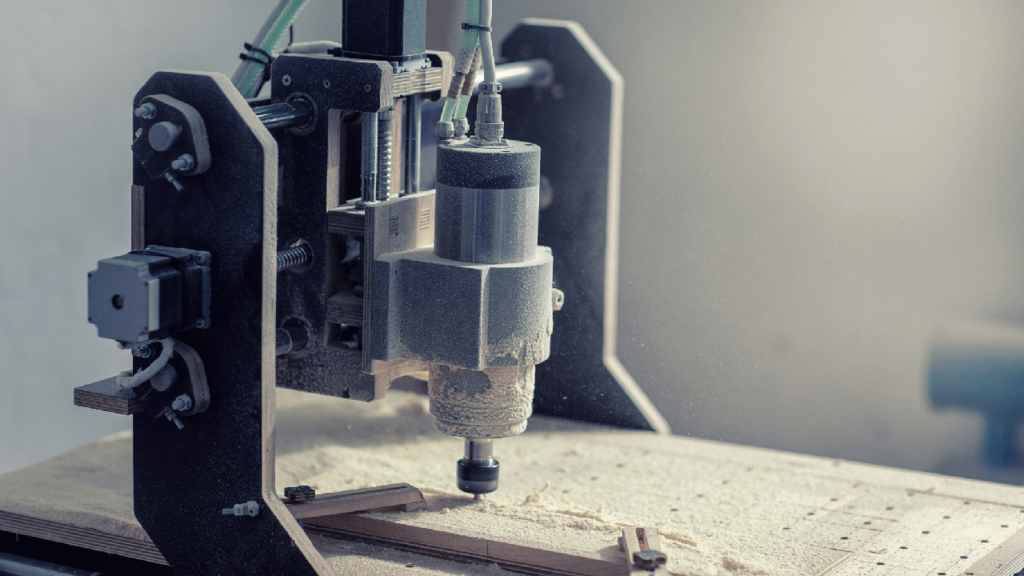
Not every small shop requires a full-size CNC milling machine, CNC router machine, CNC lathe, or other large cutting machines. Today, these shops have more options than ever, and many of their choices come from machine tools that take up little room in environments where space is at a premium.
Often going by names such as desktop CNC router, benchtop laser engraving machine, or mini mill, these small CNC machines have minimum footprints, making them ideal for hobbyists or the DIY CNC machinist working from a garage or workshop. And they can machine almost any material the big guys can, including metals, woodworking, PVC, PCB, acrylic, or MDF.
Terms like “hobbyist” and “DIYer” can give the impression that the person is in machining for fun and is not all that serious about it. However, many who start small find a niche and a profit, and as demand for their product grows, a small CNC machine becomes the answer to higher production, consistent quality, and expansion into other areas.
Whether fun, profit, or both is your goal, consider the type of work you have in mind today and what potential it could lead to in the future before you purchase your small CNC machine. Although many mini-CNC machines have an element of scalability built into them, it still pays to look ahead at the possibilities and match your machine tool to them.
Do Your Small CNC Homework Up Front
With that information in mind, check the specs for the following:
- Table Size and Travel Distance: Choose a table that can handle the largest workpiece, along with room for a vise and clamping. The X-axis and Y-axis travel distance should also cover the extremes of the work area, while the Z-axis should comfortably clear the work heights with tooling.
- Spindle System: Typically, 6,000 RPMs is the minimum speed required for machining detailed parts using small high-speed cutting tools.
- Rigid Construction: Rigidity might be a limiting factor for a CNC machine, especially if you are planning on machining steel.
- Stepper Motors: X, Y, and Z-axis micro-stepper motors keep the best CNCs from losing steps.
- Ball Screws: X, Y, and Y zero backlash ball screws with pre-loaded ball nuts will eliminate play on the table travel, and provide high-precision machining.
- Warranty and Customer Service: Make sure the machine comes with an ironclad warranty and has a history of excellent tech support.
Buying a Small CNC Makes Sense and Here’s Why
1. Small CNC Machine Tools Have an Amazing Nervous System
The control system of any small CNC machine is the CNC controller. The controller provides the link (nervous system) between the computer system (brain) and the mechanical components (body) of the CNC machine. Its primary task is to receive conditioned signals from the computer and interpret them into mechanical motion through motor output. Several components comprise the controller and work together to produce the desired motor movement.
2. It Will Save Space on a Small Shop Floor
Most home hobbyists don’t have a work area the size of a high school gymnasium, and they are either set up in their garage or have a small workshop area that shares space with a lawn mower and weed eater. In other words, there’s no room to waste space, which is one reason small CNCs are becoming so popular.
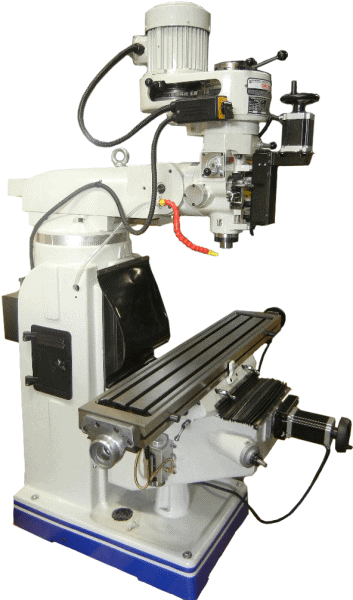
For example, CNC Masters offers a Table Top CNC Milling Machine with a footprint of under 11 square feet (38” x 38.5”). Even their Bridgeport-type Supra Vertical Knee Milling Machine is a space-saving 24 square feet. Each of these will fit in close quarters while providing full-size benefits for the small shop.
3. A CNC’s Versatility Allows You to Expand
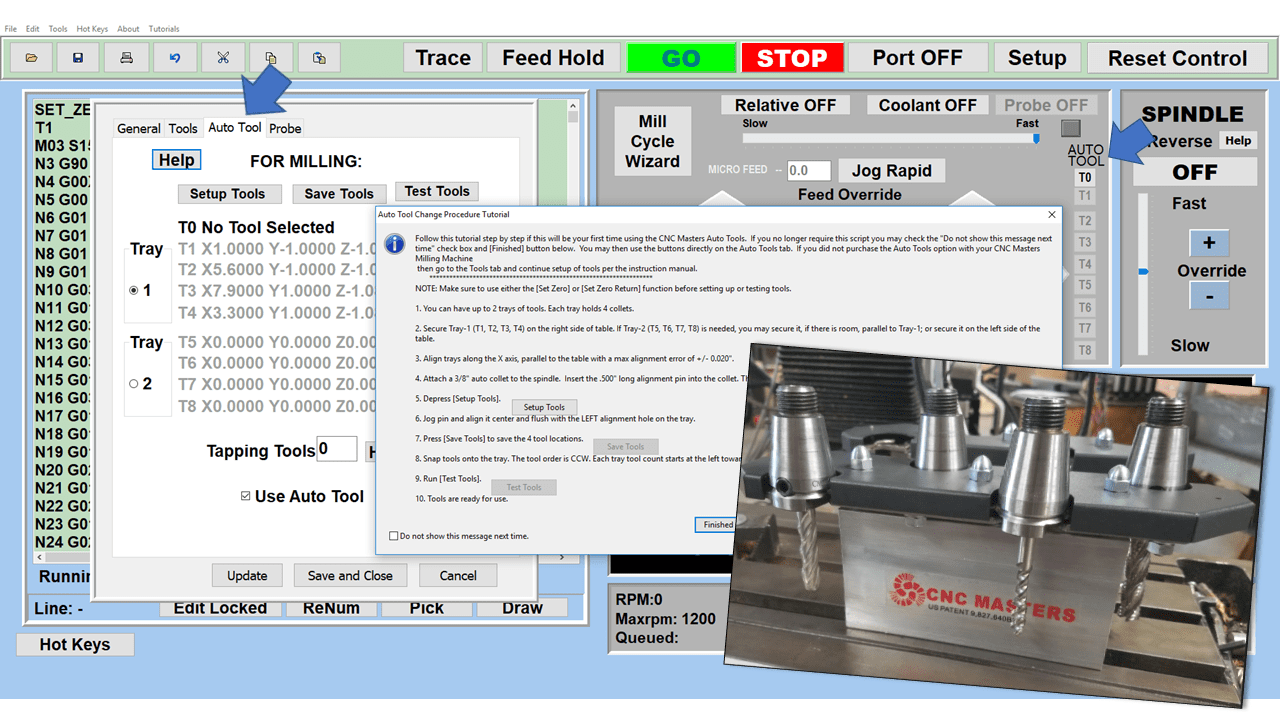
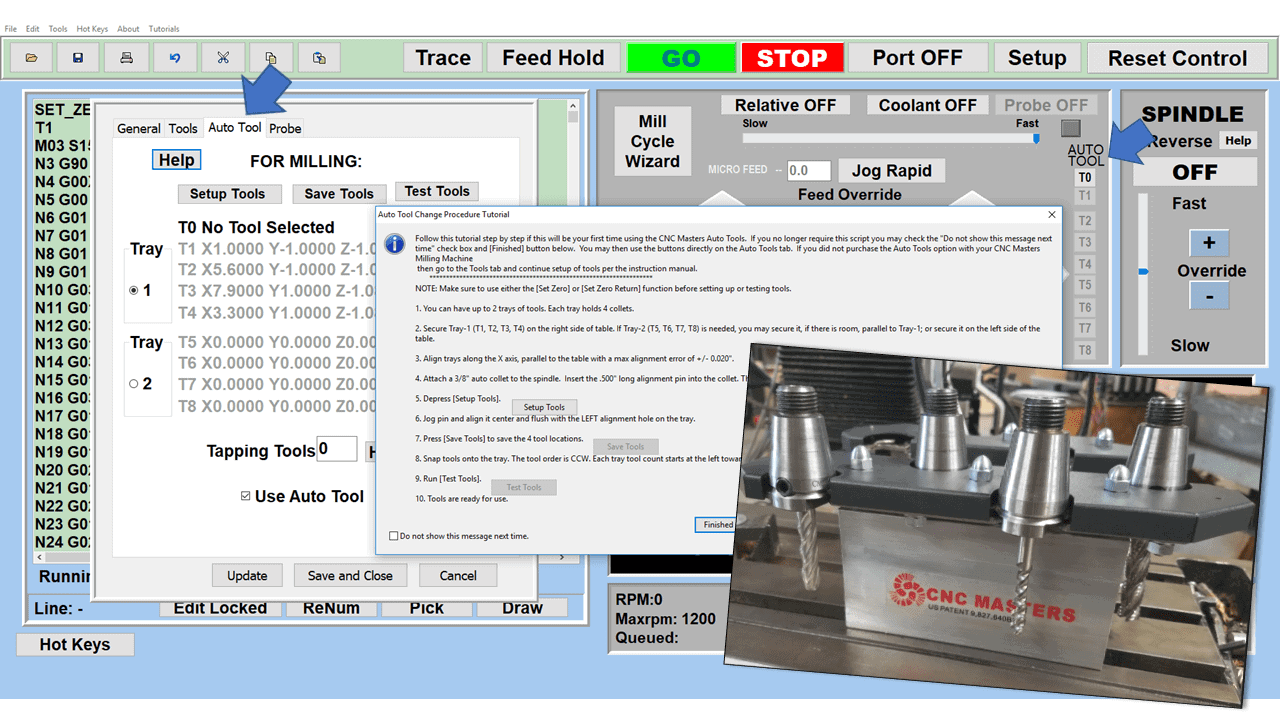
A small CNC in your shop will allow you to take on work that would be virtually impossible with traditional manual machines. You can also add a 4th axis, engraving attachment, coolant, quick tool change, and splash guard shield for safety accessories to the CNC Jr. Table Top CNC. The CNC engraving machine add-on alone could become a lucrative stream of income.
If you want to add woodworking to your resume, a mini CNC router can help you expand your capabilities to do wood carvings, plaques, games, flags, and all kinds of moneymaking projects and gifts.
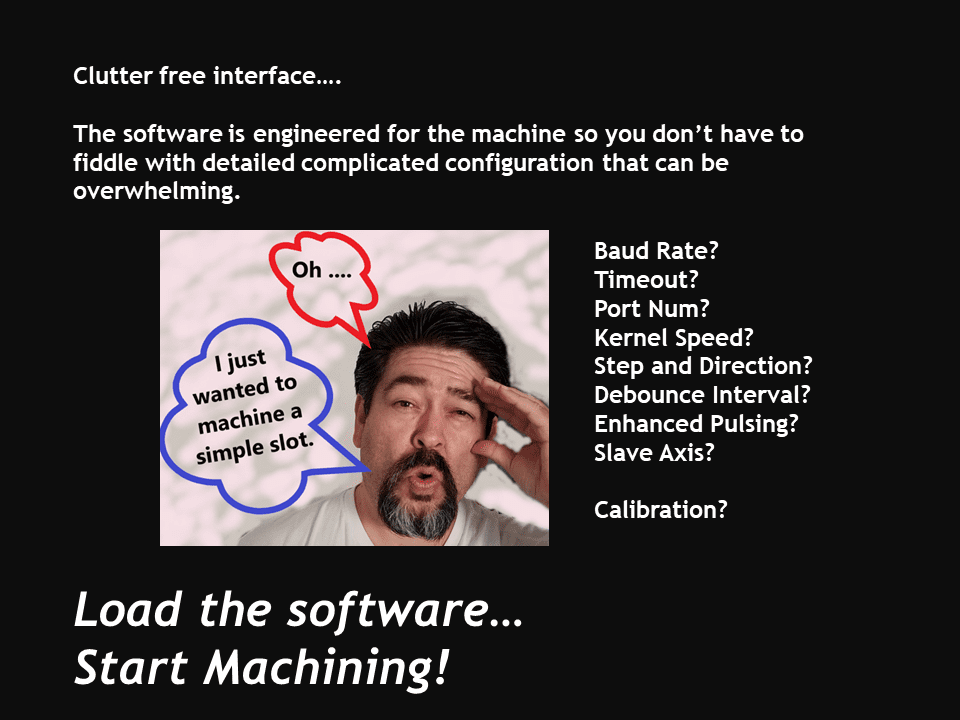
4. They are Easy to Learn and Use
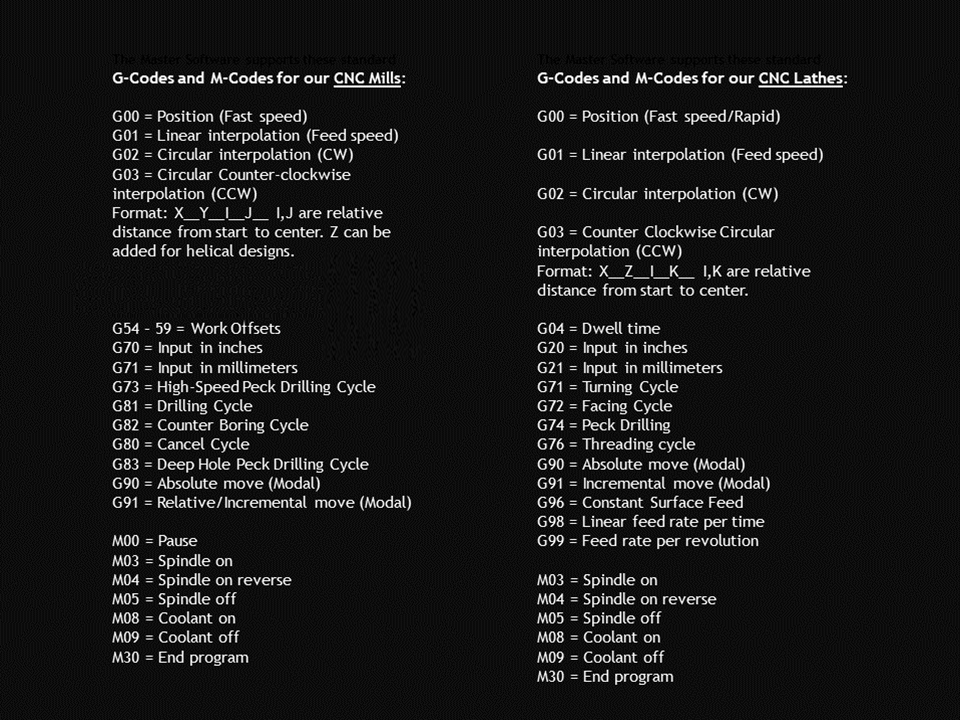
Hobbyists and beginners could find learning advanced technology overwhelming. However, CAM software has become increasingly user-friendly, and learning G-Code and programming has become less challenging. CNC programming is not very hard if you have basic technical drawing knowledge, computer and math abilities, and manual machining experience.
