Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology has been around since the 1950s; milling machines date back to the Industrial Revolution in the 19th century. Even though neither one is new, there’s still a surprising amount of confusion surrounding what CNC milling is and how it works.
Maybe you’ve heard about CNC milling before but aren’t sure what it means – or how it is different from CNC machining, CNC lathes, or any of the other machinery-related buzzwords that get tossed around.
In this article we’ll look at five fast facts about CNC milling, giving you a better understanding of the technology behind CNC milling and how it can help you.
1. All milling is machining
What is machining? Machining is a mechanical, subtractive process. That means it removes material from a workpiece through physical means – metal on metal, bits, screws, etc. Machining is nothing new of course, and the two primary means of mechanical machining in the industrial world are lathes and mills. Both of those tools are proper machine tools – they both remove material mechanically.
Mills are a bit different from lathes. Mills use a rotating tool, a milling cutter, to cut away or drill away material. The cutter spins rapidly while the workpiece is fixed in place. Depending on the exact configuration of the mill, either the workpiece or the cutter will move slowly to feed the workpiece through the machine.
Lathes switch things around. The workpiece rotates rapidly, while the cutter slowly passes along the part to remove material.
2. Not all CNC is milling (or machining!)
While all milling is machining, not all CNC machines are machining. That might be confusing, but CNC refers to a technology, not a particular process. That technology can be applied to mills and lathes as part of a traditional machining process, but CNC can also be used with Electronic Discharge Machines (EDMs), waterjet cutters, 3D printers, and a host of other machines.
When someone refers to CNC machining, it’s good to clarify what they mean. Are they talking about the whole range of CNC-equipped machinery or even the general idea of industrial automation? Or do they mean a CNC lathe or milling machine?
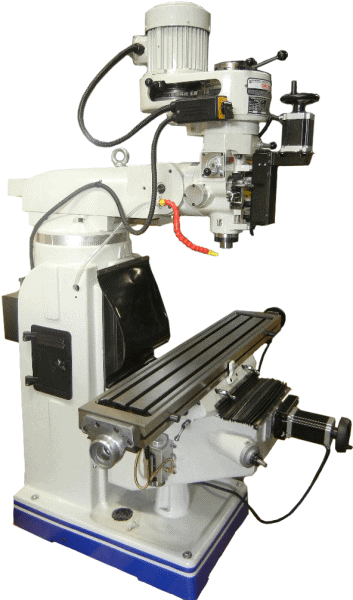
3. Mills can be vertical or horizontal
There’s more than one type of mill; the two most common types are horizontal and vertical mills, referring to the axis of movement for the mill’s cutter. To a novice, both kinds of mill appear somewhat similar, with a table for mounting the workpiece, an arm extending out over the table, and the milling cutter mounted beneath the arm.
On closer inspection, the differences become more apparent. On a horizontal mill, the cutter rests on an arbor – a bar stretching between the body of the mill and the downward arm. Essentially, the cutting moves back and forth above and parallel to the surface of the workbench beneath. On horizontal mills, it is the workbench itself that moves along an X, Y, and Z-axis.
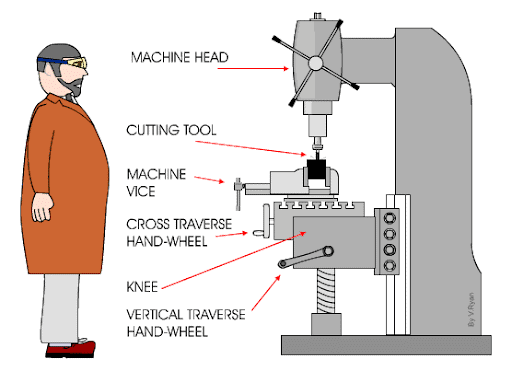
Image from: https://technologystudent.com/equip1/hormil1a.gif
Vertical mills appear roughly similar, but there’s no arbor; the arm ends in a downward-oriented cutter or drill. The cutting head moves along an X and Y axis, allowing it to be slowly drilled into a workpiece – or adjusted more slowly as the workpiece is fed through beneath it.
