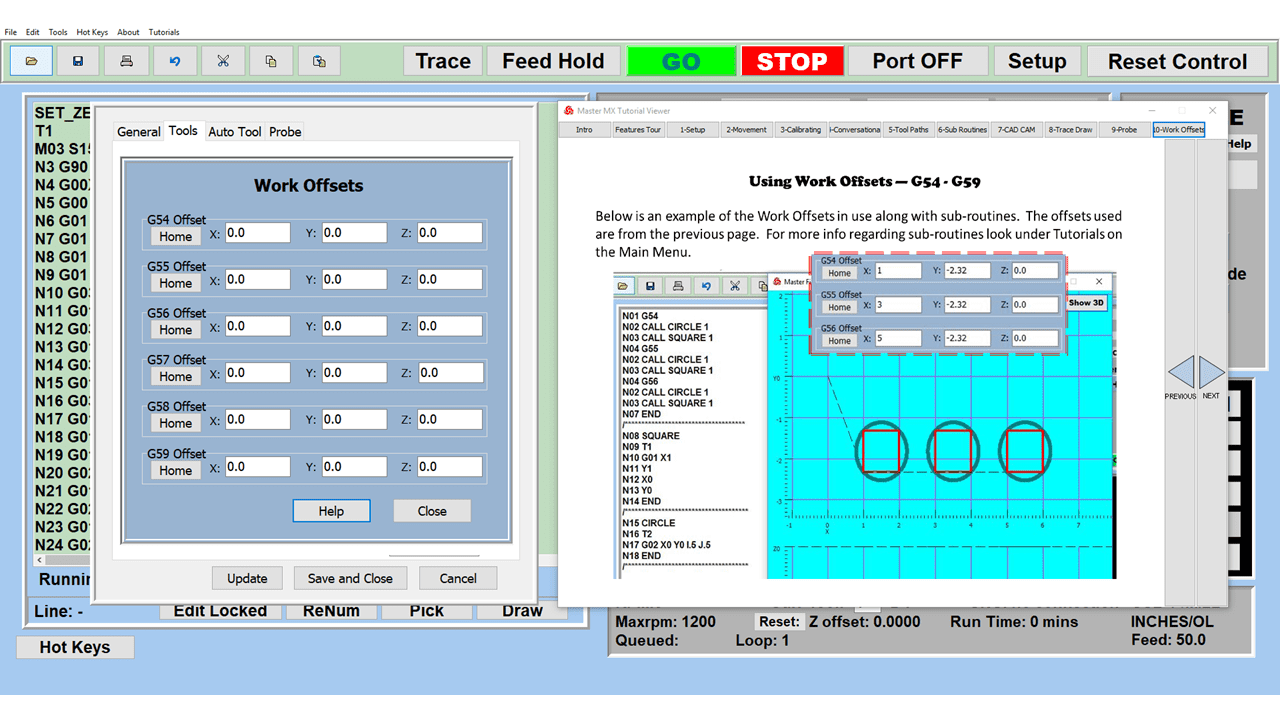
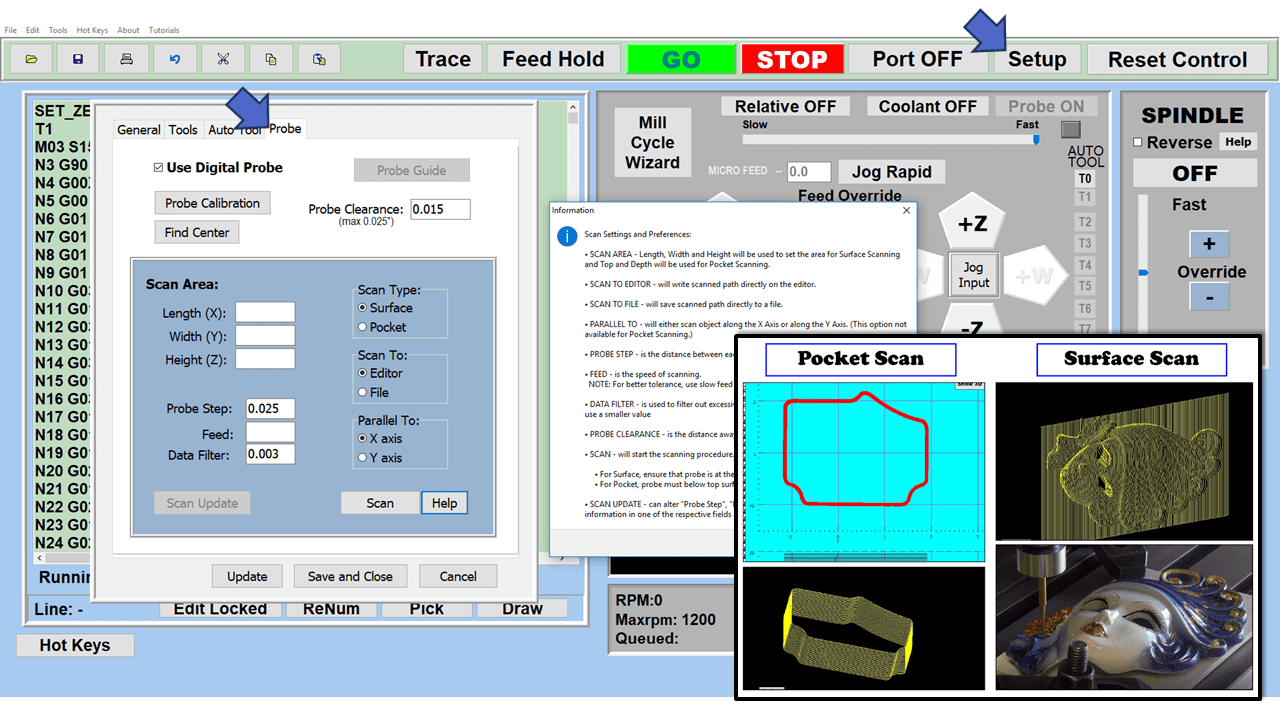
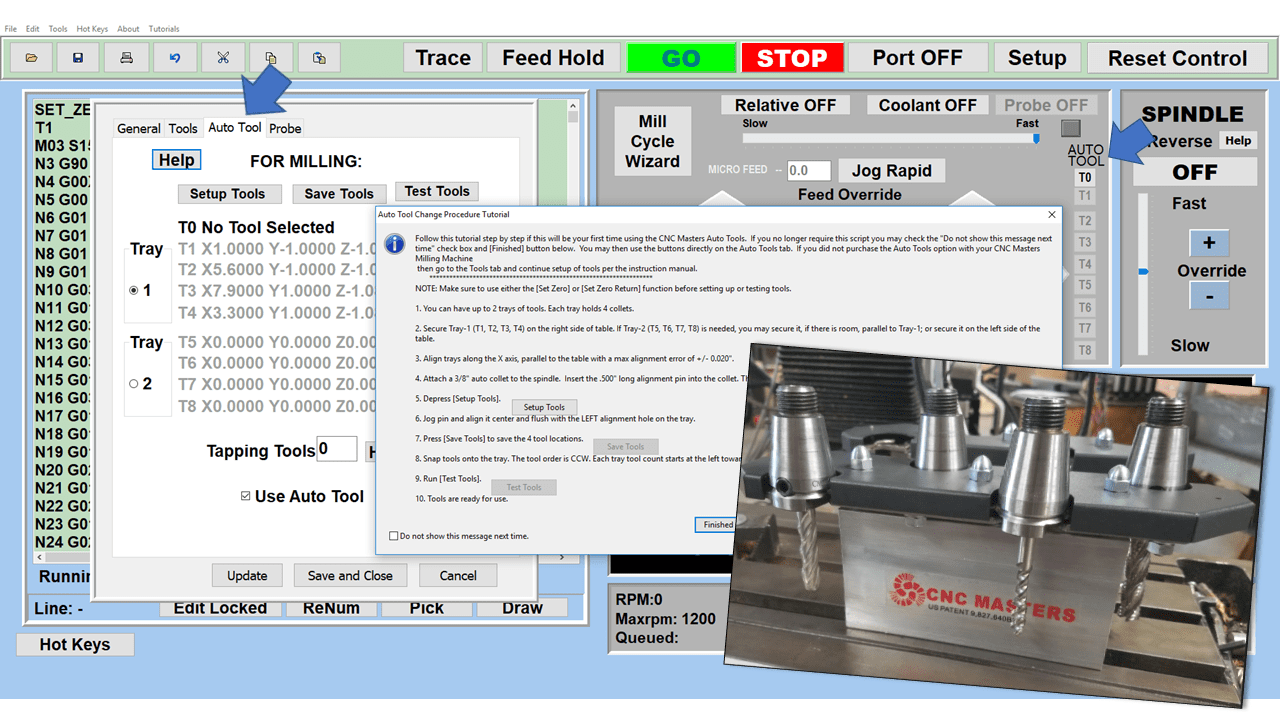
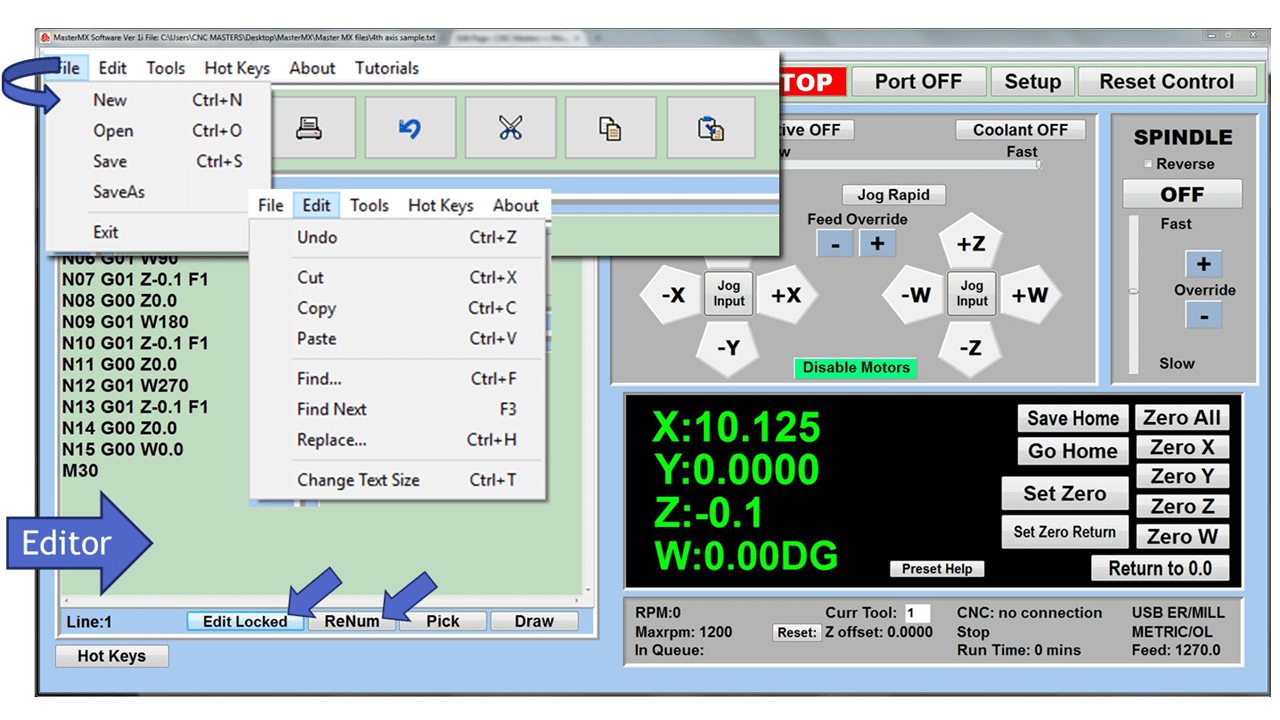
Many smaller machine shops and fabricators, along with hobbyists working from a garage or workshop, are looking to replace or add to their manual machines with computerized equipment. Many of our customers have questions, especially on machine tools that, on the surface, appear to function pretty much the same.