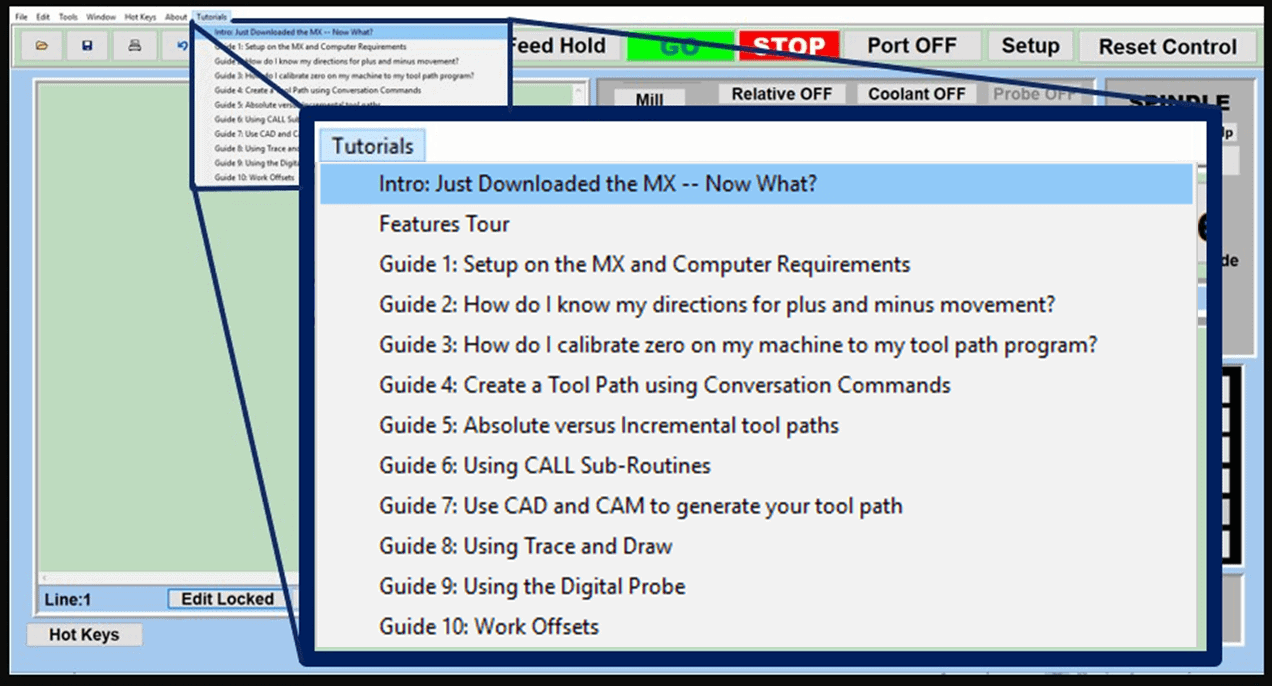
You can probably start creating G-code and 2D-CAM programs in one week, while complex topics like multi-axis CAD/CAM programming will take many months to master. CNC machines, including the smaller mini CNC machines, are designed to be easy to learn and operate. Excellent tutorials and courses teach you how to manage a modern CNC machine successfully.
5. All Parts Comes Off the Machine Within Tolerance
Repeatability is one of the words you hear in connection to CNC machine tools, and the mini CNCs are no exception. Manual machines are subject to the mistakes made by human operators, resulting in inconsistent results whenever a project requires multiple parts. Although each piece is expected to come off the machine within tolerances, human error can keep that from happening.