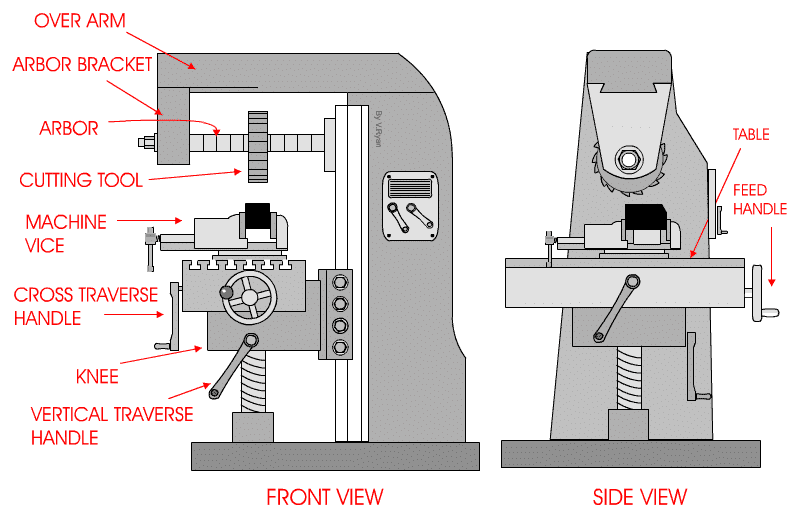
Image from: https://technologystudent.com/equip1/vert1a.gif
Each type of milling machine brings a different set of advantages, with vertical mills tending to be smaller, cheaper, and slightly easier to use than horizontal mills. The latter is better suited for large-scale industrial settings and can be quite large for milling heavy machinery.
4. CNC improves existing capabilities
Making a simple, vertical milling machine CNC-capable doesn’t magically give it a new range of motion, an extra axis of movement, or more power. Instead, CNC provides two major benefits:
- Precision
Manually-operated milling machines rarely give the same level of precision as CNC machines. CNC technology allows cutting tools to be programmed to extremely precise allowances, sharper than what could typically be done manually.