Two such machines are the CNC machine and the laser cutter. Both are high-speed machines capable of the precision cutting of parts with intricate shapes, and they are reliable, fast, and provide excellent repeatability. But the differences between the two methods are not subtle, and they require that you know the specifics of each so that you will make the right choice for your operation.
Here’s what you should know:
What is CNC cutting?
Computer Numeric Control, better known as CNC, uses dedicated tooling to produce various shapes and sizes of parts. When a designer creates a drawing based on a customer’s specifications, the process begins. Unlike the traditional blueprint made by hand on a drawing board, today’s designer is equipped with software, such as CorelDRAW or AutoCAD, allowing them to complete the drawing on a computer.
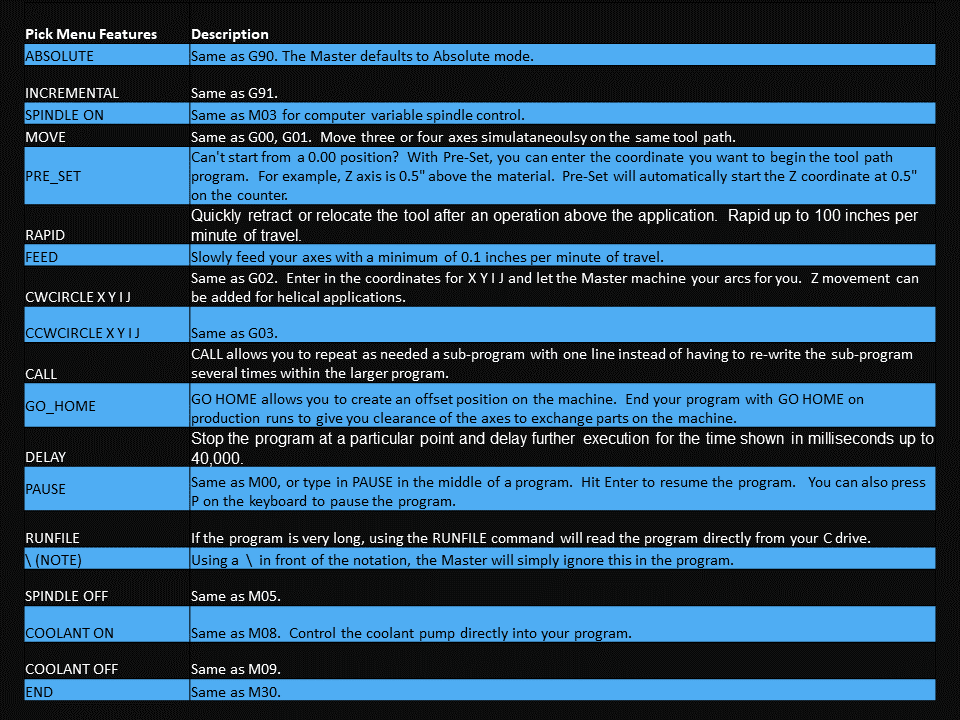
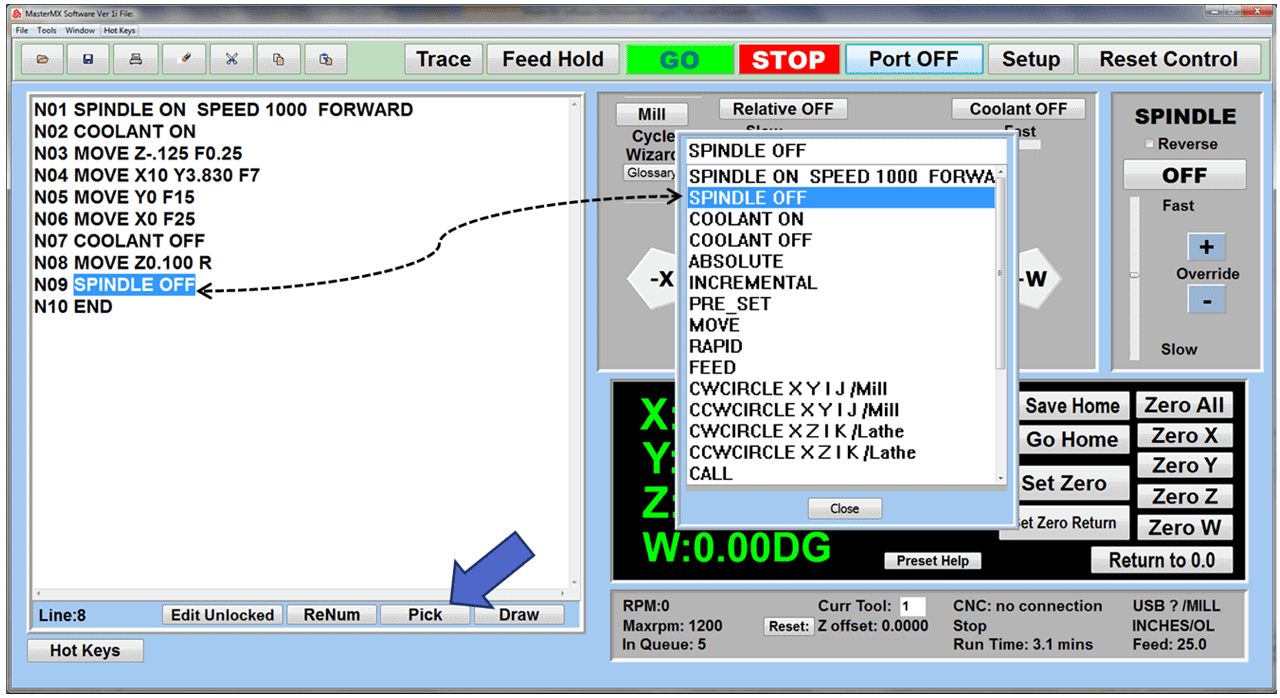
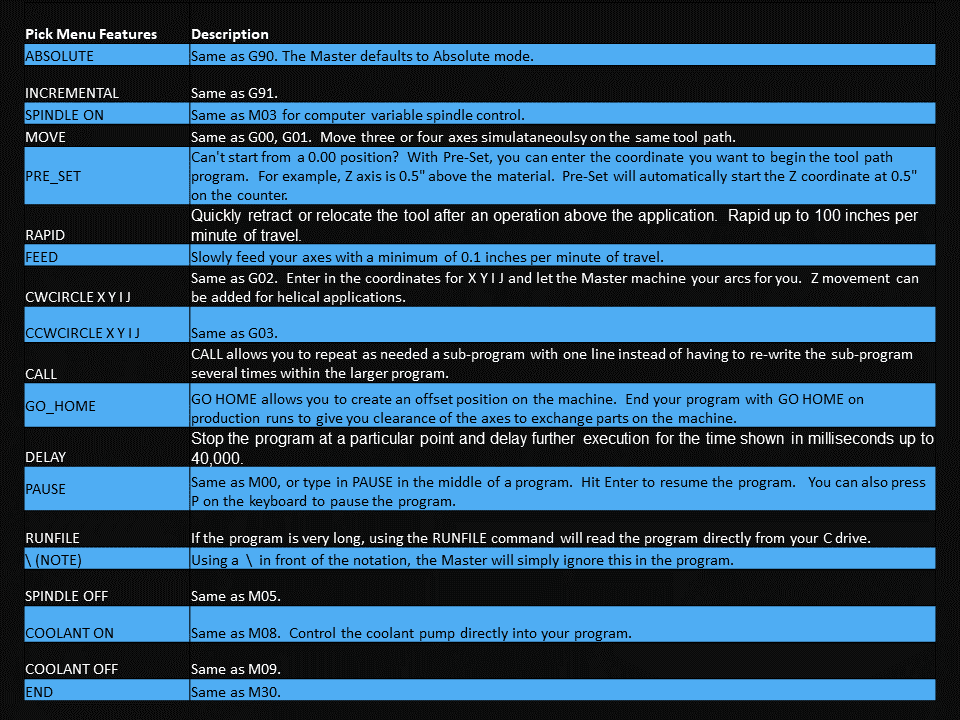
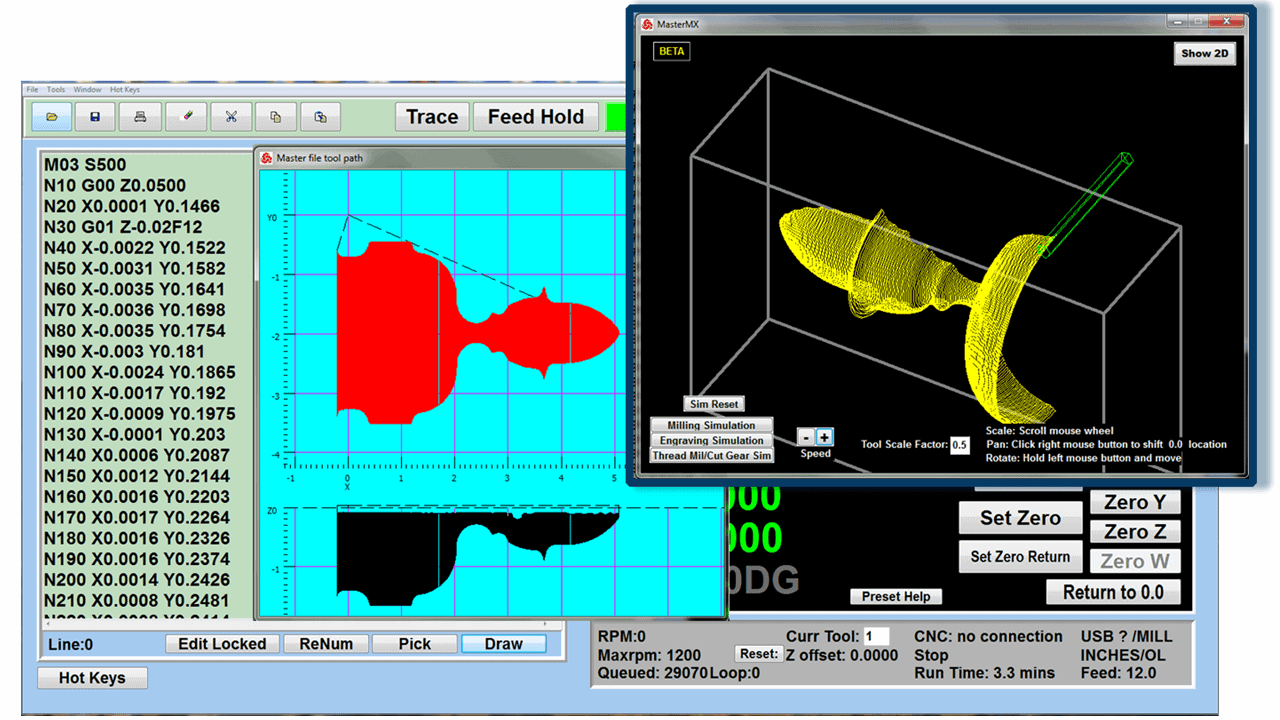
Using the computerized drawing, a CNC programmer will translate it to a workpiece with the help of computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software. The CAM software allows the programmer to create a toolpath and generate the G-code that controls the CNC machine. The computer then sends the program to a CNC machine that can interpret the design.
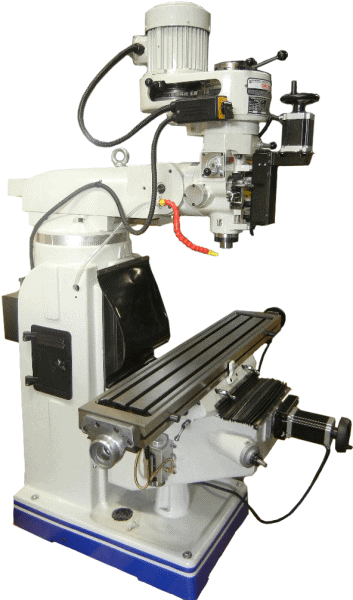
In the cases of CNC milling machines and CNC routers, the cutting tool moves side-to-side along an “X” axis, in and out along the “Y” axis, and up and down on the “Z” axis. Both a CNC milling machine and a CNC router could move and cut along all three axes simultaneously.