Repeatability is one of the primary characteristics of CNC machines, including the mini CNC router machine, small CNC mill, and CNC laser cutters. However, even though consistency is the objective of every small CNC machine, it requires the efforts of a skilled operator and a high-quality mini CNC machine to achieve those results.
6. CNCs are Considerably Faster Than Manual Machines
Whether you are zipping through a flat aluminum plate using carbide router bits on a CNC router machine, machining complex components on a CNC milling machine, or laser cutting an order of hot-rolled steel parts, it will almost always happen faster on a full-size or small CNC.
However, sometimes going through the programming process (for a minor repair job, for instance) does not make sense. In those cases, having a manual mill to hop on and off quickly is good. It’s even better to have a versatile CNC knee mill like the Supra vertical milling machine from CNC Masters since it transitions from CNC to manual mill and back effortlessly to meet your needs.
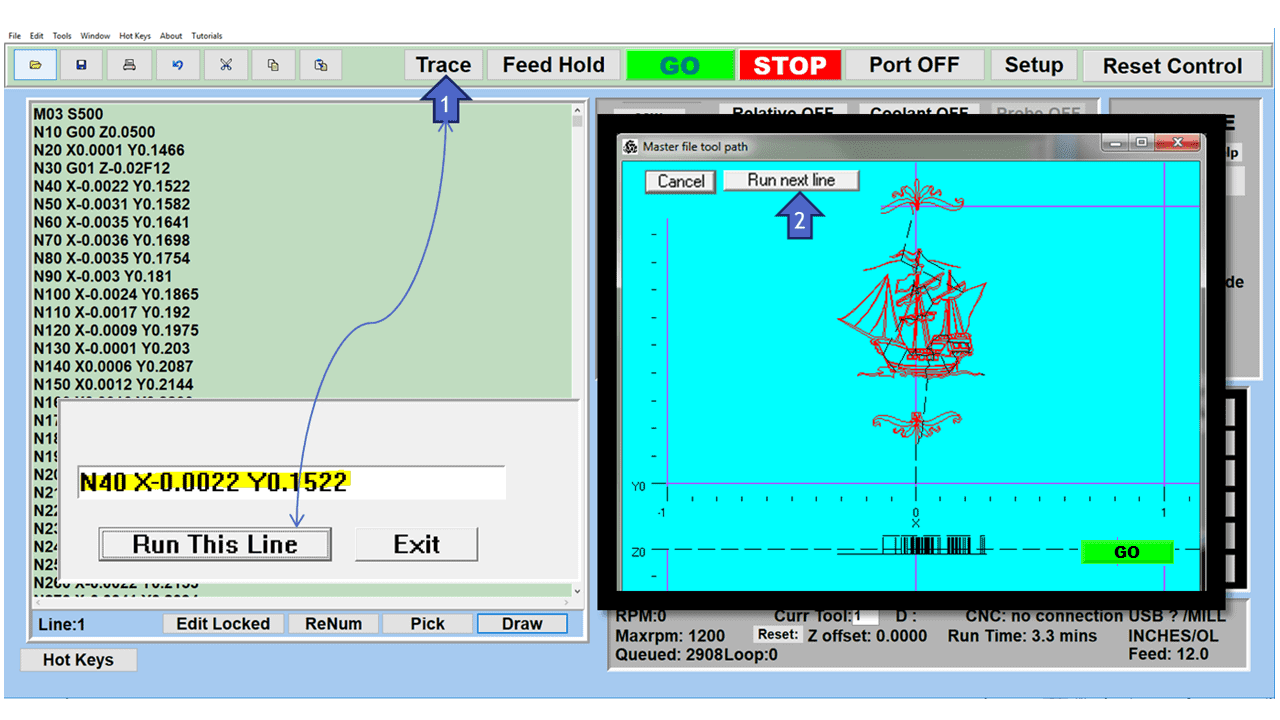
7. CAD/CAM Software is Just as Effective on Mini CNCs
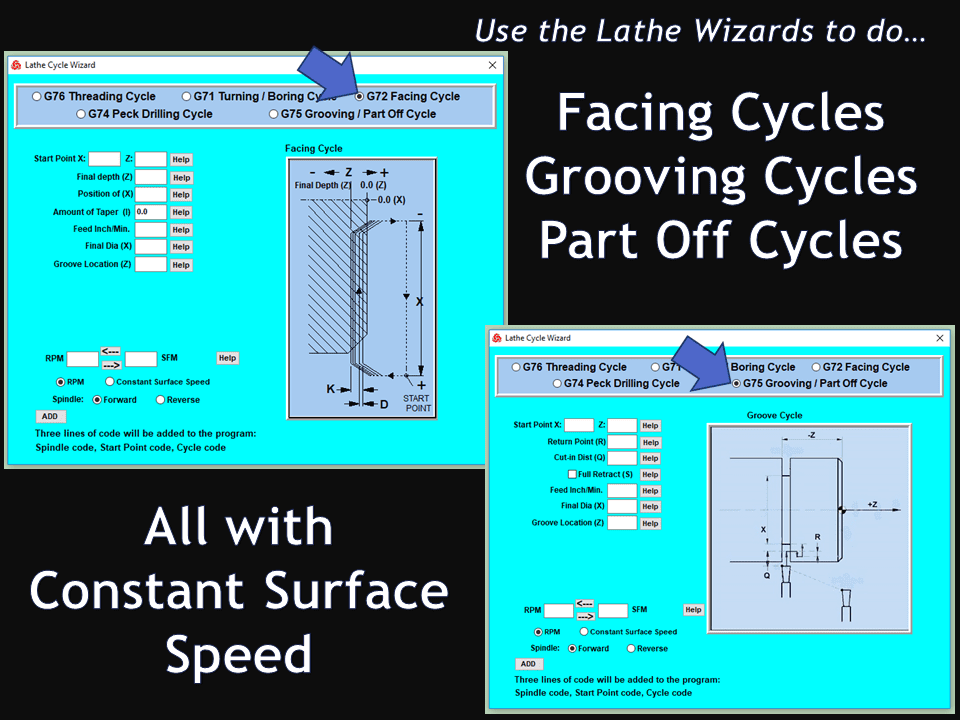
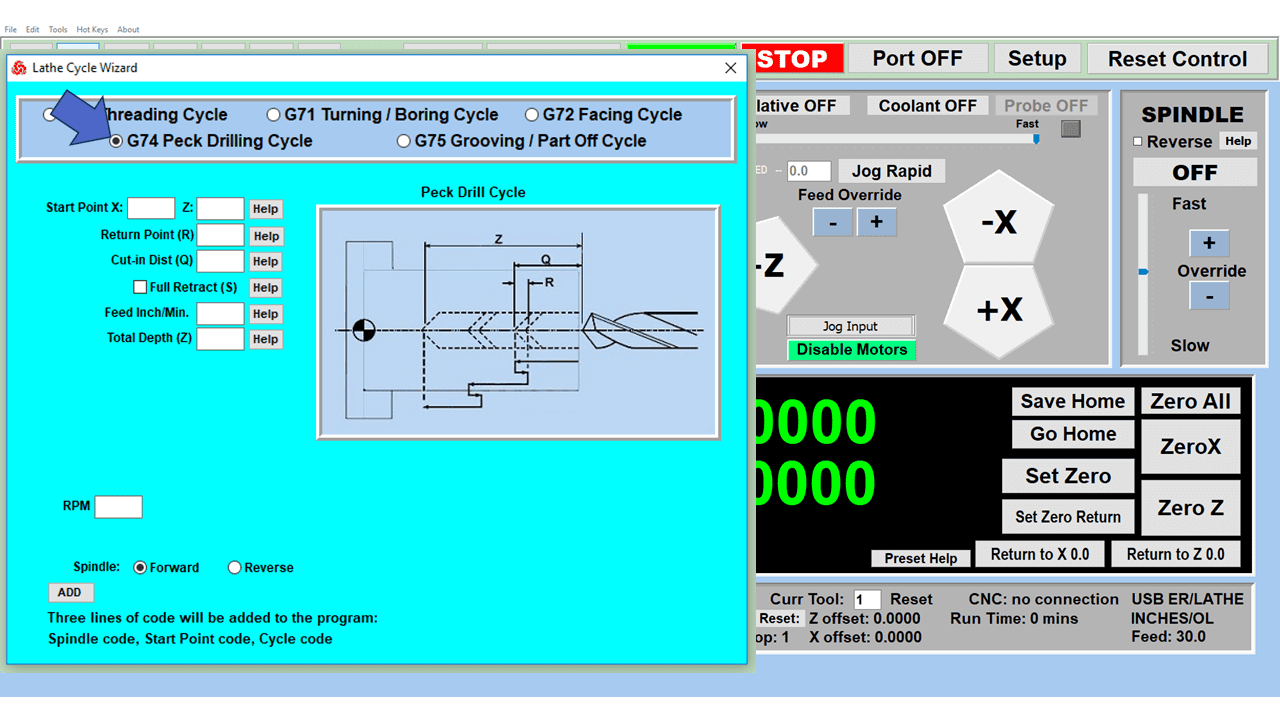
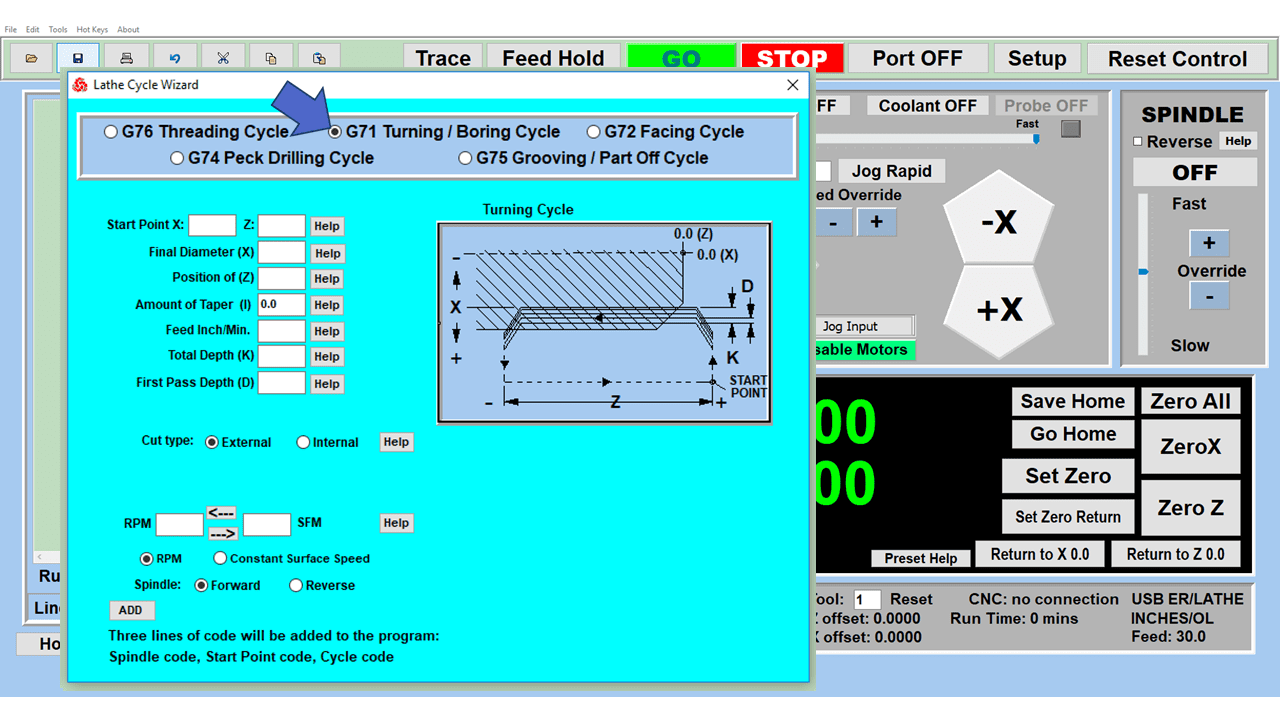
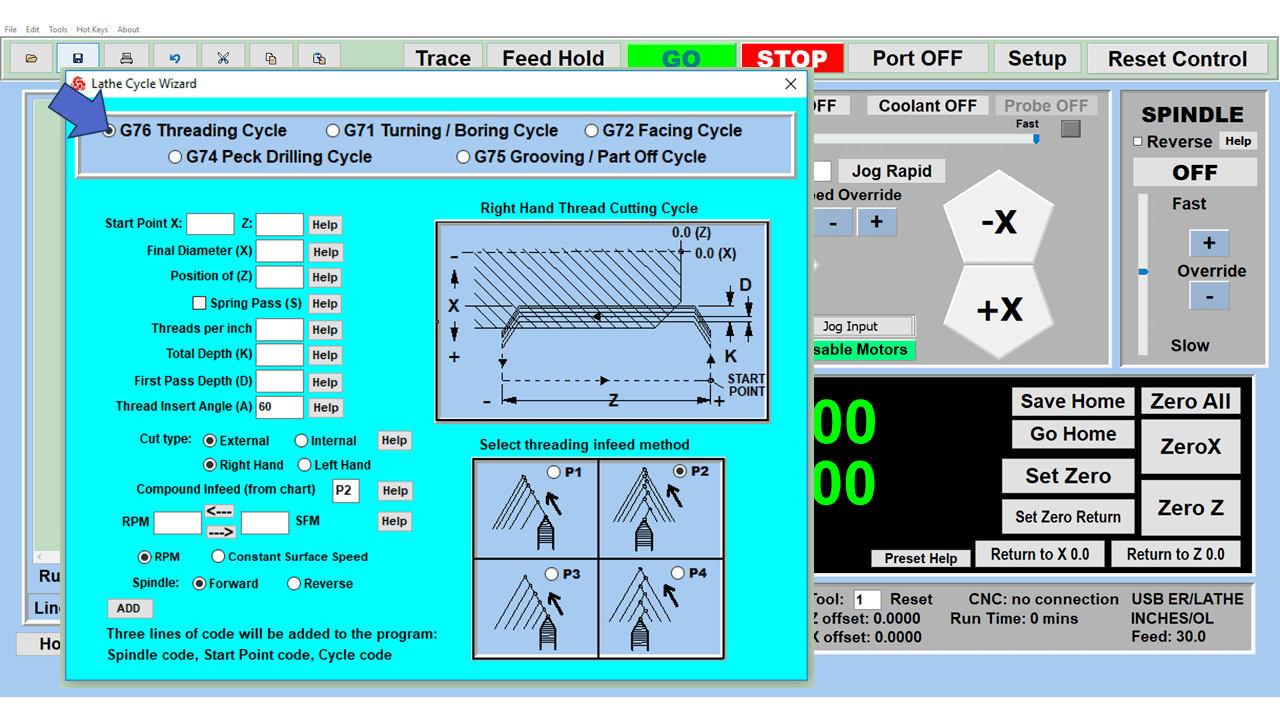
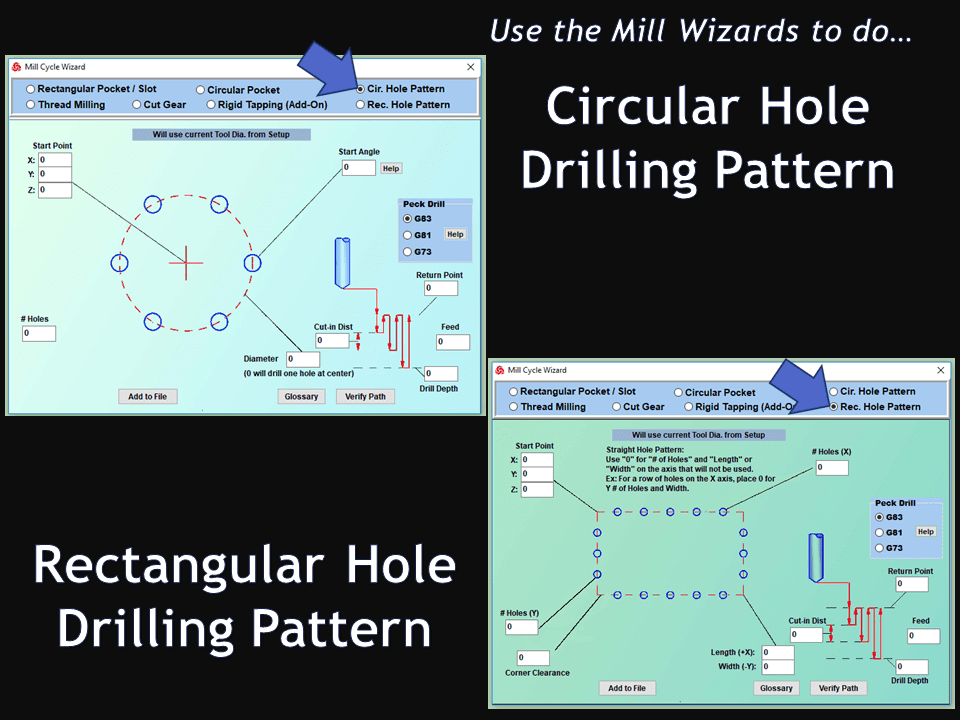
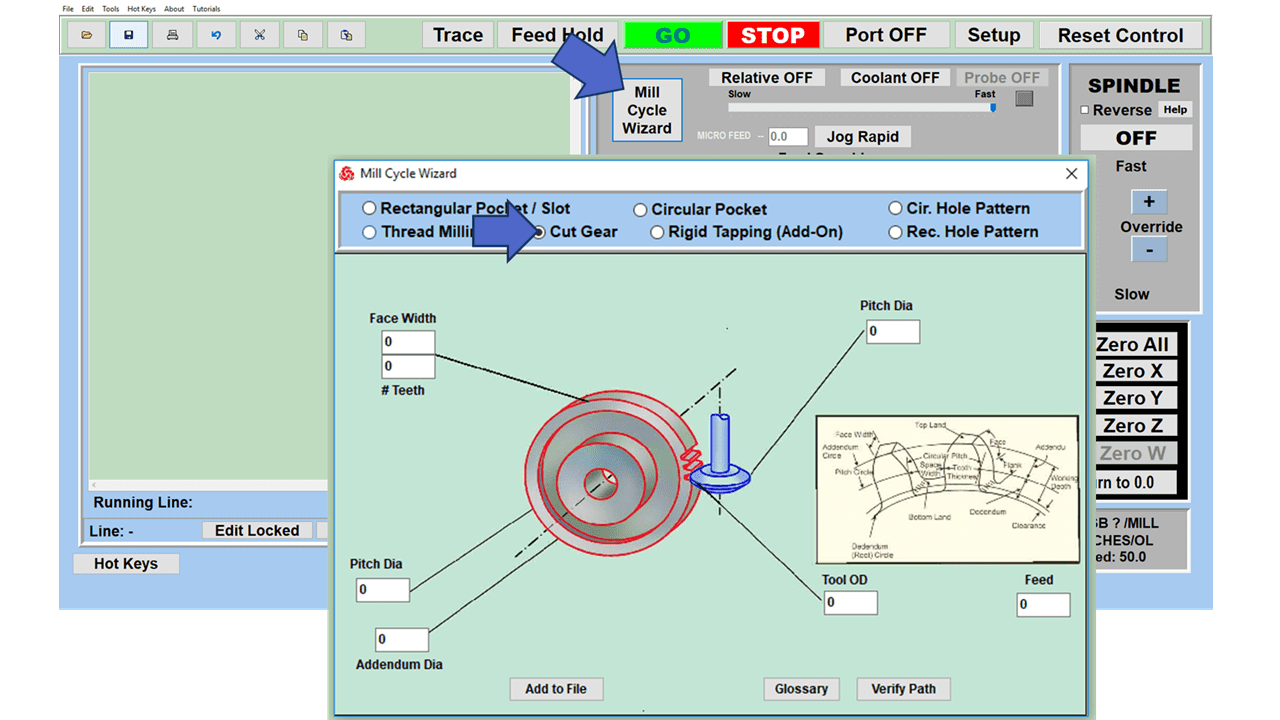
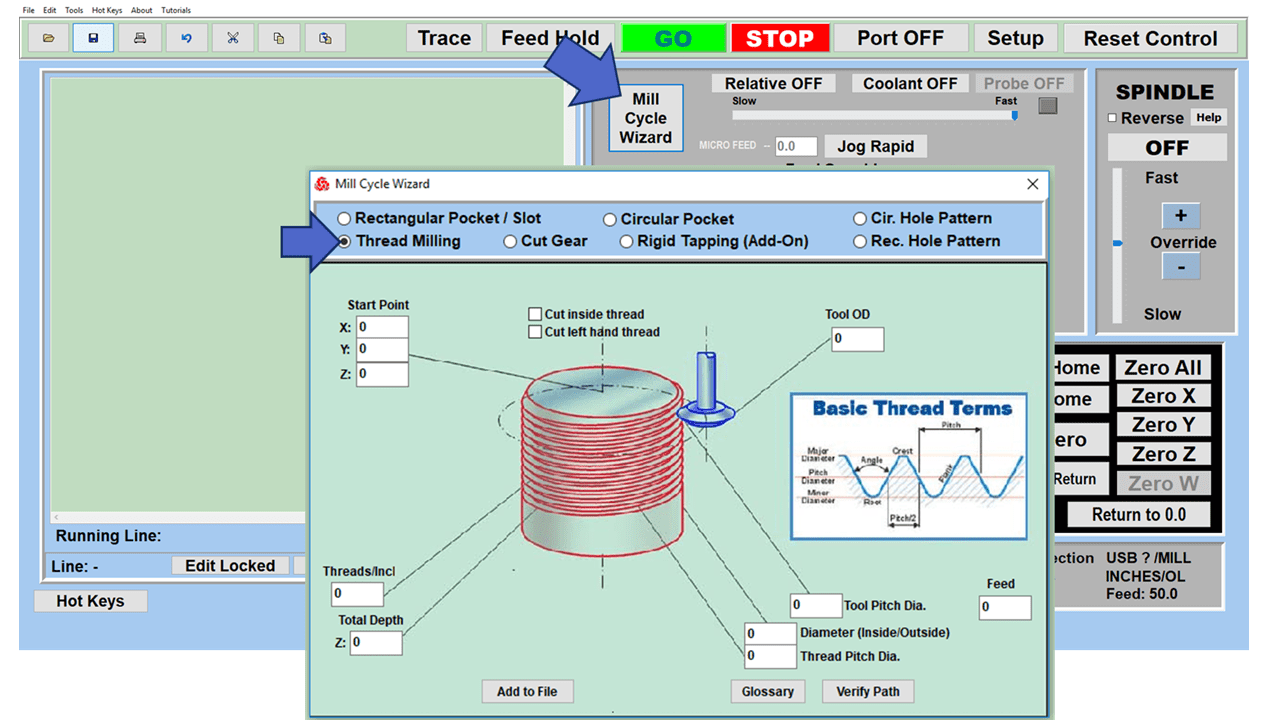
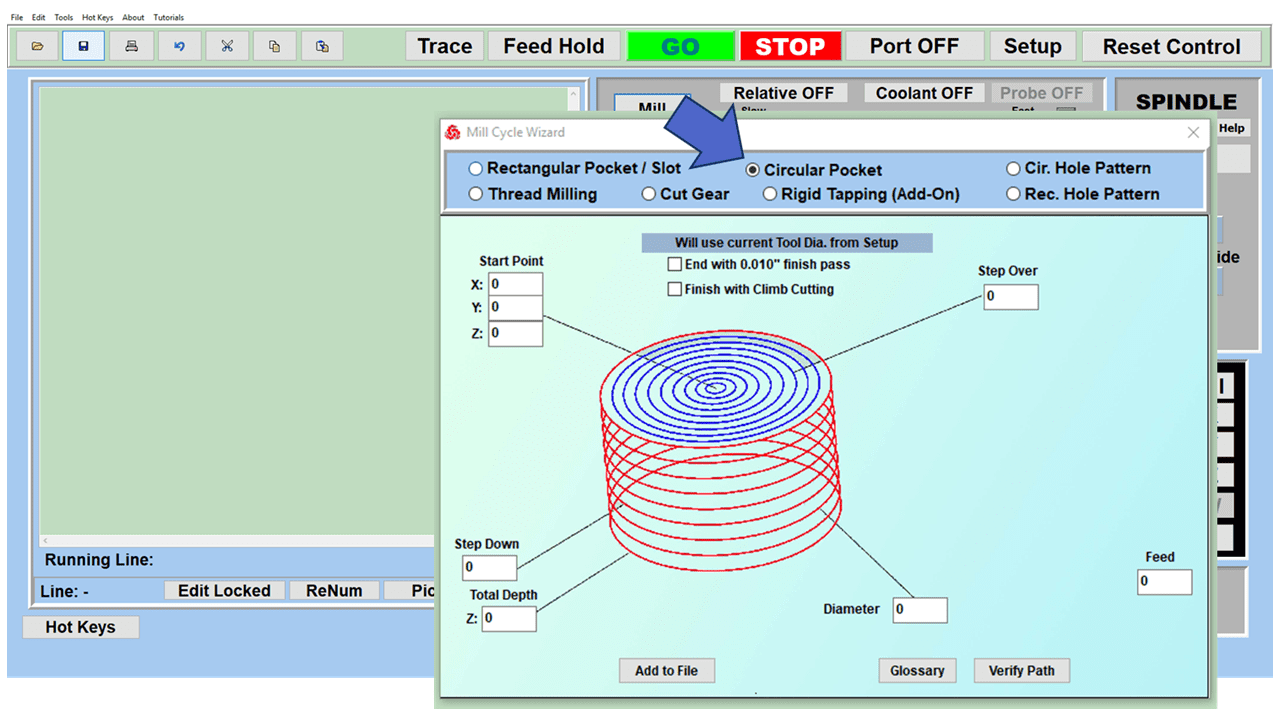
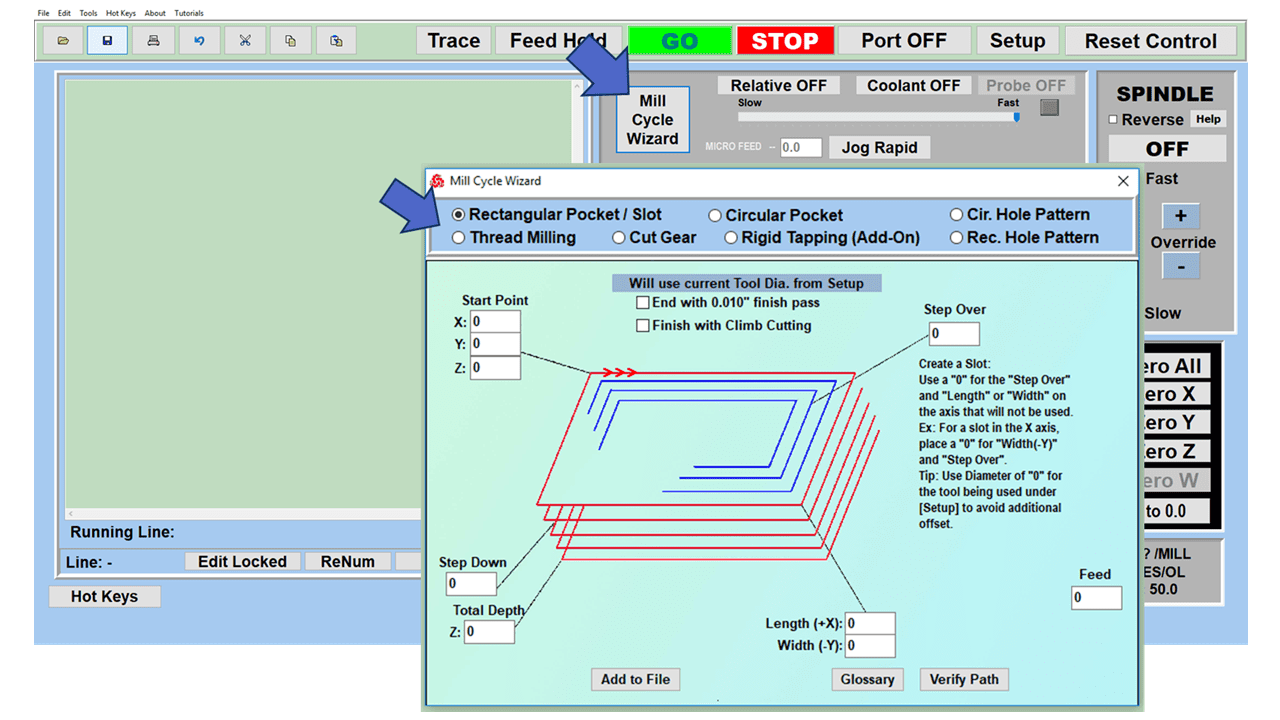
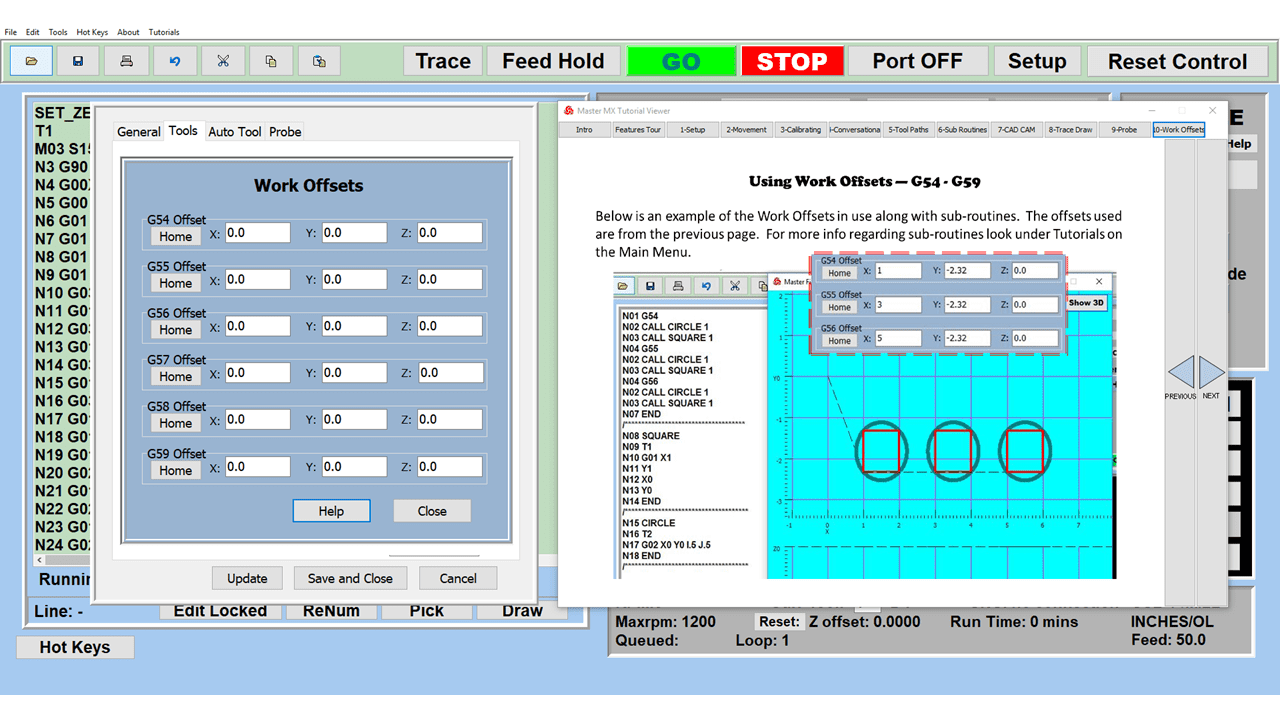
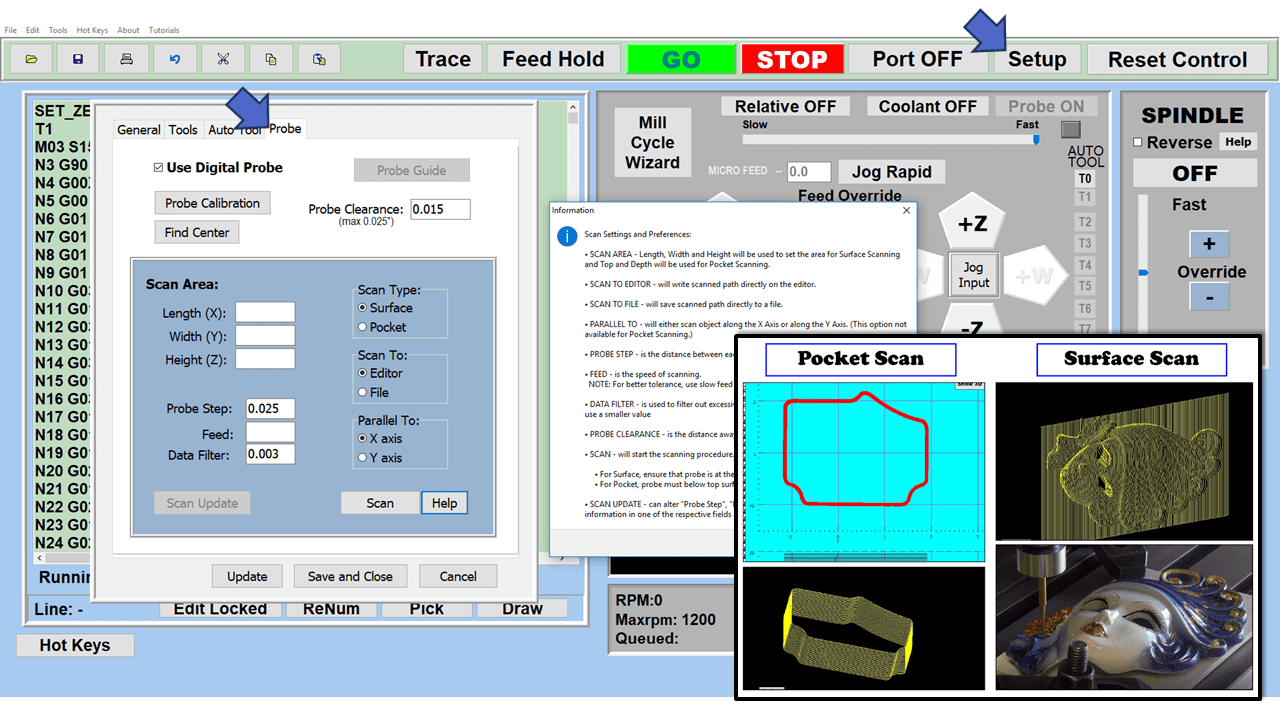
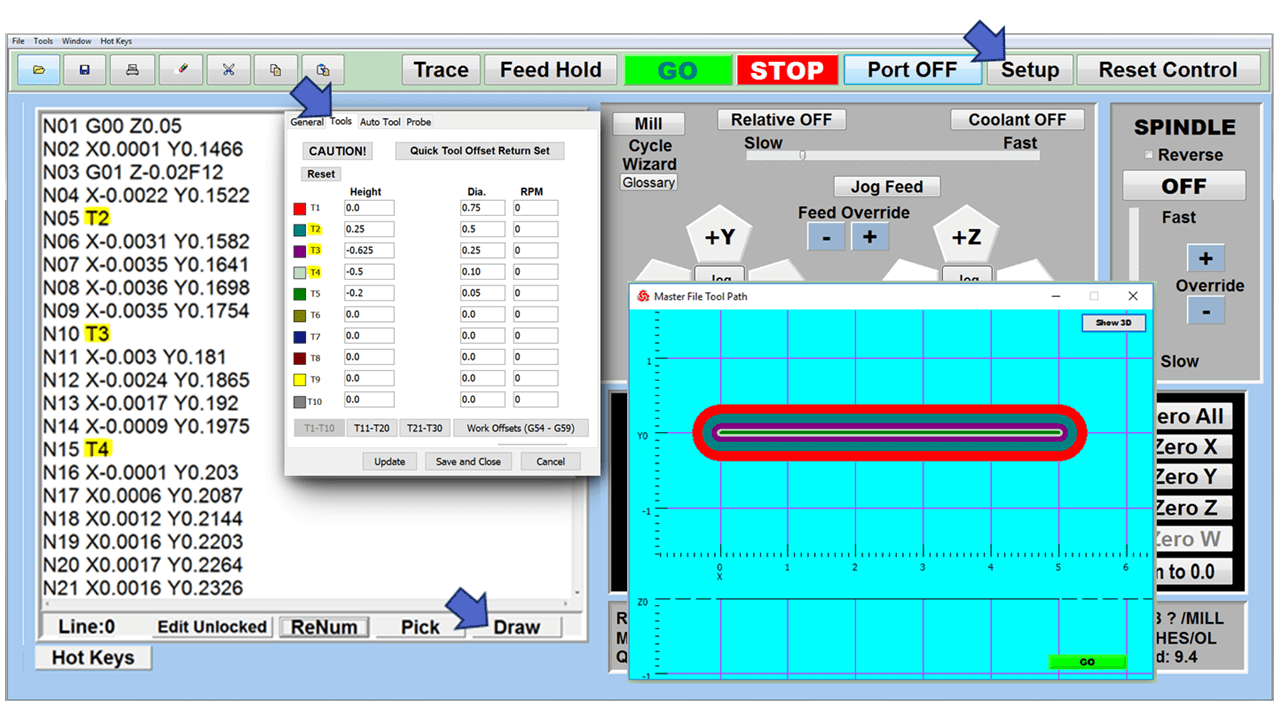
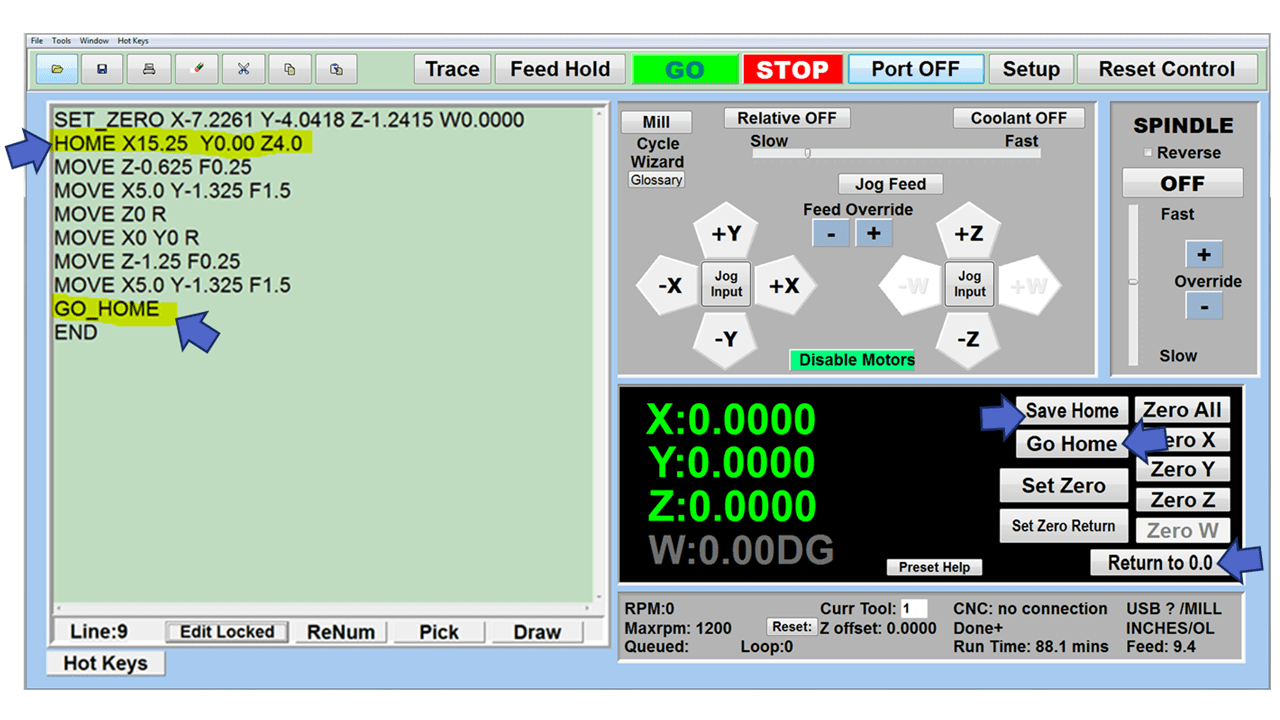
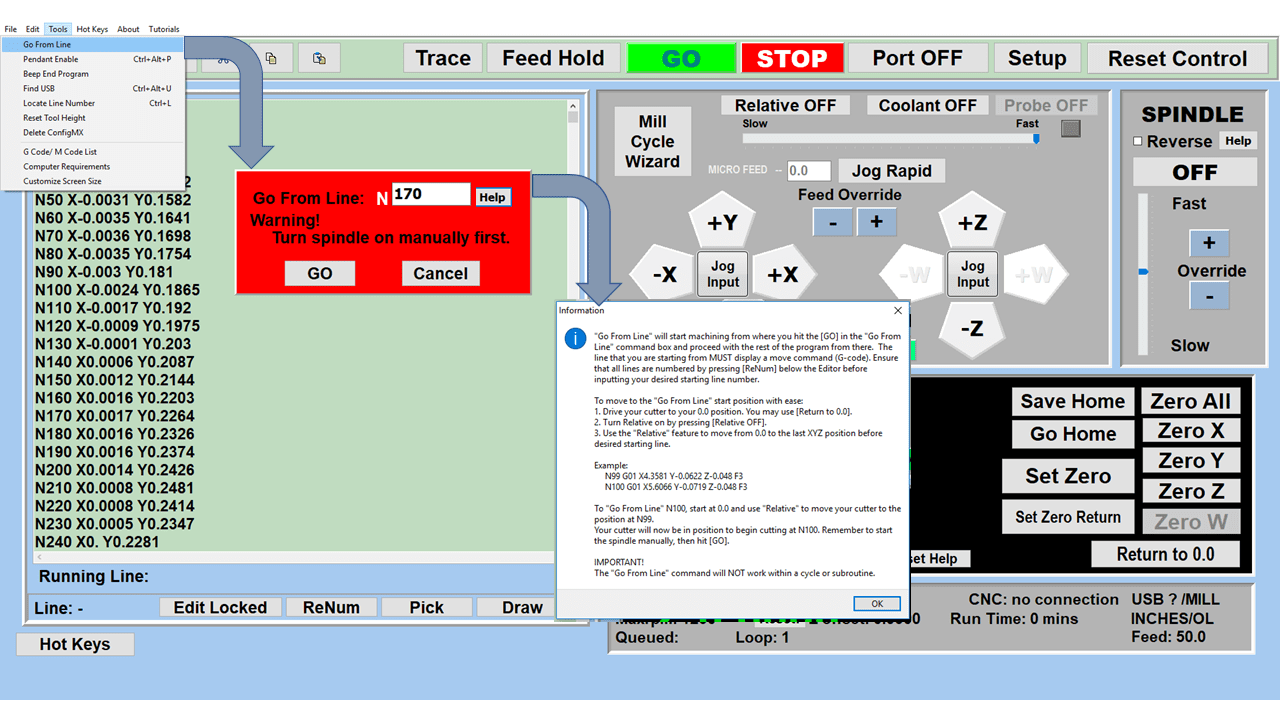
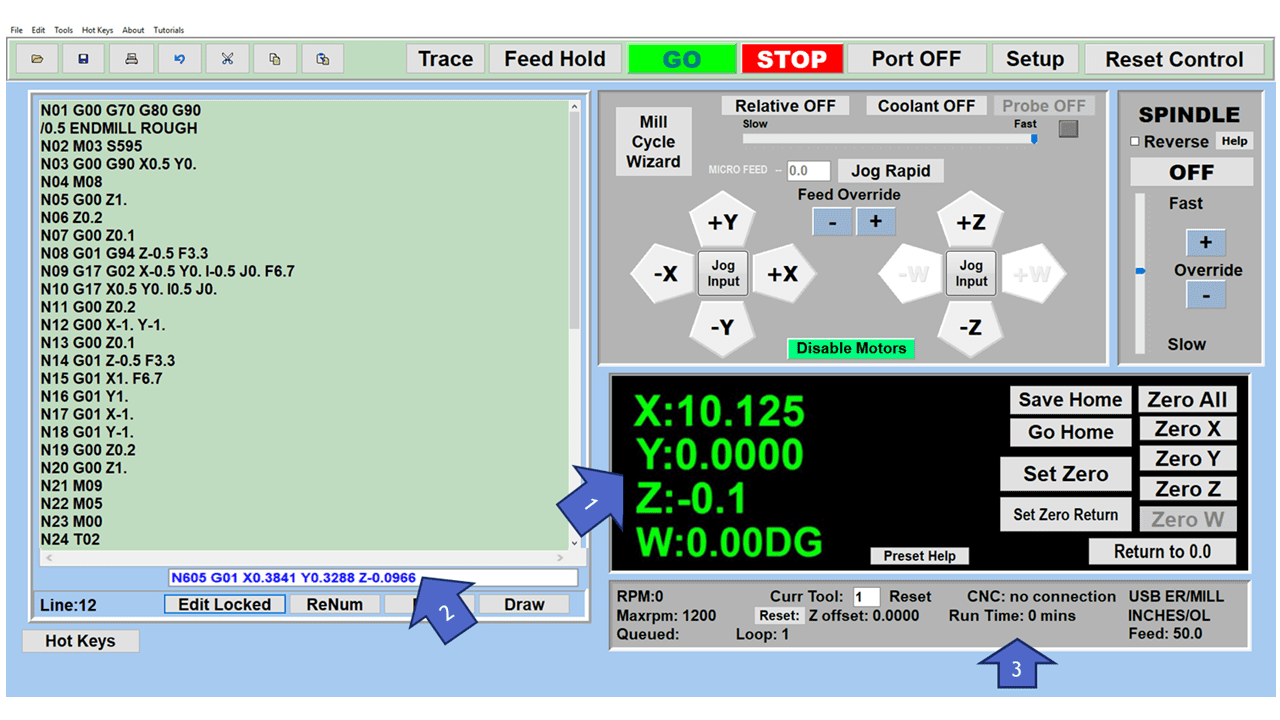
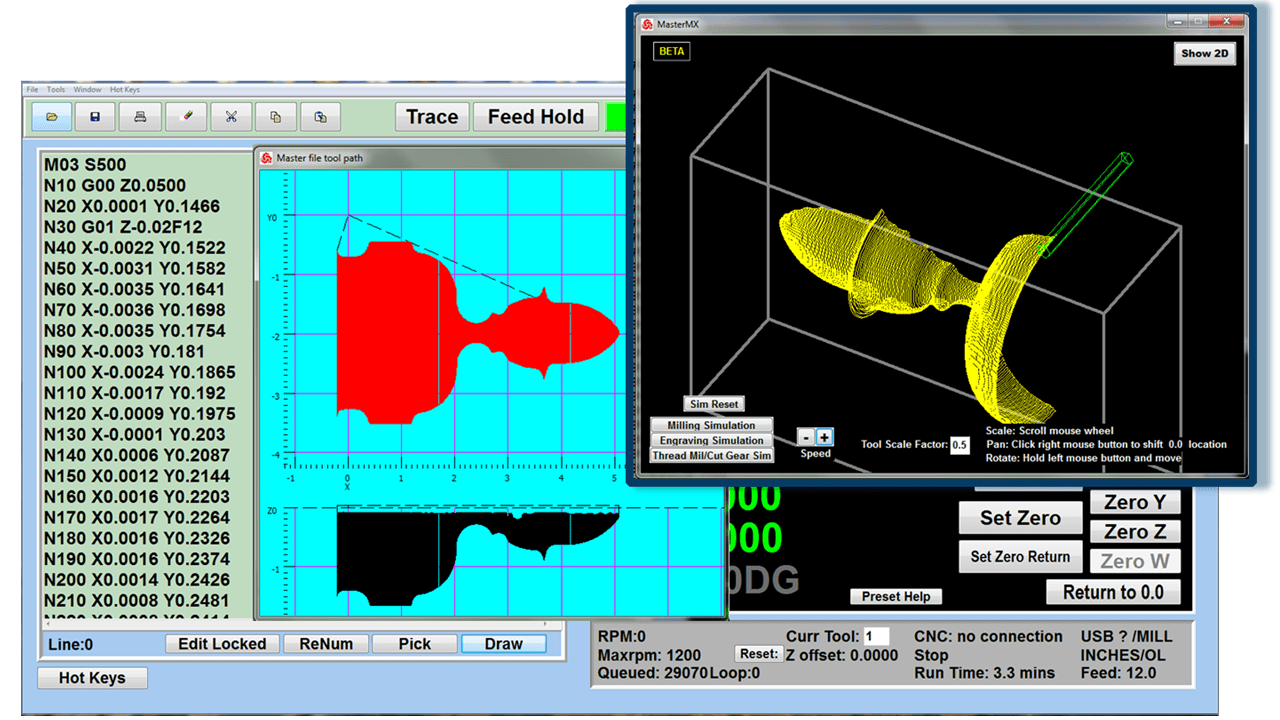