More precise cuts deliver cleaner, better-quality parts, but they also make the entire process more efficient. There’s less waste, fewer defective parts, and an overall more streamlined process.
- Automation
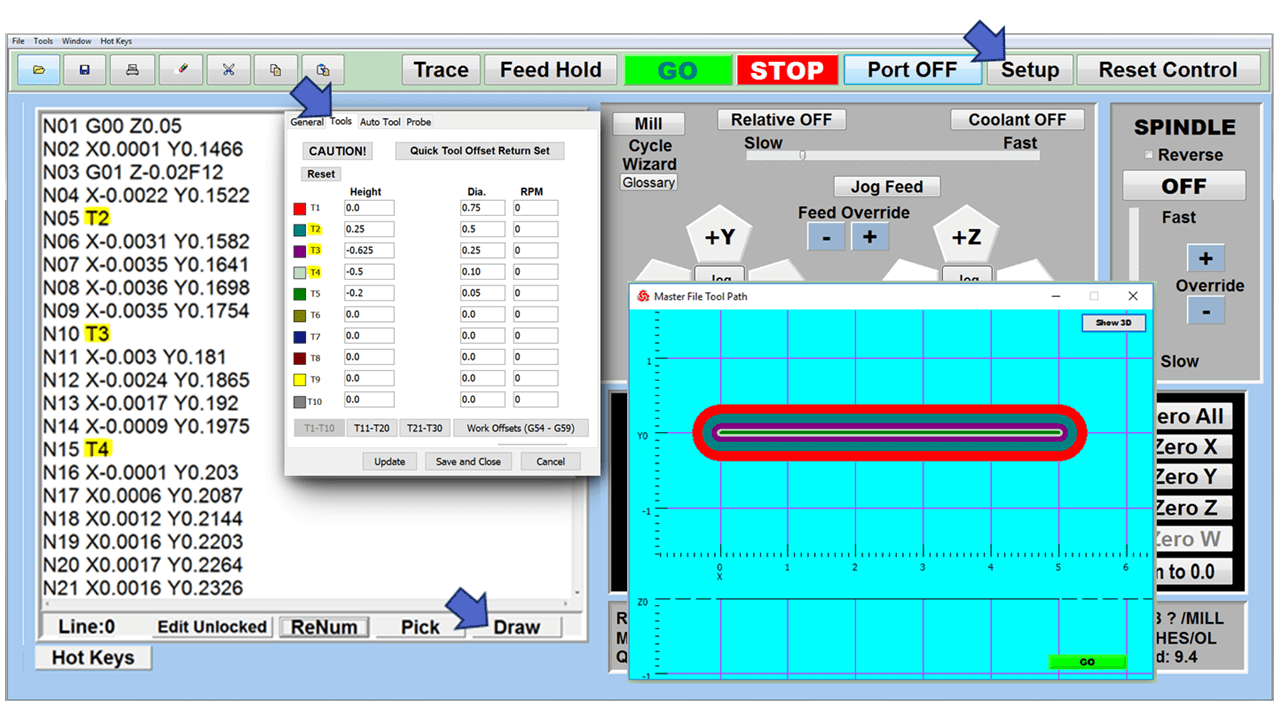
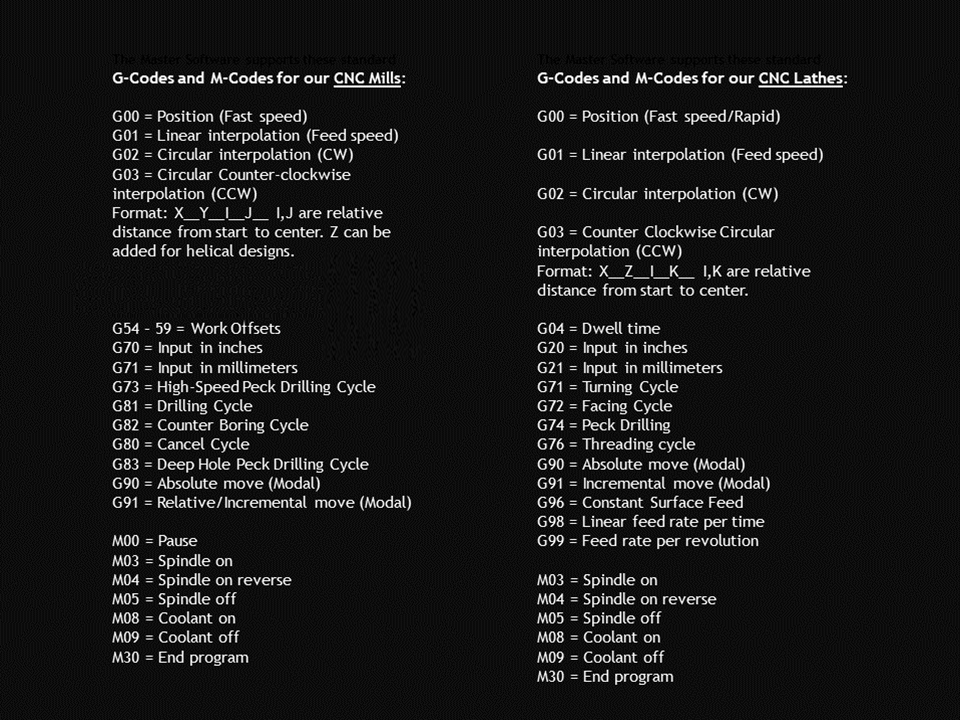
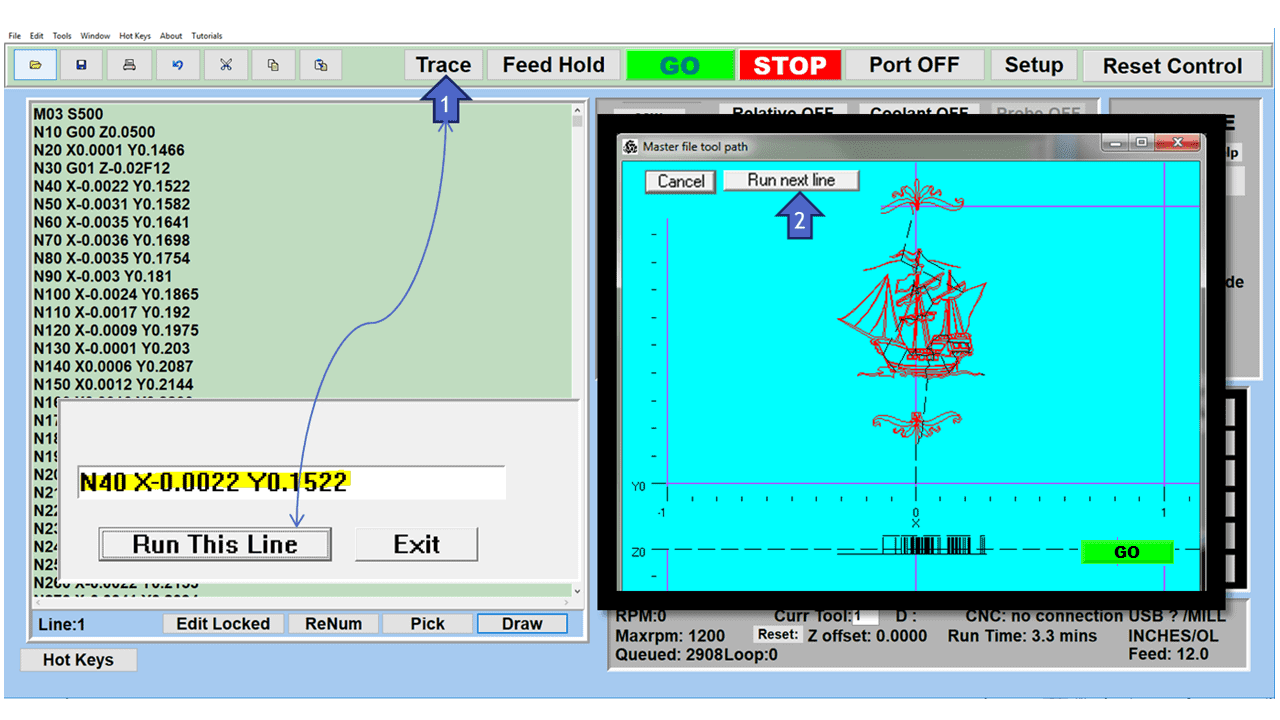
Today’s CNC machines use a computer interface to program a set of operations. A skilled human operator, trained in a Computer Assisted Design (CAD) program or able to program directly in g-code (the general language for CNC machines), can design a program, enter it, and then walk away. There’s no need for direct, moment-by-moment supervision except in cases where troubleshooting is needed.
CNC allows a single operator to oversee several CNC machines at once, but it also lets an operator design a single program to produce hundreds or even thousands of identical parts.
5. The more (axes) the merrier
Most milling machines operate with three axes of movement – X, Y, and Z. On a typical vertical mill, the Y and Z axis would be the movement of the workbench, while the X (up-and-down) axis is provided by the cutting tool.
CNC machines allow an even greater range of movement. Workpieces can be flipped, providing an “A” and “B” axis, all without ever being adjusted on the workbench itself.
Of course, these advanced 5-axis CNC milling machines cost a lot more than their 3-axis counterparts, but they allow incredibly complex operations to be undertaken in one go – all without any human involvement.
There’s much more to learn about CNC milling machines, such as how to program one, how they work with CAD programs, and what materials can be used in a CNC milling machine. But for now, take these five fast facts to get you started.