Both types of CNC machines employ cutting tools to remove material. CNC milling requires end mills made of numerous materials, diameters, and cutting lengths, while router bits also come in many different materials and shapes to accommodate various applications. The types of CNC cutting tools are extensive and depend on several factors, including the types of cutting materials, the depth of cut, and the type of cutting you’re doing.
What are the primary benefits of the CNC machine?
So far, we have talked about CNC milling and CNC routing under the blanket term of CNC machines. However, although these two types have much in common, there are a few differences. They both use cutting tools to mill, drill, and cut steel, aluminum, plastic, and wood to create parts or products.
The differences lie in two areas: the types of materials and the movements of the cutting heads. Generally speaking, the companies will use a CNC router to cut wood and other softer materials like acrylic and MDF. Also, the cutting head will move around a stationary cutting area in all three axes.
On the other hand, they tend to choose CNC milling machines for metalworking, and the workpiece moves while the cutting head remains stationary. These machines can make thicker cuts and move more slowly because of their high power and torque. By contrast, the CNC router is a high-speed machine.
Here are just some of the advantages of CNC machines:
- These CNC machines run on sophisticated software that determines the best way to machine a component with a minimum of waste.
- Because they do their machining without human intervention, there is little chance for human error, resulting in zero defects and higher accuracy.
- CNC machines can be set to the highest speeds and feeds to ensure higher productivity and efficiency.
- CNC machines reduce power consumption, helping to lower overall production costs.
- Most importantly, CNC machines produce parts without having an operator in harm’s way, reducing the risk of workplace accidents
Who would use a CNC machine?
Because a CNC machine provides a versatile and relatively low-cost cutting process, a diverse assortment of industries and sectors have them on their shop floors for various applications. They can manage practically all metallic materials, along with others as well. The types of parts, components, and products they can produce are virtually limitless.
And because they are available as a desktop CNC milling machine for the smaller shop and hobbyist to the sophisticated multi-axis machine tool for larger corporations, you will find them practically everywhere.
Here are just some of the industries and applications for CNC cutting:
- Defense industry: CNC cutting is ideal for a military sector needing parts that hold up under extreme conditions. The CNC can also produce replacement parts updated for security or improvement.
- Oil and gas industry: The CNC machine provides the critical tolerances that a safety-conscious sector requires.
- Aerospace industry: Aircraft components come in many shapes, sizes, and materials, and they all have one thing in common: they require the high level of precision that a CNC machine can provide.
- Healthcare: CNC machines provide specific medical components, including implants, electronic enclosures, orthotics, and surgical instruments.
- Rapid prototyping in all industries: A CNC machine can produce a prototype quickly after a digital design is created.
- Indirect manufacturing processes: CNC machines can produce molds for injection molding or metal patterns used for sand castings.
- Jobbing work: Although the CNC machine is perfect for production, many jobbing shops use it for custom work. In many cases, programming, setting up, and machining a few parts is faster (and more accurate) than using a manual machine.
- Hobbyists and moonlighters: CNC benchtop mills and freestanding knee mills are at home in many garages and home workshops. Whether it’s for a hobby or to make extra cash, the CNC mill is an affordable and accessible piece of equipment.