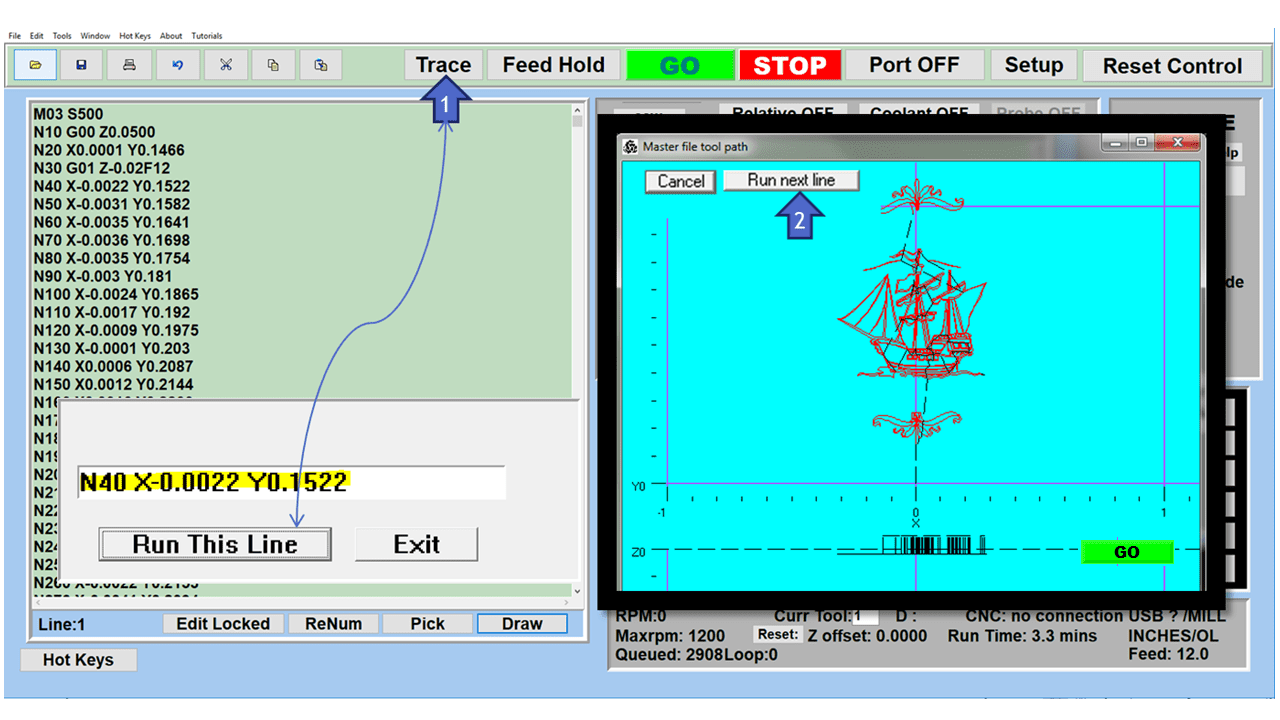
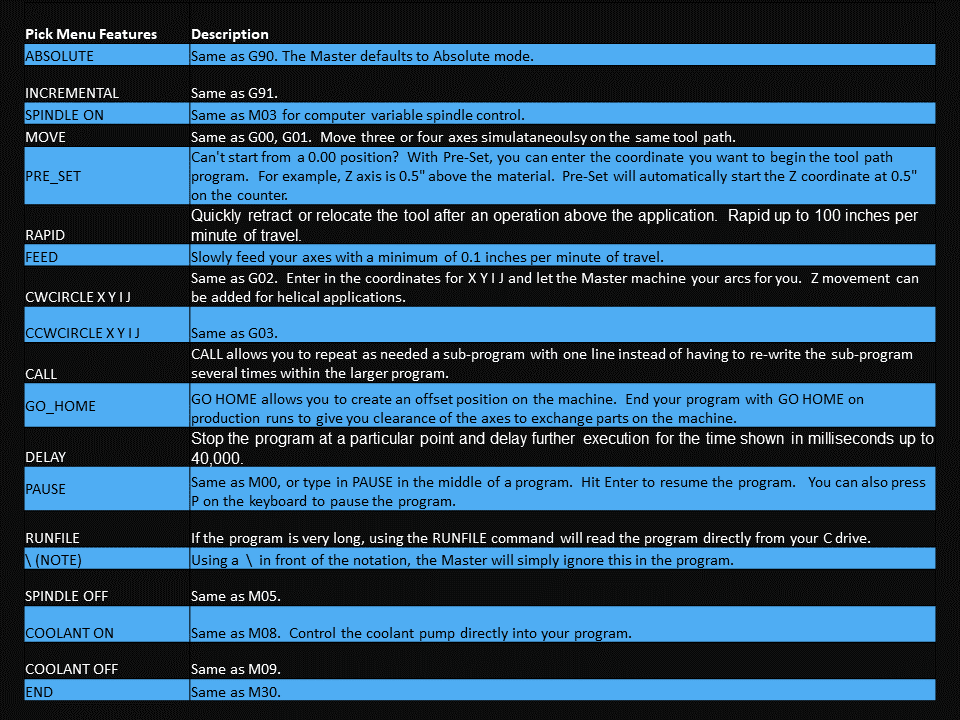
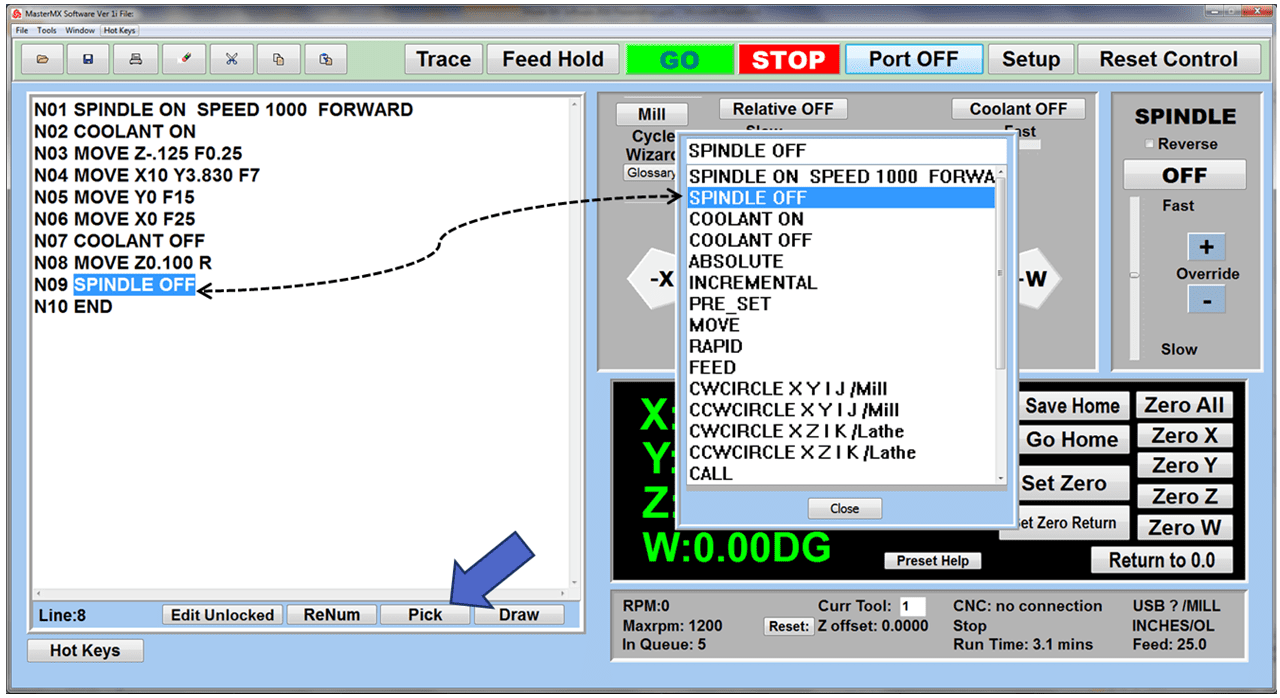
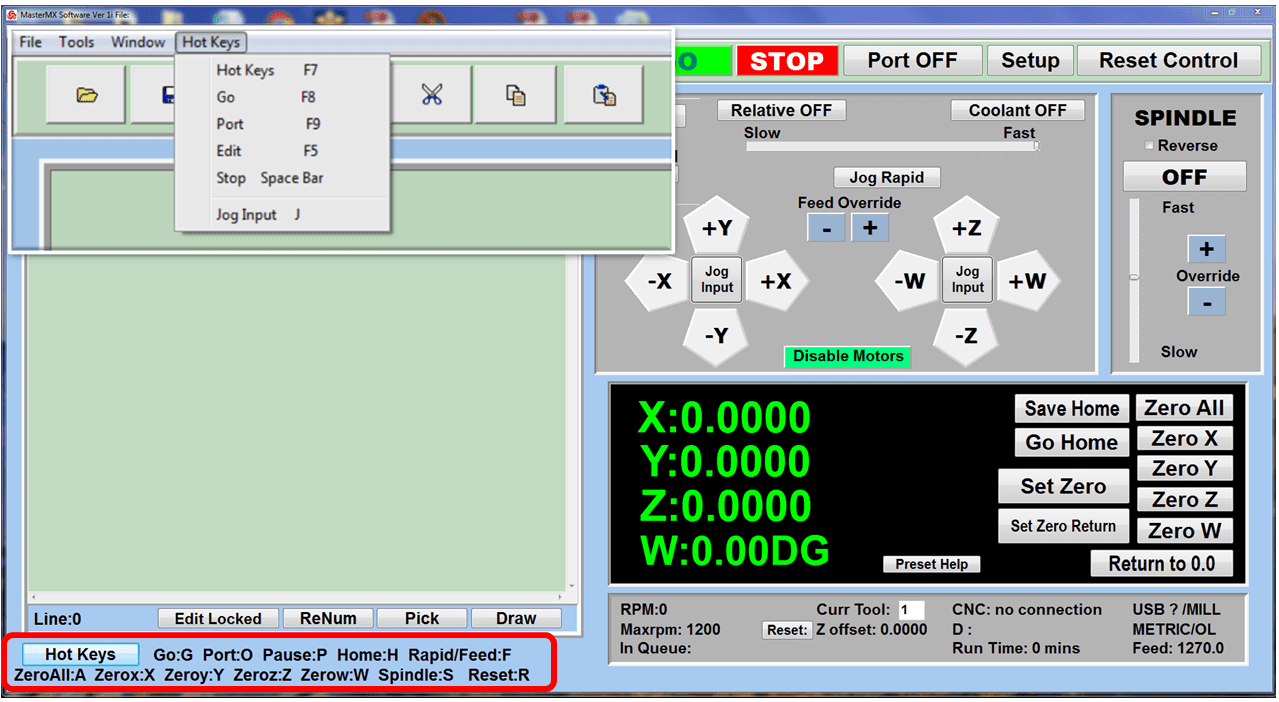
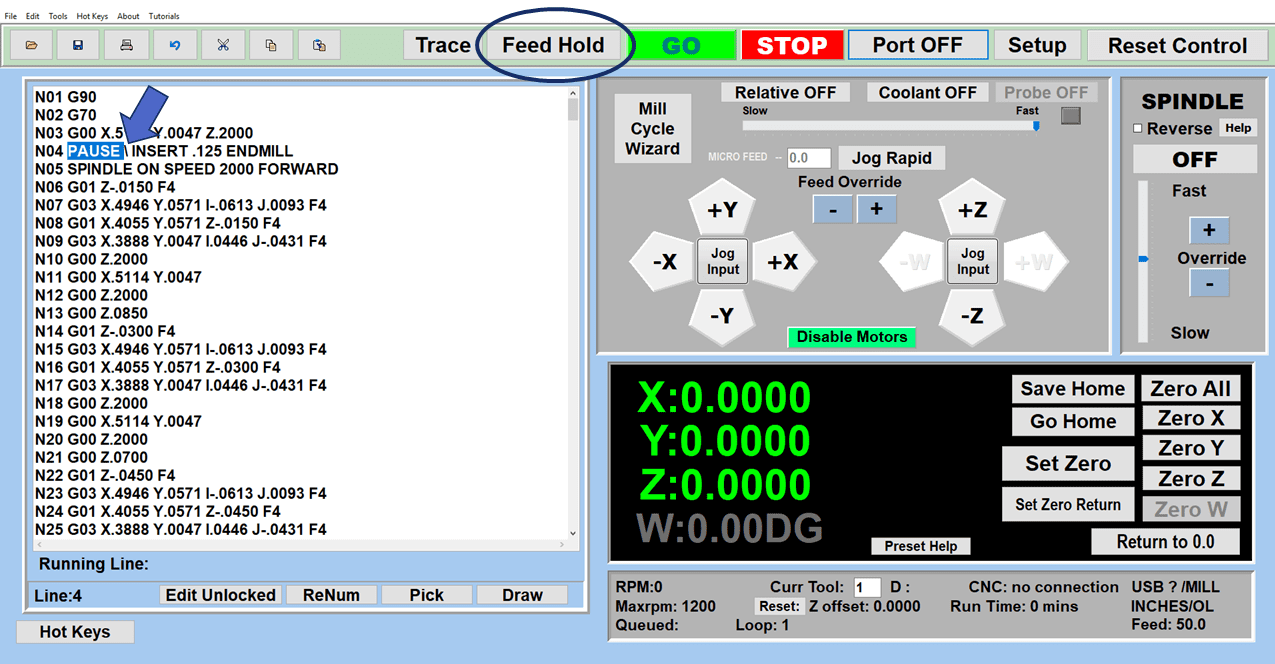
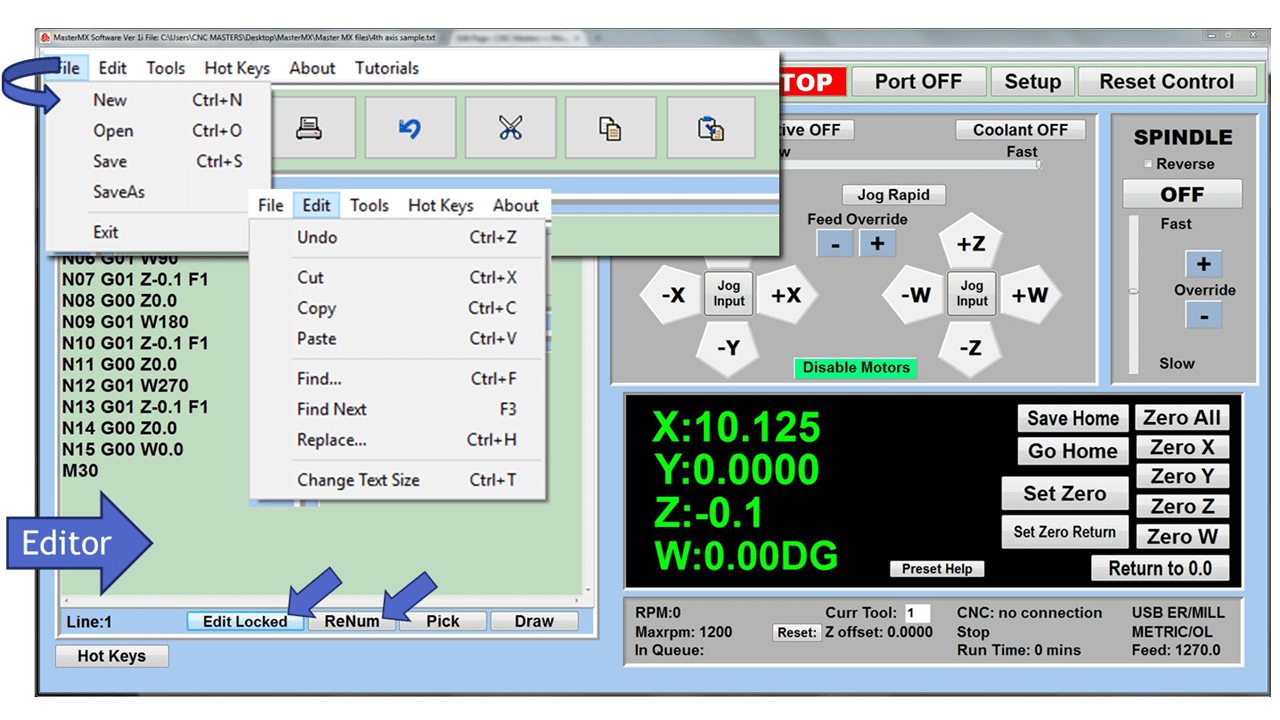
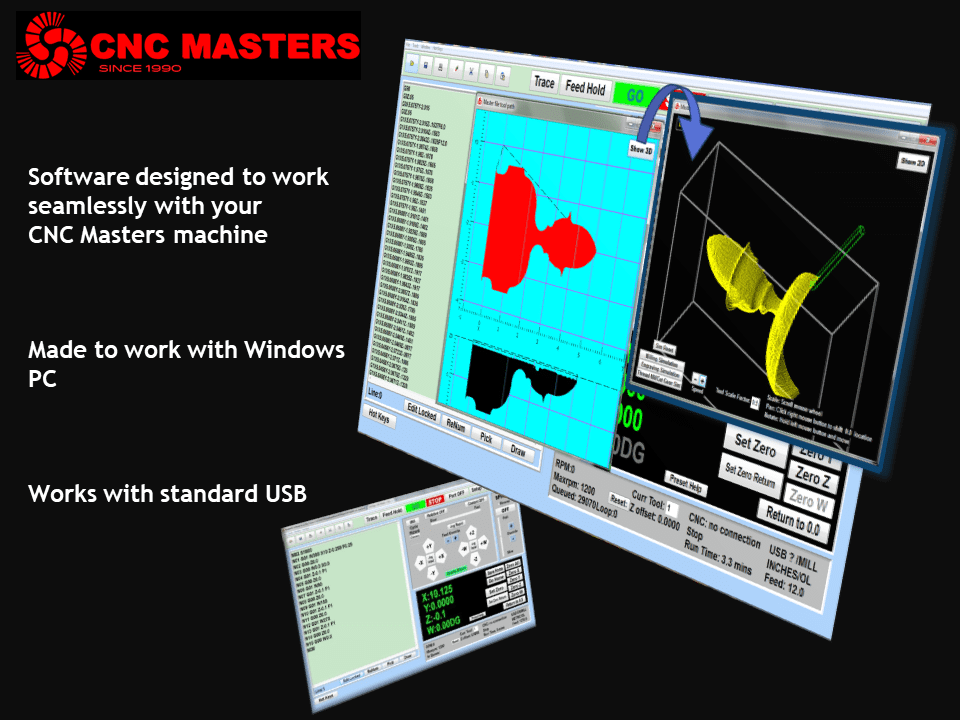
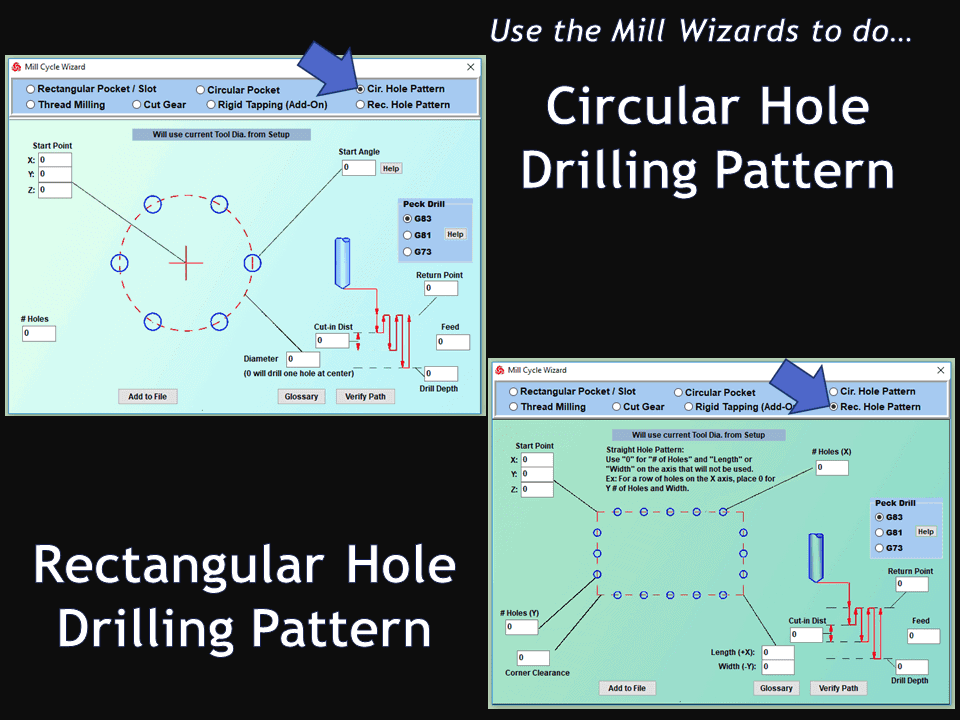
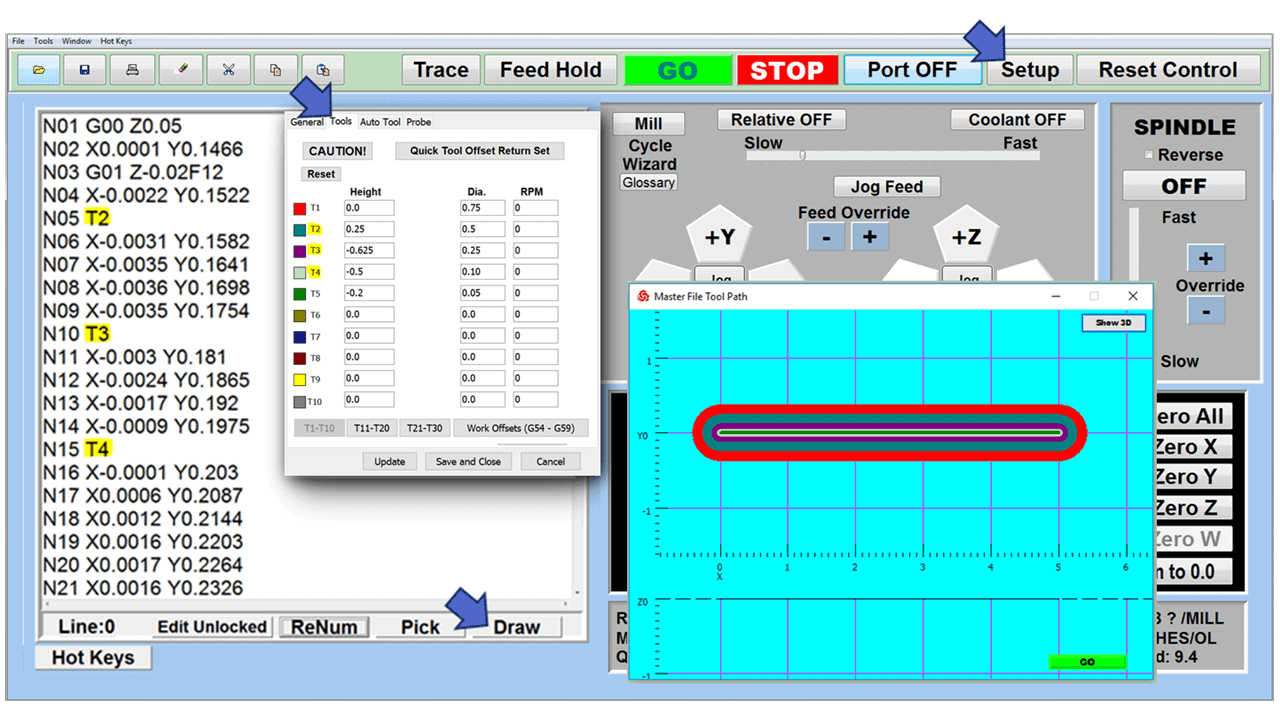
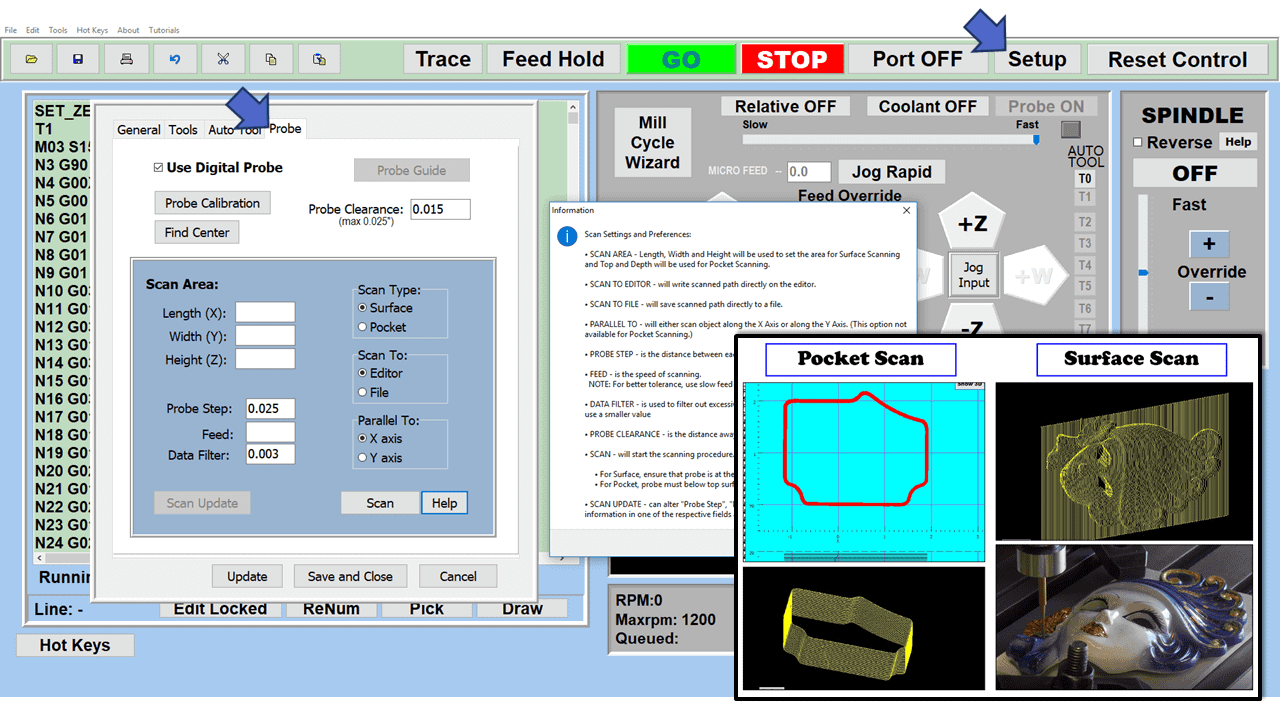
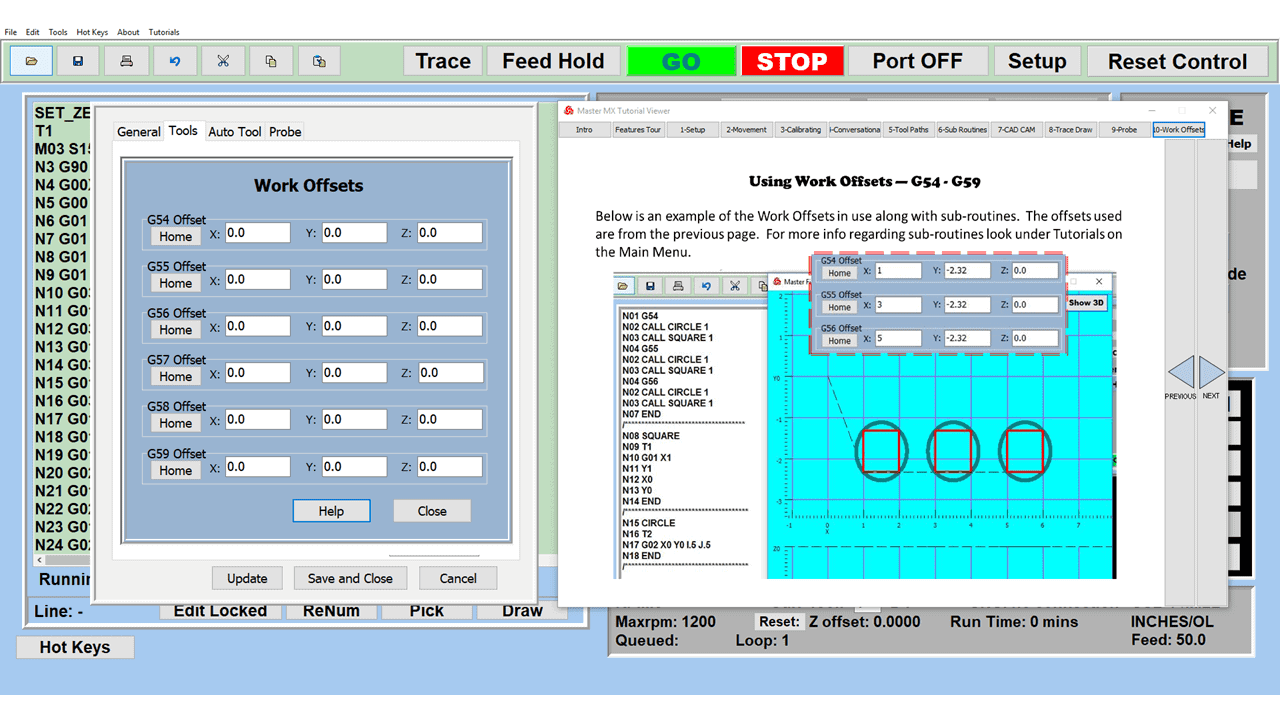
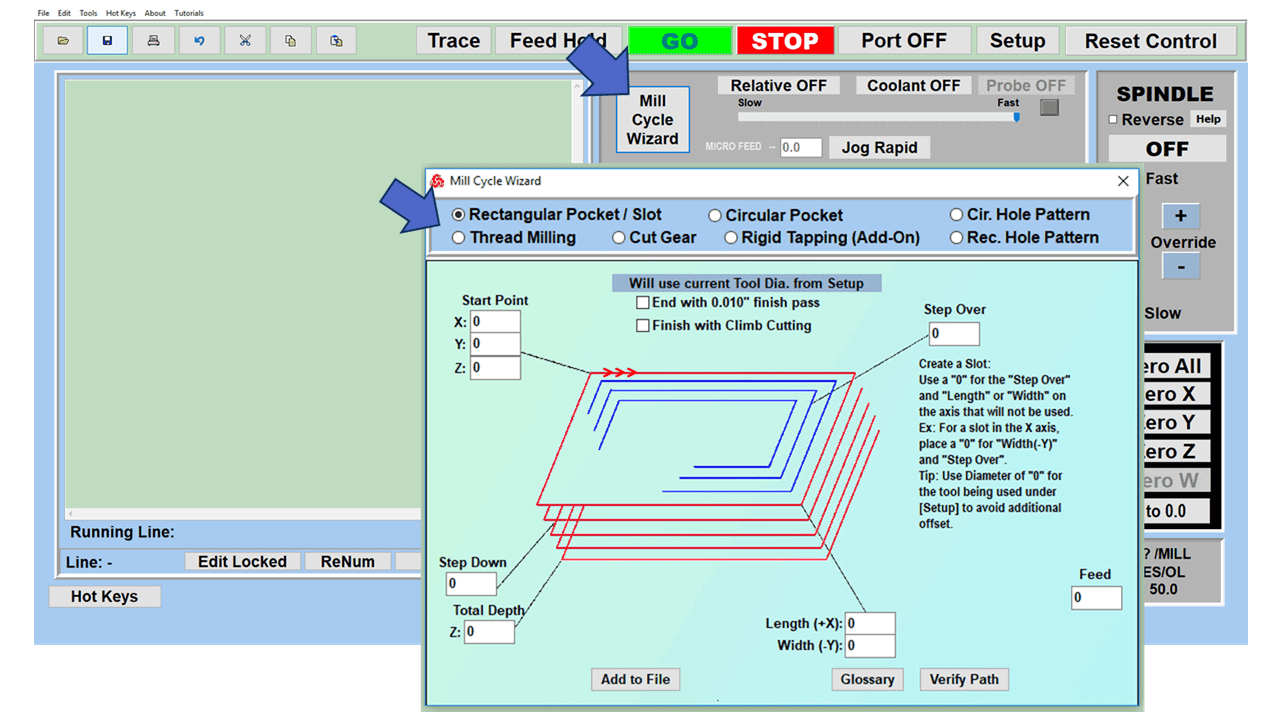
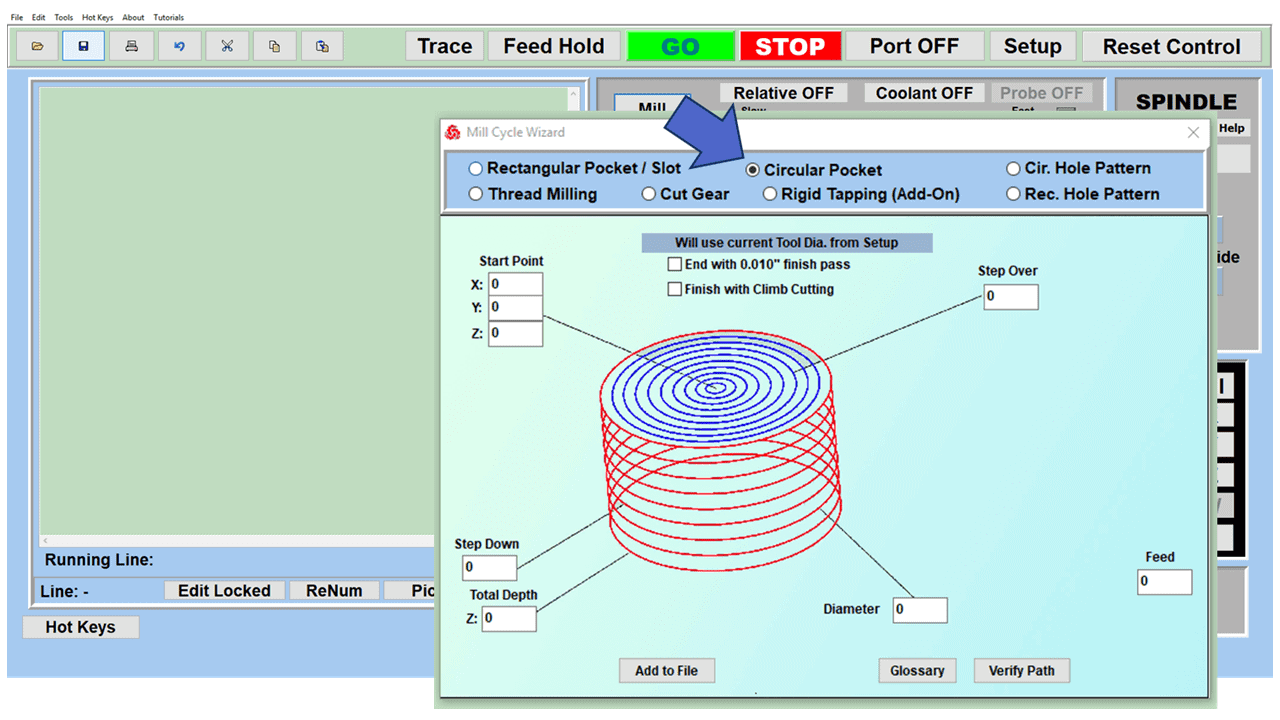
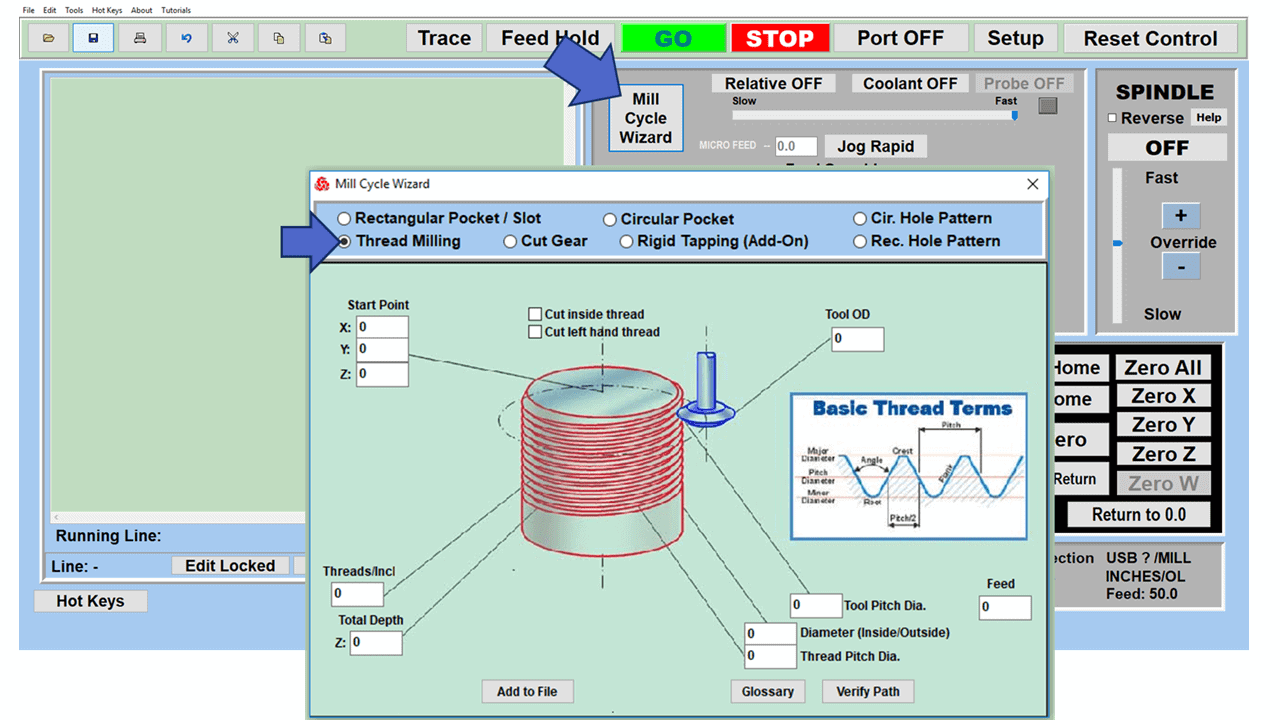
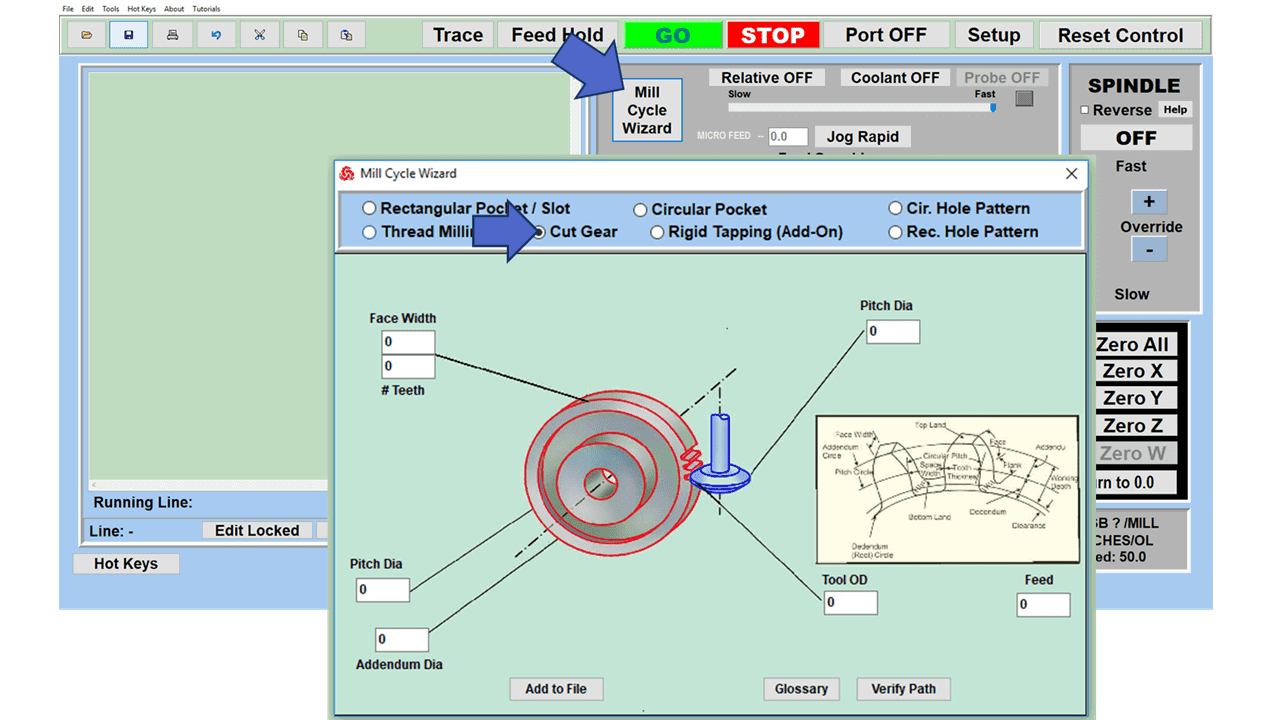
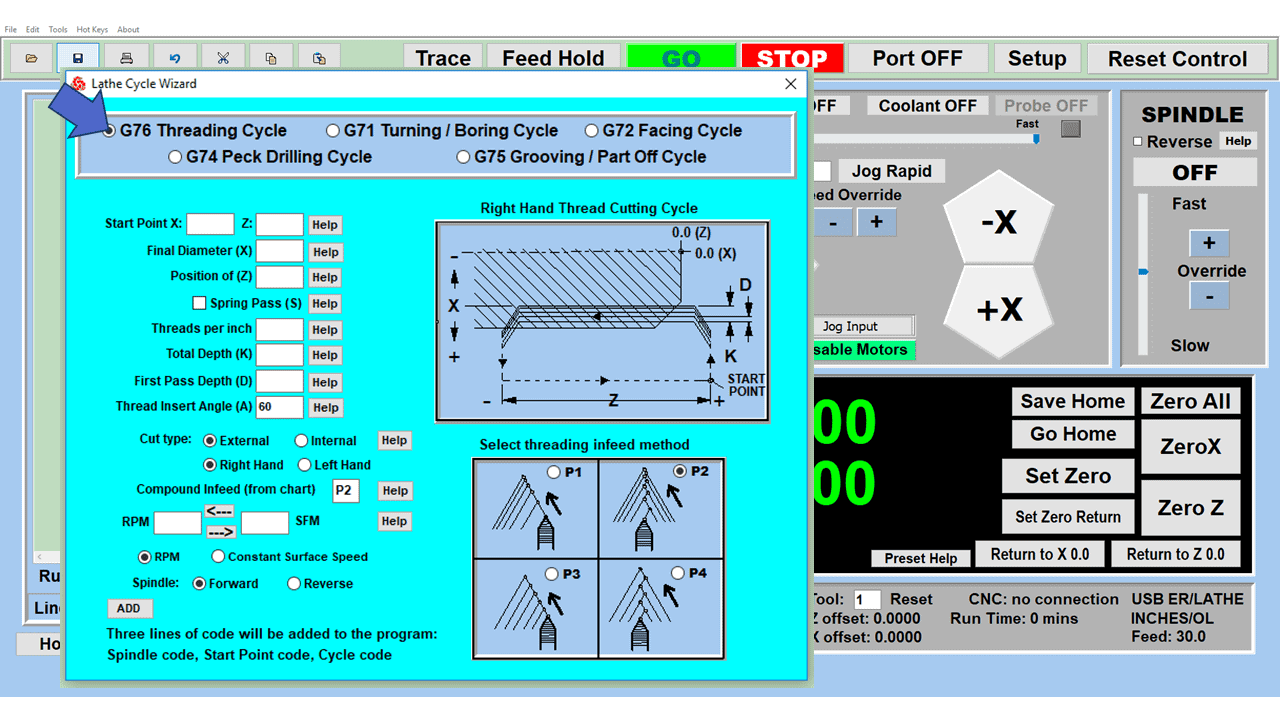
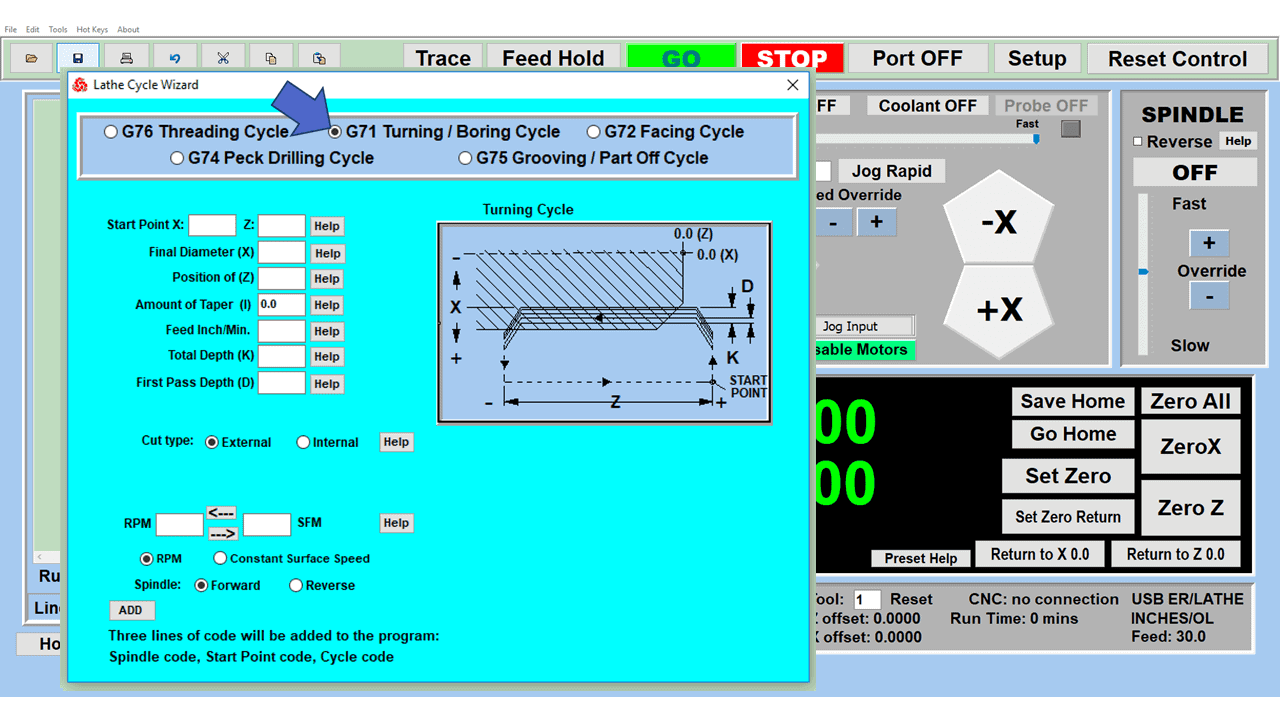
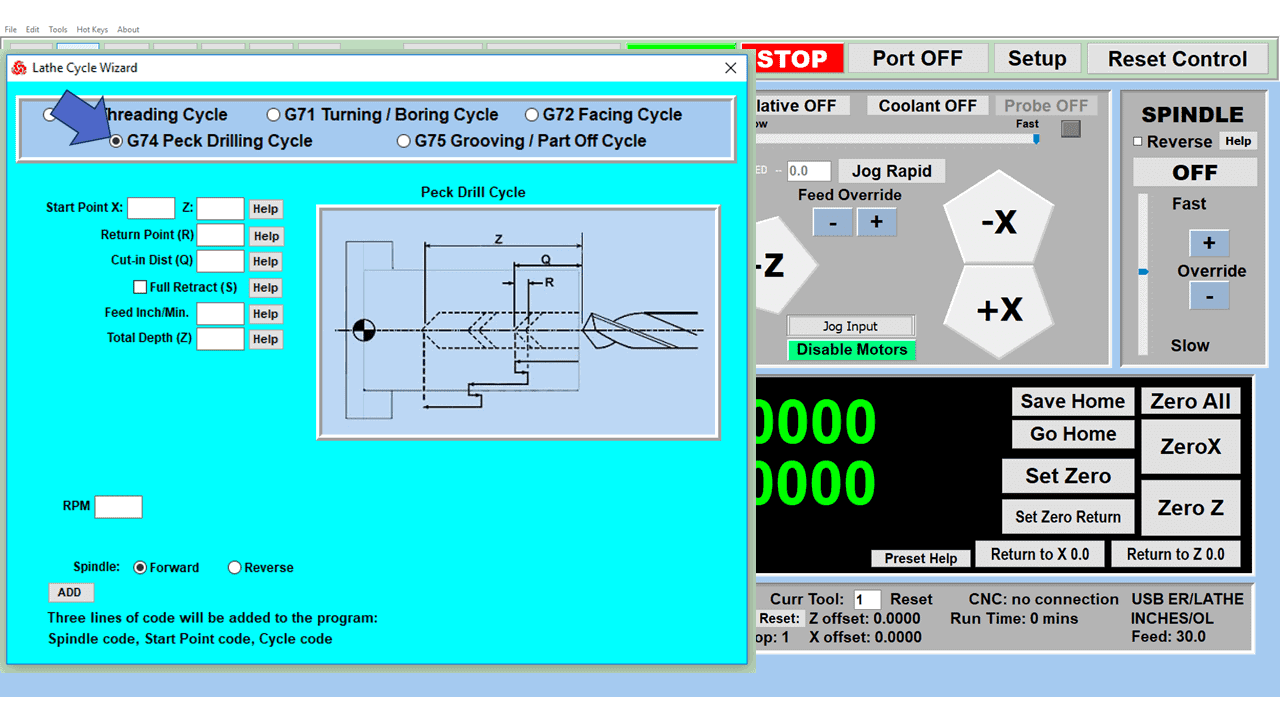
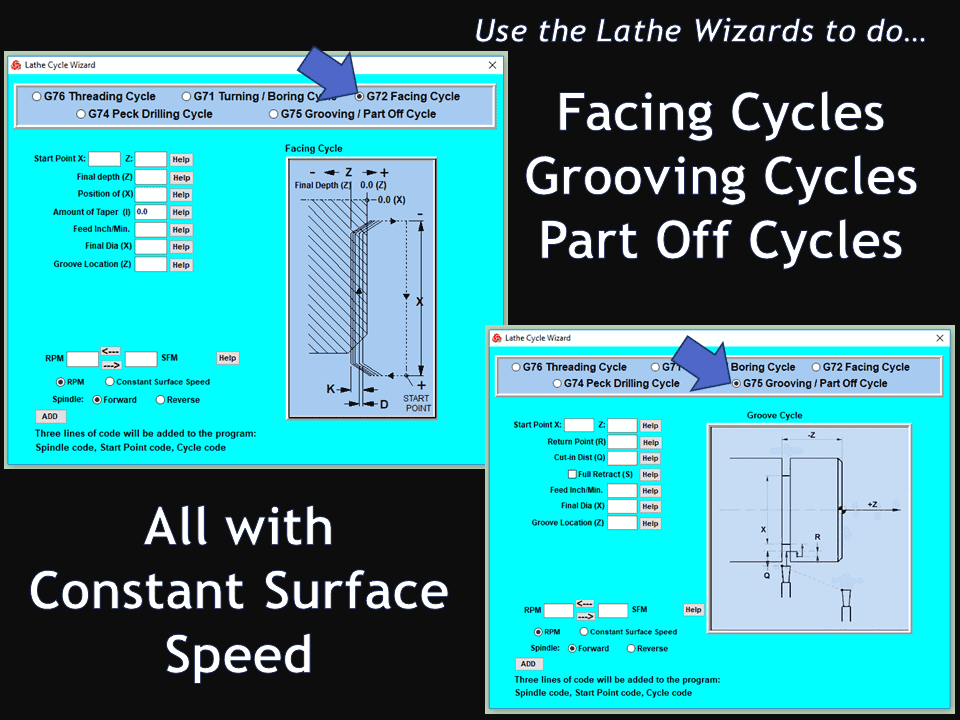
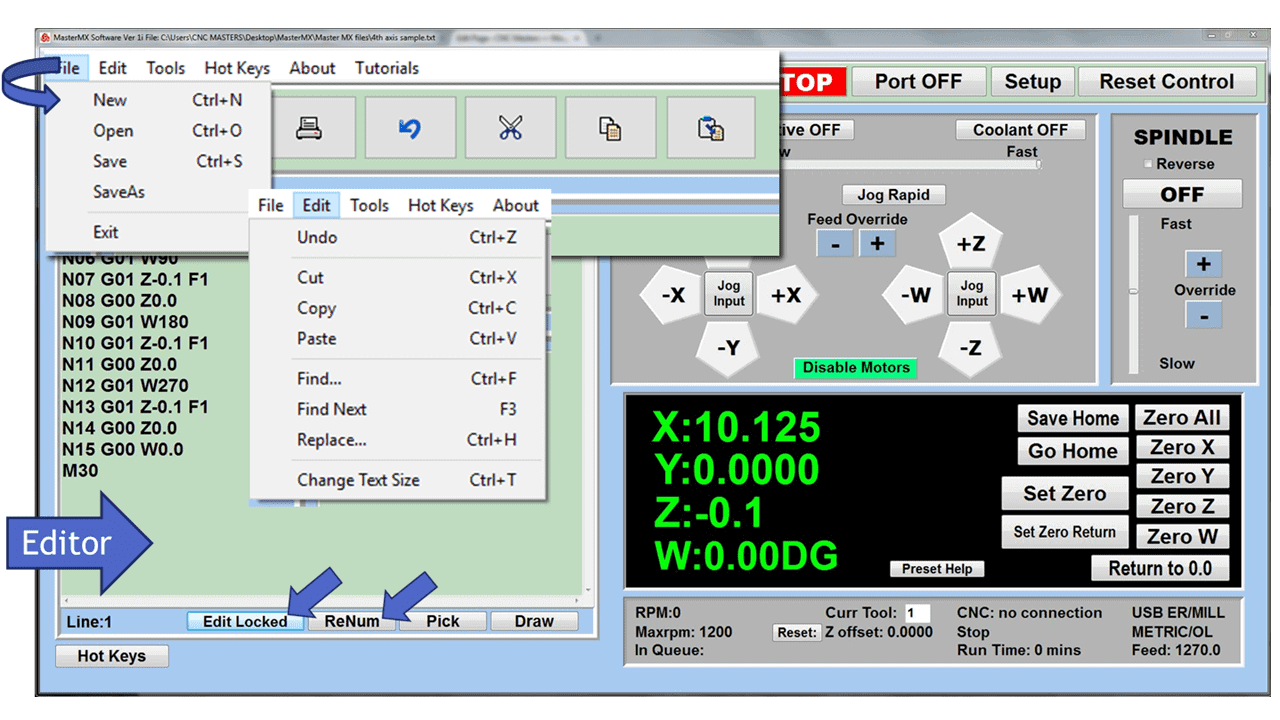
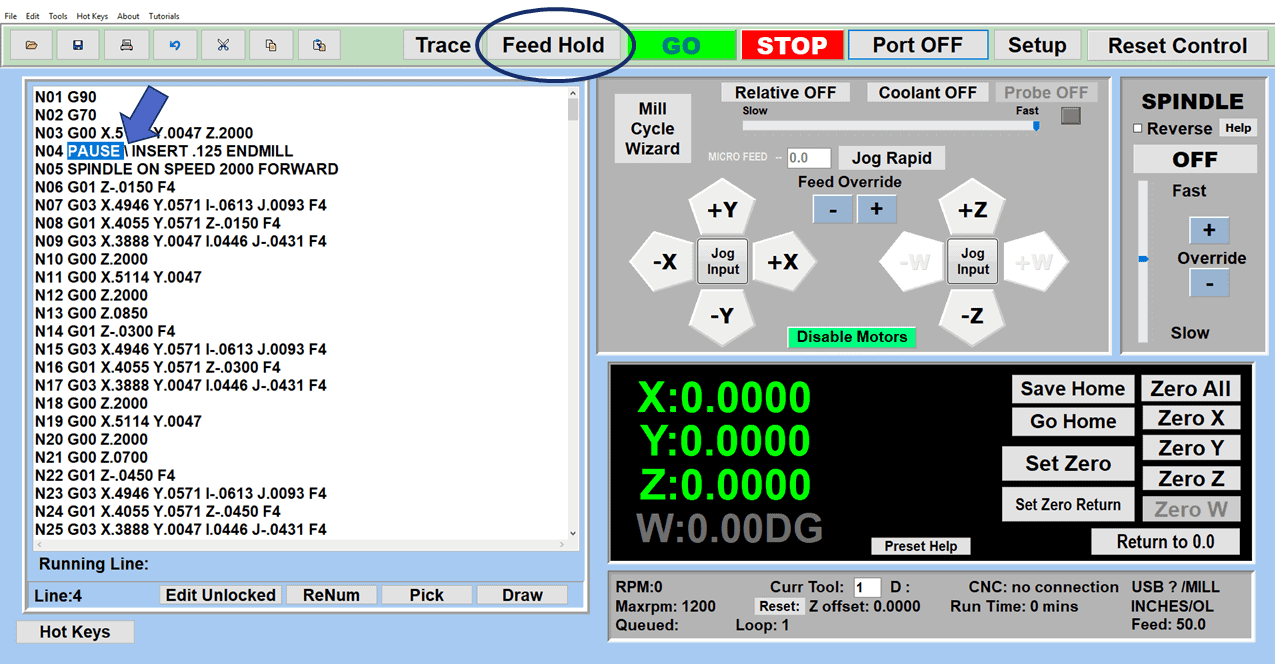
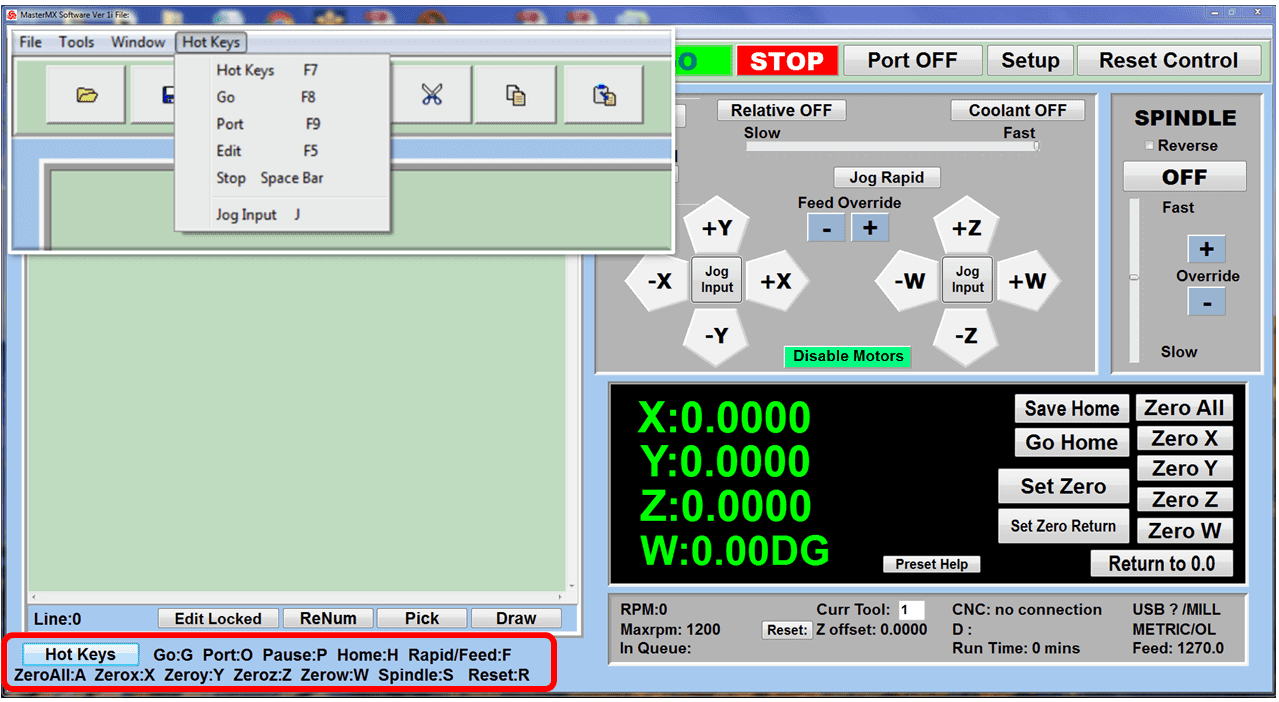
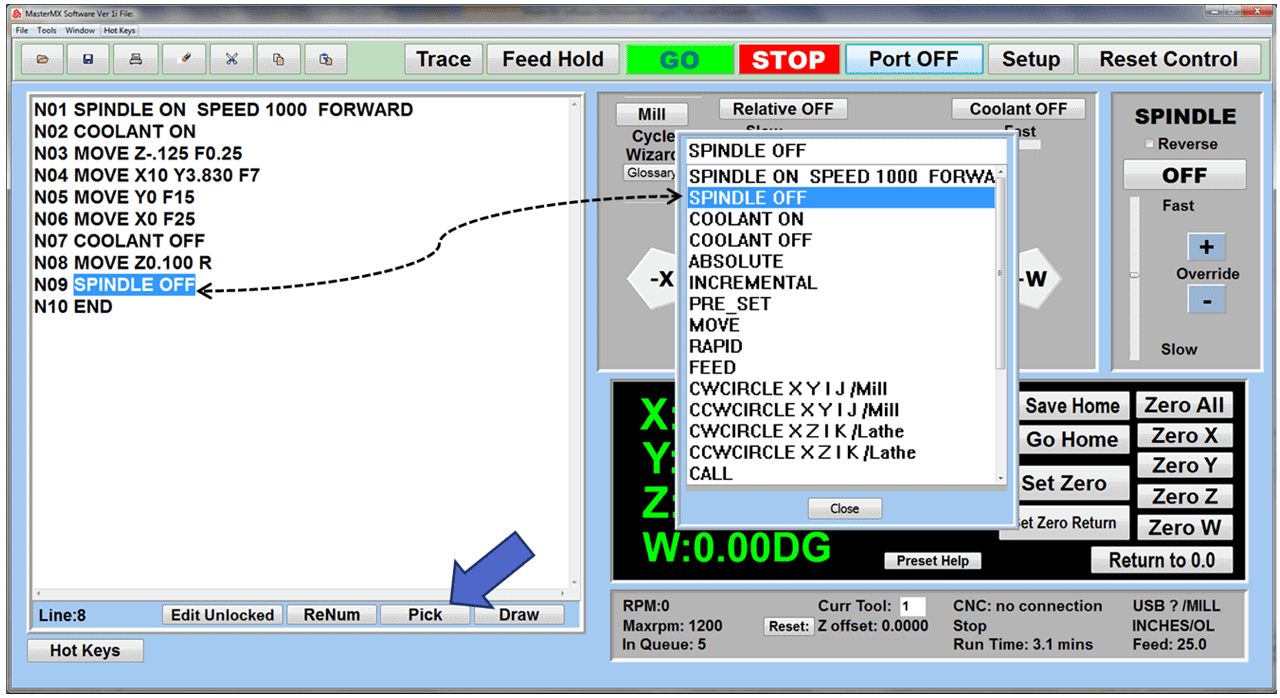
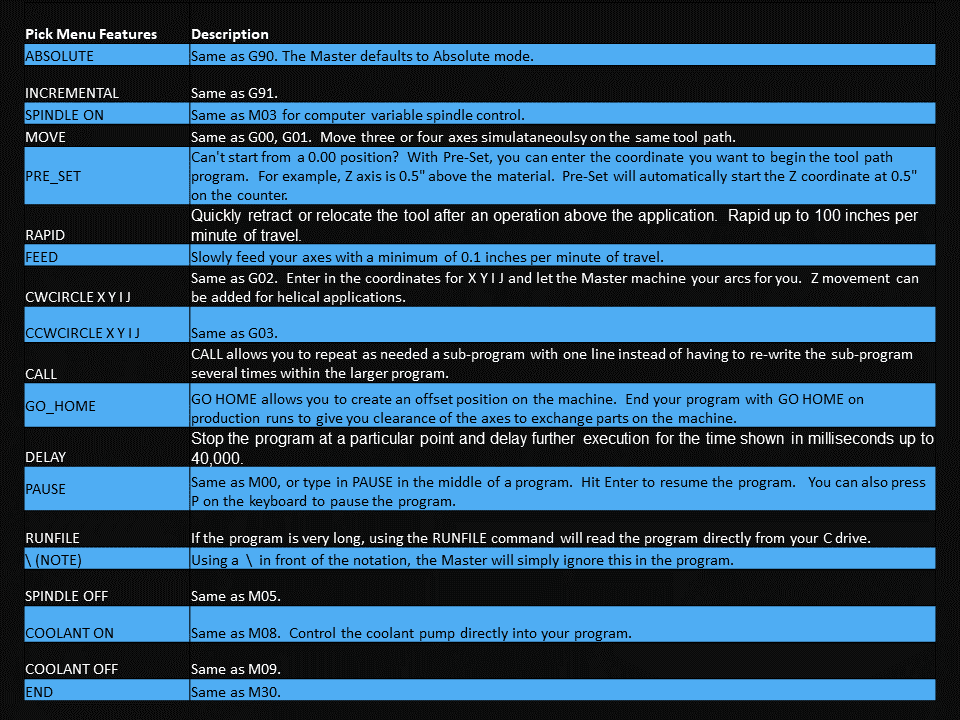
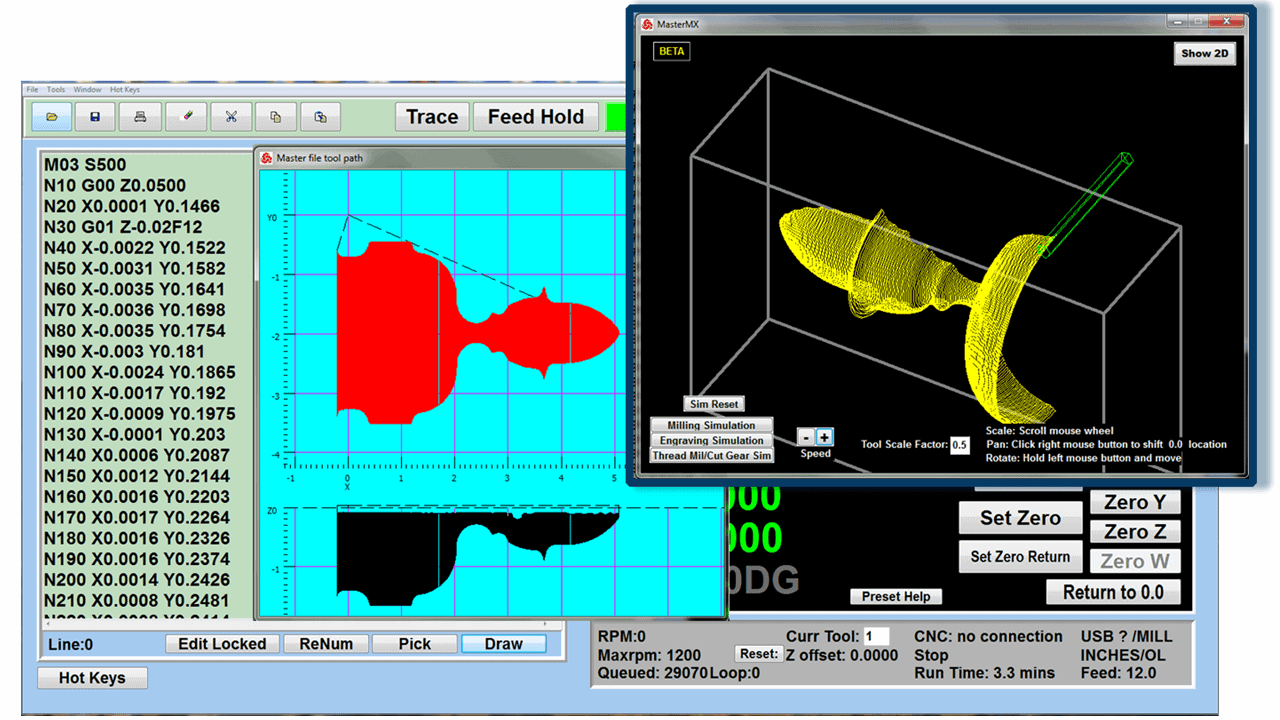
Modern software handles the CNC’s control unit via USB, and all axis motors plug directly into the Control Unit, driving the axes to their coordinates. Software like the Master MX from CNC Masters comes with “wizards” to quickly generate files without using Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) or 3D CAD software.
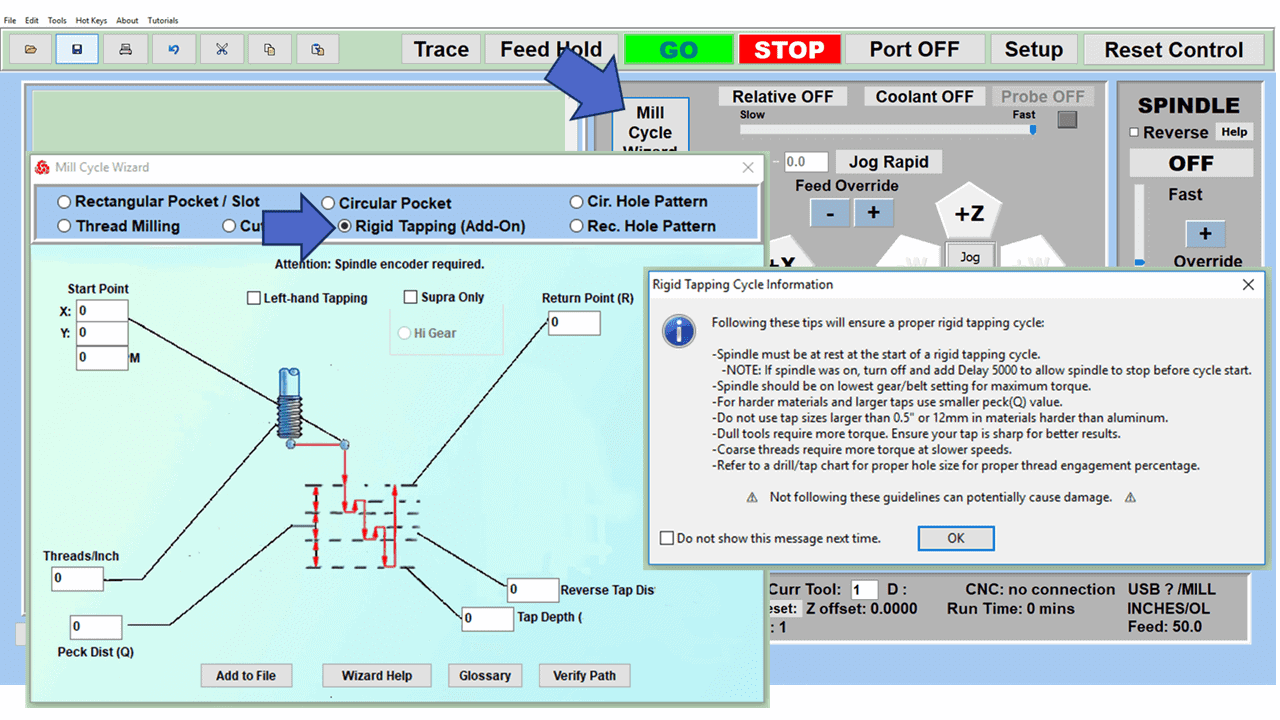
Quick tool path creations are possible with circle pocketing, slots, rectangular pocketing, gear cutting, thread milling, rigid tapping (with optional encoder kit), and peck drilling applications. Everything that large corporations have access to is also available on a small CNC.
8. You Control Price and Delivery With a Small CNC Machine