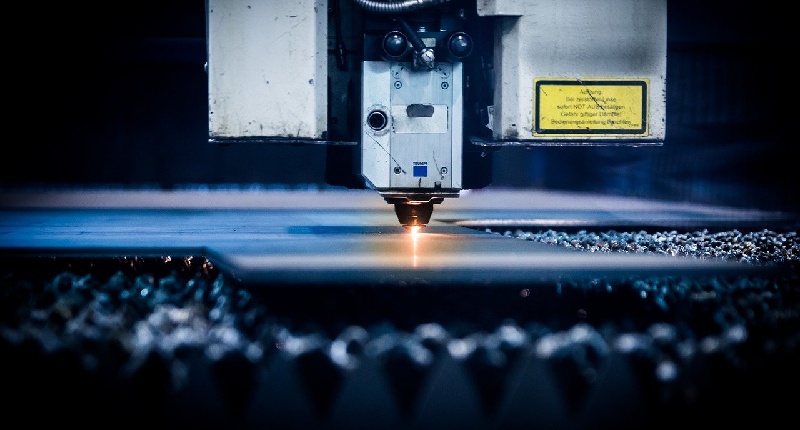
What is laser cutting?
The laser cutter is similar to CNC milling and routing since they all follow a path that is programmed in advance. However, how they accomplish the cutting is as different as night and day. Instead of a cutting tool or router bit, the laser cutter relies on a high-energy light beam to burn through the material. By aiming a high-power laser (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) through optics, the extreme heat burns the shape into the workpiece.
The laser cutting machine comes in three primary types:
- The CO2 laser runs electricity through a tube filled with a mixture of carbon dioxide, hydrogen, nitrogen, and helium. While the CO2 laser can cut thin metal sheets, it is typically used in woodworking and as an engraving machine.
- A fiber laser is a solid-state machine that amplifies its beam using special glass fibers. Known as versatile machines, fiber lasers work with metals, alloys, and non-metals such as wood, plastic, and even glass.
- The Nd: YAG laser allows for high power cutting using nd:Yag crystals. Unfortunately, these machines have a hefty price tag and a relatively short life expectancy.
What are the main advantages of the laser cutter?
- One of the most notable advantages of laser cutting is getting detailed cuts. The smallest inside radius you can expect with a cutting tool is around .062″ using a 1/8″ diameter end mill. By contrast, a laser operator can set the laser beam to get a radius of about .005″, providing finer detail.
- Laser cutting leaves the edges clean and sealed, improving the functionality and appearance of finished parts.
- Laser cutting maximizes the number of usable parts and produces less waste.
- CNC laser cutting tools have few moving parts, which reduces maintenance and repair costs.
- No clamping necessary
Who would choose a CNC laser for their cutting process?
Laser cutting serves various industries, with the shipbuilding, aerospace, and medical sectors leading the way. Steel plates make up most of the materials used in shipbuilding. With the precision that laser cutters afford, the transfer accuracy and hull segmentation required by shipbuilders make the CNC laser a good choice.
Aerospace has many of the same requirements as shipbuilding, and the medical sector needs lasers to manufacture some of their intricate medical devices. Other industries that utilize laser cutting machines include:
- Automotive for the thousands of small parts that make up the typical vehicle
- Electronics because laser cutting machines can cut and perforate complex parts and tiny components.
- Tool manufacturers use laser engravers to mark and engrave their products and also to manufacture some of their hand tools
- Fabricators have a constant need for sheet metal components, and the laser cutter can provide a large cutting area for them
- Musical instruments are often hand-crafted, but many mass manufacturers count on CNC lasers for quality control.
- Jewelry making is another sector where the precision of laser cutting makes it a good choice.
Be aware that a laser cutter’s complexity, complicated maintenance, and the high cost of ownership may be prohibitive factors for some small businesses and hobbyists. As the above list of users indicates, laser cutting technology is well-suited to large companies.
Also, keep in mind that although some laser cutters can cut material as thick as 3/4″, most of them work better on 1/2″ or less material. And when it comes to wood, a CNC router is a better choice to handle thick materials
Transition to a CNC machine by first talking to the experts
At CNC Masters, we have been providing high-quality CNC tabletop mills, milling machines, and CNC lathes for 20 years. Business owners, machinists, scientists, researchers, teachers, and even hobbyists have discovered our California-based company’s superior quality, affordable prices, and professional service.
Call us at 626-962-9300 or email us at sales@cncmasters.com. Better yet, call us for an appointment and visit our facility in Irwindale, CA.