Another reason to buy a small CNC for your shop is control. Without in-house automation, you are at the mercy of other CNC companies, and they control the price. Their schedule also constrains you; sooner or later, your relationship with your customers may be damaged.
Rather than pay inflated prices to your competition and stand in line with their other customers to get your parts, you could buy a mini CNC machine for your business, set your rates, and manage your customers’ deliveries to suit their needs.
9. New Entry-Level CNCs are Reasonably Priced
Curious about how much a small CNC machine will cost? Although a DIY mini router kit is available for around $1,500, you can buy a top-of-the-line CNC Benchtop Mill with software, a warranty, and excellent customer service for less than $6,000 from CNC Masters.
10. CNCs Give You the Opportunity to Turn a Profit
Many manual machine shops today are struggling to make a profit because they are competing against CNC machine tools that make few mistakes, run faster, turn over work quickly, and allow them to accept work that manual machines cannot complete without multiple setups and secondary operations.
Even if you had an opportunity for complex and production work, you would have little chance of turning a profit. Having a CNC machine on board puts you right in the game and on the road to higher revenue.
Talk to Us Before You Purchase a Small CNC
CNC Masters offers options in small CNC machines to fit your work and budget. We sell only high-quality, USA-built machine tools with ball screws, a warranty, excellent service, and all at a competitive price!
Please email us directly at sales@cncmasters.com, call us at 626-962-9300, or visit our contact page. We look forward to hearing from you!